DNA Notesheet
... DNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Directions: Use the accompanying PowerPoint (www.uhstitans.com/avid-biology) to complete this sheet. This sheet will be due the day of the test. 1. DNA is 2. It is kept in the ...
... DNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Directions: Use the accompanying PowerPoint (www.uhstitans.com/avid-biology) to complete this sheet. This sheet will be due the day of the test. 1. DNA is 2. It is kept in the ...
EOC review packet answers Biology EOC
... coping of DNA during S phase of interphase. DNA is copied in the nucleus of a cell that will soon divide so each new cell has an exact copy of the DNA 35. Explain how replication makes a new DNA molecule that is made up of one strand of “old” DNA and one strand of “new” DNA. DNA unzips and each side ...
... coping of DNA during S phase of interphase. DNA is copied in the nucleus of a cell that will soon divide so each new cell has an exact copy of the DNA 35. Explain how replication makes a new DNA molecule that is made up of one strand of “old” DNA and one strand of “new” DNA. DNA unzips and each side ...
fuels and tissues
... synthesizes lipoproteins and forms VLDL for delivery of fats to other tissues. ...
... synthesizes lipoproteins and forms VLDL for delivery of fats to other tissues. ...
as PDF - Nutrient Reference Values
... CARBOHYDRATE BACKGROUND The primary role of dietary carbohydrate is the provision of energy to cells, particularly the brain that requires glucose for its metabolism. Other nutrients (eg fat , protein and alcohol) can provide energy but there are good reasons to limit the proportion of energy provid ...
... CARBOHYDRATE BACKGROUND The primary role of dietary carbohydrate is the provision of energy to cells, particularly the brain that requires glucose for its metabolism. Other nutrients (eg fat , protein and alcohol) can provide energy but there are good reasons to limit the proportion of energy provid ...
test - Scioly.org
... 17. How does maltose differ from other sugars during a fermentation process? ...
... 17. How does maltose differ from other sugars during a fermentation process? ...
Topic - Structure and Function
... form amino acids and/or other large carbon-based molecules. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on using evidence from models and simulations to support explanations.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the details of the specific chemical reactions or identification of macromolecul ...
... form amino acids and/or other large carbon-based molecules. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on using evidence from models and simulations to support explanations.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the details of the specific chemical reactions or identification of macromolecul ...
MEMBRANES Fluid mosaic of phopholipid bilayer, cholesterol
... Marine animals must work to retain water FW animals must work to eliminate water What about salmon and eels that move between the two What about estuarine animals that deal with daily saline fluctuations Facilitated Transport or Diffusion: movement down concentration gradient but with help Carrier P ...
... Marine animals must work to retain water FW animals must work to eliminate water What about salmon and eels that move between the two What about estuarine animals that deal with daily saline fluctuations Facilitated Transport or Diffusion: movement down concentration gradient but with help Carrier P ...
transcription_and_translation
... connected, the tRNA releases its amino acid which is added to the chain of amino acids growing from the ribosome. • The amino acids are joined by peptide bonds. As each is added, a water molecule is released. (Dehydration hydrolysis) ...
... connected, the tRNA releases its amino acid which is added to the chain of amino acids growing from the ribosome. • The amino acids are joined by peptide bonds. As each is added, a water molecule is released. (Dehydration hydrolysis) ...
transcription_and_translation_2
... connected, the tRNA releases its amino acid which is added to the chain of amino acids growing from the ribosome. • The amino acids are joined by peptide bonds. As each is added, a water molecule is released. (Dehydration hydrolysis) ...
... connected, the tRNA releases its amino acid which is added to the chain of amino acids growing from the ribosome. • The amino acids are joined by peptide bonds. As each is added, a water molecule is released. (Dehydration hydrolysis) ...
Chapter 1 HW
... not need to rewrite the questions. 1. Explain how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are necessary to provide energy that is required to sustain your life. 2. Describe how cellular respiration produces energy that can be stored in ATP 3. Explain why ATP is required for human activities and brea ...
... not need to rewrite the questions. 1. Explain how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are necessary to provide energy that is required to sustain your life. 2. Describe how cellular respiration produces energy that can be stored in ATP 3. Explain why ATP is required for human activities and brea ...
Protein Synthesis Simulation Lab
... make proteins. Summary diagram: DNA (in nucleus) transcribed to mRNA ...
... make proteins. Summary diagram: DNA (in nucleus) transcribed to mRNA ...
Proteins_Fats
... rather than by their structures. • Therefore, they differ widely in size, structure and functions. • They are not soluble in water (inorganic solvent) but soluble in organic solvents (like benzene, ether, chloroform). ...
... rather than by their structures. • Therefore, they differ widely in size, structure and functions. • They are not soluble in water (inorganic solvent) but soluble in organic solvents (like benzene, ether, chloroform). ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 16: Reciprocal regulation of glycolysis and
... deactivates PFK2 (Lehninger p.732-733). Glucagon is the hormone that signals low blood glucose, and stimulates the protein kinase A cascade in liver. This causes fructose-2,6-bisphosphate levels to fall, and thus promote gluconeogenesis. This drives the liver to export glucose and restore the blood ...
... deactivates PFK2 (Lehninger p.732-733). Glucagon is the hormone that signals low blood glucose, and stimulates the protein kinase A cascade in liver. This causes fructose-2,6-bisphosphate levels to fall, and thus promote gluconeogenesis. This drives the liver to export glucose and restore the blood ...
Transcription - Kenmore Tonawanda UFSD
... Let’s practice Translation! • The strand we made earlier is: • If 3 bases code for 1 amino acid, how many amino acids are coded for in our strand? 3 of course! • Using your CODON SHEET, translate the mRNA codons into 3 amino acids ...
... Let’s practice Translation! • The strand we made earlier is: • If 3 bases code for 1 amino acid, how many amino acids are coded for in our strand? 3 of course! • Using your CODON SHEET, translate the mRNA codons into 3 amino acids ...
Section 1.3 Name:
... that it contains the sugar ____________________ instead of _____________________. The second difference is that RNA has the nitrogen base _______________ (U) instead of _______________ (T). Uracil always pairs with _______________ (A), while cytosine (C) will still always pair with ______________ (g ...
... that it contains the sugar ____________________ instead of _____________________. The second difference is that RNA has the nitrogen base _______________ (U) instead of _______________ (T). Uracil always pairs with _______________ (A), while cytosine (C) will still always pair with ______________ (g ...
DNA Replication
... A.1. Abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry B.2. Structures and properties of matter C.1.c. Cells store and use information to guide their functions C.1.d. Cell functions are regulated C1. f. Cells can differentiate, and complex multi-cellular organisms are formed as a highly organized arrange ...
... A.1. Abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry B.2. Structures and properties of matter C.1.c. Cells store and use information to guide their functions C.1.d. Cell functions are regulated C1. f. Cells can differentiate, and complex multi-cellular organisms are formed as a highly organized arrange ...
The Citric Acid Cycle
... Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2 H2O 2CO2 +3NADH + FADH2 + GTP + CoA + 3H+ • Carbons of acetyl groups in acetyl-CoA are oxidized to CO2 • Electrons from this process reduce NAD+ and FAD • One GTP is formed per cycle, this can be converted to ATP • Intermediates in the cycle are not depleted ...
... Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2 H2O 2CO2 +3NADH + FADH2 + GTP + CoA + 3H+ • Carbons of acetyl groups in acetyl-CoA are oxidized to CO2 • Electrons from this process reduce NAD+ and FAD • One GTP is formed per cycle, this can be converted to ATP • Intermediates in the cycle are not depleted ...
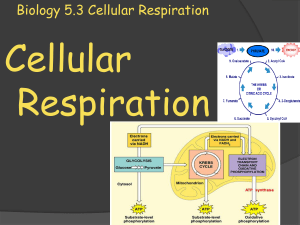
Biology 5.3 Cellular Respiration
... Cellular respiration has two stages. First glucose is broken down to pyruvate during glycolysis, making some ATP. The Krebs cycle is a series of reactions that produce energy-storing molecules during anaerobic respiration During aerobic respiration, large amounts of ATP are made in an electron trans ...
... Cellular respiration has two stages. First glucose is broken down to pyruvate during glycolysis, making some ATP. The Krebs cycle is a series of reactions that produce energy-storing molecules during anaerobic respiration During aerobic respiration, large amounts of ATP are made in an electron trans ...
Why Fermentation
... the absence of oxygen Glycolysis and fermentation together only produces 2 ATP. This is not efficient!! ...
... the absence of oxygen Glycolysis and fermentation together only produces 2 ATP. This is not efficient!! ...
The Genetic Code is Read in Three Bases at a Time
... Within a few years of the Watson-Crick model, a logical hypothesis of DNA coding had been advanced by the physicist George Gamow, who suggested that the RNA polymerase read three-base increments of DNA while moving along the DNA one base at a time. The polymerase would therefore “read” the DNA in ov ...
... Within a few years of the Watson-Crick model, a logical hypothesis of DNA coding had been advanced by the physicist George Gamow, who suggested that the RNA polymerase read three-base increments of DNA while moving along the DNA one base at a time. The polymerase would therefore “read” the DNA in ov ...
2010 Protein Metabolism I
... Microbial protein synthesis related to: 1. Available NH3 and amino acids (DIP) 2. Fermentation of CHOH - Energy ...
... Microbial protein synthesis related to: 1. Available NH3 and amino acids (DIP) 2. Fermentation of CHOH - Energy ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.