This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... Bureau of Economic Research
... One purpose of setting forth this framework is to document my belief that the basic differences among economists are empirical, not theoretical: How important are changes in the supply of money cornpared with changes in the demand for money? Are transactions variables or asset variables most importa ...
... One purpose of setting forth this framework is to document my belief that the basic differences among economists are empirical, not theoretical: How important are changes in the supply of money cornpared with changes in the demand for money? Are transactions variables or asset variables most importa ...
Economics for business
... by changes in interest rates. In the case of public expenditure, an increase in interest rates will raise the cost of servicing the national debt. If there are economic or political constraints on the total level of public spending, this increase in debt servicing will limit the ability of the gover ...
... by changes in interest rates. In the case of public expenditure, an increase in interest rates will raise the cost of servicing the national debt. If there are economic or political constraints on the total level of public spending, this increase in debt servicing will limit the ability of the gover ...
The Macroeconomics Of Down-Shifting: A Suitable Case For Modelling?
... macroeconomic terms it means less consumption (of goods and services). For mainstream macroeconomists this is no problem: Say’s Law ensures that aggregate supply falls at the same speed as aggregate demand, so that the adjustment to a down-shifted economy will be very largely painless. There may be ...
... macroeconomic terms it means less consumption (of goods and services). For mainstream macroeconomists this is no problem: Say’s Law ensures that aggregate supply falls at the same speed as aggregate demand, so that the adjustment to a down-shifted economy will be very largely painless. There may be ...
CHAPTER 36: CURRENT ISSUES IN MACRO - jb
... and prices. In the same way, neoclassical economists believe the economy will self-correct over time. Economists from the neoclassical school of thought tend to be either monetarists or believers of the Rational Expectations Theory. The Rational Expectations Theory holds that consumers and firms are ...
... and prices. In the same way, neoclassical economists believe the economy will self-correct over time. Economists from the neoclassical school of thought tend to be either monetarists or believers of the Rational Expectations Theory. The Rational Expectations Theory holds that consumers and firms are ...
FinalExamReviewGuide
... Substitutes, normal good, inferior good, Invisible Hand, Price Ceilings, Price Floors, Surplus, Shortage, Change in Demand, Change in Quantity Demanded, Complements, Substitutes, Marginal Utility, Diminishing Marginal Utility, ...
... Substitutes, normal good, inferior good, Invisible Hand, Price Ceilings, Price Floors, Surplus, Shortage, Change in Demand, Change in Quantity Demanded, Complements, Substitutes, Marginal Utility, Diminishing Marginal Utility, ...
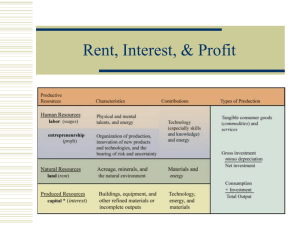
Rent, Interest, and Profit
... Usually closest to long-term, near riskless securities and bonds ...
... Usually closest to long-term, near riskless securities and bonds ...
File - VaNDERNOMICS
... Assume Expansionary Fiscal Policy (G↑ and/or T↓ .: government budget moves toward deficit) deficit spending .: DLF → or SLF ← .: r%↑ .: D$ → .: $↑ .: U.S. goods/services relatively expensive and foreign goods/services are relatively cheap .: X↓ and/or M↑ .: XN ↓ ...
... Assume Expansionary Fiscal Policy (G↑ and/or T↓ .: government budget moves toward deficit) deficit spending .: DLF → or SLF ← .: r%↑ .: D$ → .: $↑ .: U.S. goods/services relatively expensive and foreign goods/services are relatively cheap .: X↓ and/or M↑ .: XN ↓ ...
Macro_online_chapter_11_14e
... 1. Resource prices and interest rates are not very flexible so they won’t direct an economy to equilibrium 2. Changes in output will direct an economy to equilibrium ...
... 1. Resource prices and interest rates are not very flexible so they won’t direct an economy to equilibrium 2. Changes in output will direct an economy to equilibrium ...
What caused the Great Depression?
... in 1931 investors demanded deposits be exchanged for gold (bleeding Austrian gold reserves) Austria stopped honoring gold standard commitments panic spread Germany froze gold exchanges Great Britain left the gold standard foreign depositors rushed to make withdrawals from ...
... in 1931 investors demanded deposits be exchanged for gold (bleeding Austrian gold reserves) Austria stopped honoring gold standard commitments panic spread Germany froze gold exchanges Great Britain left the gold standard foreign depositors rushed to make withdrawals from ...
Word
... On the contrary, the non-term (one day) deposits – featuring considerably higher liquidity compared to terms deposits – further grew (+12.5 % year-on-year), especially on the giro accounts of households (+13.3 %). Strong accumulation of funds however continues on the current accounts of companies (+ ...
... On the contrary, the non-term (one day) deposits – featuring considerably higher liquidity compared to terms deposits – further grew (+12.5 % year-on-year), especially on the giro accounts of households (+13.3 %). Strong accumulation of funds however continues on the current accounts of companies (+ ...
The Macroeconomy
... consumers begin to purchase less expensive foreign goods. This results in less domestic consumption which leads to decreased production. • FOREX Market ...
... consumers begin to purchase less expensive foreign goods. This results in less domestic consumption which leads to decreased production. • FOREX Market ...
Money Demand and the Quantity Theory
... interest rates alone. Furthermore, as Friedman (1968) explains, very low interest rates like those seen around the world during the Great Depression and perhaps again today can sometimes reflect deflationary expectations that signal that monetary policy, far from being appropriately accommodative, i ...
... interest rates alone. Furthermore, as Friedman (1968) explains, very low interest rates like those seen around the world during the Great Depression and perhaps again today can sometimes reflect deflationary expectations that signal that monetary policy, far from being appropriately accommodative, i ...
Eco 212_____Name
... to be stable when governments do not attempt to manage the economy – but unstable when governments do try to manage the economy. This outcome is best explained by: a. b. c. d. e. ...
... to be stable when governments do not attempt to manage the economy – but unstable when governments do try to manage the economy. This outcome is best explained by: a. b. c. d. e. ...
Midterm 3
... Implicit Contract Theory Real Business Cycle Theory Lucas Misperceptions Theory Keynesian Business Cycle Theory Reverse Causation Theory ...
... Implicit Contract Theory Real Business Cycle Theory Lucas Misperceptions Theory Keynesian Business Cycle Theory Reverse Causation Theory ...
Notes
... that is what is most relevant for any actual impact of interest rate changes or shifts in liquidity. impact on interest rates: look at the data! (excel spreadsheet) So in conclusion: 1. Fed can react quickly 2. Fed can only affect short-term interest rates - these feed into the "prime rate" but the ...
... that is what is most relevant for any actual impact of interest rate changes or shifts in liquidity. impact on interest rates: look at the data! (excel spreadsheet) So in conclusion: 1. Fed can react quickly 2. Fed can only affect short-term interest rates - these feed into the "prime rate" but the ...
Keynesian interpretation of the quantity theory of money
... 2. Prices, and especially wages, respond slowly to changes in supply and demand, resulting in periodic shortages and surpluses, especially of labor. ...
... 2. Prices, and especially wages, respond slowly to changes in supply and demand, resulting in periodic shortages and surpluses, especially of labor. ...
Chapter 11 - University of Alberta
... unemployment rate is always greater than zero, but also why it rises so sharply in recessions. ...
... unemployment rate is always greater than zero, but also why it rises so sharply in recessions. ...
Keynes and the Classical theory
... According to the classical model, increase in the money supply will increase aggregate demand for goods and services directly. Keynes argued that classical economists overstated the impact of the money supply on the ...
... According to the classical model, increase in the money supply will increase aggregate demand for goods and services directly. Keynes argued that classical economists overstated the impact of the money supply on the ...
Chapter 16
... creative forms of financing proliferate, including interest-only loans and shared equity mortgages (for people who cannot afford any down payment). • Real housing prices also have a strong negative correlation with mortgage rates. So when rates drop, housing prices rise faster. That encourages more ...
... creative forms of financing proliferate, including interest-only loans and shared equity mortgages (for people who cannot afford any down payment). • Real housing prices also have a strong negative correlation with mortgage rates. So when rates drop, housing prices rise faster. That encourages more ...
S.6 Economics Methodology 92`6. Selfishness and scarcity A imply
... Would there still be economics if the concept of ‘utility’ had never been invented? And would there still be economics if the postulate of ‘constrained maximization’ had never been invented? (8) Economics would still exist if there had not been the concept of ‘utility’, because it can be substituted ...
... Would there still be economics if the concept of ‘utility’ had never been invented? And would there still be economics if the postulate of ‘constrained maximization’ had never been invented? (8) Economics would still exist if there had not been the concept of ‘utility’, because it can be substituted ...
Reliving the Crash of `29: How Hoover`s Policies Blazed the Trail for
... paper currencies – all, that is, except for the United States, which was embroiled in the war for a relatively short time and could therefore afford to remain on the gold standard. After the war the nations faced a world currency breakdown with rampant inflation and chaotically falling exchange rate ...
... paper currencies – all, that is, except for the United States, which was embroiled in the war for a relatively short time and could therefore afford to remain on the gold standard. After the war the nations faced a world currency breakdown with rampant inflation and chaotically falling exchange rate ...
Lecture O: Overview
... economics seeks to do and to describe. Economics analyzes the allocation of the resources of a society or nation. A nation has limited labor, production facilities, and technology to produce things for it’s members. Thus, choices must be made about the mix of products that will be produced. There wi ...
... economics seeks to do and to describe. Economics analyzes the allocation of the resources of a society or nation. A nation has limited labor, production facilities, and technology to produce things for it’s members. Thus, choices must be made about the mix of products that will be produced. There wi ...
Instructor: Prof Robert Hill Friedman and Monetarism Lewis and
... What matters here is the real rate of interest, not the nominal rate. A contractionary monetary policy causes the real interest rate to rise, which reduces investment by firms and consumer expenditure on housing and consumer durables (such as cars and refrigerators). In recent years there has been a ...
... What matters here is the real rate of interest, not the nominal rate. A contractionary monetary policy causes the real interest rate to rise, which reduces investment by firms and consumer expenditure on housing and consumer durables (such as cars and refrigerators). In recent years there has been a ...