More Exam Practice - Iowa State University
... their bundle sheath cells as an adaption to hot, dry climates. If they were to open their stomata to take in CO2 during the day, they would also lose too much water. This way, they can keep their stomata partially closed during the day and use CO2 that is concentrated in bundle-sheath cells to gener ...
... their bundle sheath cells as an adaption to hot, dry climates. If they were to open their stomata to take in CO2 during the day, they would also lose too much water. This way, they can keep their stomata partially closed during the day and use CO2 that is concentrated in bundle-sheath cells to gener ...
Chapter 17 Notes : From Gene to Protien
... The 5 end is capped with a modified G, which helps prevent degredation by hydrolytic enzymes, and signals as an attachment spot for ribosomes. At the 3 end, a polytail A is added (repetitive AAA sequence 50-250 nucleotides long.) It serves the same functions as the G cap, but also helps export mRN ...
... The 5 end is capped with a modified G, which helps prevent degredation by hydrolytic enzymes, and signals as an attachment spot for ribosomes. At the 3 end, a polytail A is added (repetitive AAA sequence 50-250 nucleotides long.) It serves the same functions as the G cap, but also helps export mRN ...
Lecture, Gene Expression
... • Codons code for amino acids • Start codon is AUG but stop codon varies • Enzyme* that does this is called tRNA • Takes place in cytoplasm at a ribosome • After folding of polypeptide, a protein is formed! ...
... • Codons code for amino acids • Start codon is AUG but stop codon varies • Enzyme* that does this is called tRNA • Takes place in cytoplasm at a ribosome • After folding of polypeptide, a protein is formed! ...
Chapter 10
... form, electrons are shared or swapped between specific atoms in specific ways. So, chemical reactions- when chemical bonds change- are all about moving electrons around. Each atom, and each molecule, needs a certain number of electrons to be stable (less reactive); certainly, the molecules of cells ...
... form, electrons are shared or swapped between specific atoms in specific ways. So, chemical reactions- when chemical bonds change- are all about moving electrons around. Each atom, and each molecule, needs a certain number of electrons to be stable (less reactive); certainly, the molecules of cells ...
Nucliec acids and dna review
... 84. What are ribosomes made of and in what 2 places can they be found in a cell? 91. __________________________ are linked to make proteins as a ______________________ moves along the mRNA transcript. 92. What ends translation? 93. Can more than one ribosome at a time translate an mRNA transcript? E ...
... 84. What are ribosomes made of and in what 2 places can they be found in a cell? 91. __________________________ are linked to make proteins as a ______________________ moves along the mRNA transcript. 92. What ends translation? 93. Can more than one ribosome at a time translate an mRNA transcript? E ...
BioKnowledgy Quick Quiz on DNA replication, transcription, and
... What is the sequence of the amino acids that is being translated from the following mRNA sequence? ...
... What is the sequence of the amino acids that is being translated from the following mRNA sequence? ...
2.7 quiz - Peoria Public Schools
... What is the sequence of the amino acids that is being translated from the following mRNA sequence? ...
... What is the sequence of the amino acids that is being translated from the following mRNA sequence? ...
Cell Membrane Structure & Function
... – 1.Membrane selects what substances will enter – 2.Take up molecules present in high concentration – 3 Part of protein extends through bilayer – 4.May be non polar helix beta-pleated sheets of non polar amino acids – 5.Non polar portion held within interior of bilayer – 6.Polar ends protrude from b ...
... – 1.Membrane selects what substances will enter – 2.Take up molecules present in high concentration – 3 Part of protein extends through bilayer – 4.May be non polar helix beta-pleated sheets of non polar amino acids – 5.Non polar portion held within interior of bilayer – 6.Polar ends protrude from b ...
Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 12 Notes
... Role of the citric acid cycle in anabolism. Intermediates of the citric acid cycle are drawn off as precursors in many biosynthetic pathways. Shown in red are four anaplerotic reactions that replenish depleted cycle intermediates ...
... Role of the citric acid cycle in anabolism. Intermediates of the citric acid cycle are drawn off as precursors in many biosynthetic pathways. Shown in red are four anaplerotic reactions that replenish depleted cycle intermediates ...
prepex3
... 20 and 22. The topics begin with amino acid oxidation and end with the synthesis of nucleotides. Nitrogen is the theme for all of the reactions. It should be understood that the below list, while comprehensive over this section of the course, must not be considered complete. It is intended only as a ...
... 20 and 22. The topics begin with amino acid oxidation and end with the synthesis of nucleotides. Nitrogen is the theme for all of the reactions. It should be understood that the below list, while comprehensive over this section of the course, must not be considered complete. It is intended only as a ...
(DOCX, Unknown)
... 32. After stenuous exercise, a muscle cell would contain decreased amounts of ________ and increased amounts of _________. A. glucose; ATP B. ATP; glucose C. ATP; lactic acid D. lactic acid; ATP E. CO2; pyruvic acid 33. Where in the cell is ATP synthase located? A. in the plasma membrane B. in the n ...
... 32. After stenuous exercise, a muscle cell would contain decreased amounts of ________ and increased amounts of _________. A. glucose; ATP B. ATP; glucose C. ATP; lactic acid D. lactic acid; ATP E. CO2; pyruvic acid 33. Where in the cell is ATP synthase located? A. in the plasma membrane B. in the n ...
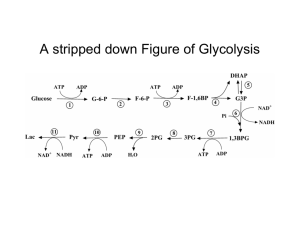
Figure 17-3 Degradation of glucose via the glycolytic pathway.
... which must be generated in the mitochondria. OAA cannot be transported out so it must be converted to PEP or malate (or Asp but lets ...
... which must be generated in the mitochondria. OAA cannot be transported out so it must be converted to PEP or malate (or Asp but lets ...
Proteins and amino acids
... Hydrophobicity is the most important property It drives the folding of a protein The sticky amino acids glue together The non-sticky amino acids point to the water The waters must be ‘happy’ ...
... Hydrophobicity is the most important property It drives the folding of a protein The sticky amino acids glue together The non-sticky amino acids point to the water The waters must be ‘happy’ ...
Practice Exam #1
... 13. As the nerve of a slow twitch motor unit has a small soma, it is easiest to recruit during exercise. 14. Epinephrine is the neurotransmitter released at all neuromuscular junctions. 15. Muscle pH is 7 at rest and can decrease to about 6.2 during severe acidosis. ...
... 13. As the nerve of a slow twitch motor unit has a small soma, it is easiest to recruit during exercise. 14. Epinephrine is the neurotransmitter released at all neuromuscular junctions. 15. Muscle pH is 7 at rest and can decrease to about 6.2 during severe acidosis. ...
D (+)-Glucose, anhydrous
... Glucose is a carbohydrate compound consisting of six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group and they are referred to as aldohexose. The glucose structure can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) and ring (cyclic) form. It occurs in many fruits, animal tissues and fluids, etc. Glucose has several optically d ...
... Glucose is a carbohydrate compound consisting of six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group and they are referred to as aldohexose. The glucose structure can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) and ring (cyclic) form. It occurs in many fruits, animal tissues and fluids, etc. Glucose has several optically d ...
An Overview of Protein Synthesis
... 1) mRNA = messenger RNA – carries the code for the protein to the ribosome. Made from the DNA template. 2) tRNA = transfer RNA – transfers amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome for polypeptide synthesis. 3) rRNA = ribosomal RNA – structural component of ribosomes. Provides the site where po ...
... 1) mRNA = messenger RNA – carries the code for the protein to the ribosome. Made from the DNA template. 2) tRNA = transfer RNA – transfers amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome for polypeptide synthesis. 3) rRNA = ribosomal RNA – structural component of ribosomes. Provides the site where po ...
pbl – night starvation - UQMBBS-2013
... (b) State whether energy stores in these organs can be used to maintain blood glucose concentrations during fasting, and if not, explain why (3 marks) Liver glycogen can be degraded into glucose and released into the blood to maintain BGL. Muscle glycogen is broken down the glucose but cannot exit ...
... (b) State whether energy stores in these organs can be used to maintain blood glucose concentrations during fasting, and if not, explain why (3 marks) Liver glycogen can be degraded into glucose and released into the blood to maintain BGL. Muscle glycogen is broken down the glucose but cannot exit ...
Full Text
... We have developed a novel representation of protein motifs that permits the rapid discovery of structural features in sets of protein sequences with a common structure or function. Many popular methods for representing protein motifs (consensus sequences, weight matrices, profiles, etc.) emphasize c ...
... We have developed a novel representation of protein motifs that permits the rapid discovery of structural features in sets of protein sequences with a common structure or function. Many popular methods for representing protein motifs (consensus sequences, weight matrices, profiles, etc.) emphasize c ...
biology a2
... Blood from right ventricle is pushed into pulmonary artery; via semi – lunar valve; from the pulmonary artery the blood enters the capillary system on the lung alveoli at the arterial bed; At this point carbonic acid and carbonmonohaemoglobin dissociates; to release carbon (iv) oxide; which diffuses ...
... Blood from right ventricle is pushed into pulmonary artery; via semi – lunar valve; from the pulmonary artery the blood enters the capillary system on the lung alveoli at the arterial bed; At this point carbonic acid and carbonmonohaemoglobin dissociates; to release carbon (iv) oxide; which diffuses ...
Integration and regulation of fuel metabolism in maintaining
... weapons, and fire. The absence of predation led to a change in the population distribution of body fatness due to random mutations and genetic drift. According to Speakman [2], such random drift, rather than directed selection, explains why some individuals are able to remain thin while living in an ...
... weapons, and fire. The absence of predation led to a change in the population distribution of body fatness due to random mutations and genetic drift. According to Speakman [2], such random drift, rather than directed selection, explains why some individuals are able to remain thin while living in an ...
Chapter 9 - Mrs. O`Hare Barrows` Classroom Web
... O transport or carrier proteins create an opening through the membrane for these particles to pass through O still passive transport because particles are moving from high concentration to low ...
... O transport or carrier proteins create an opening through the membrane for these particles to pass through O still passive transport because particles are moving from high concentration to low ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.