Introduction to macroeconomics
... by businesses on new equipment, new factories, and new buildings. Classical economists believed that investment spending depended primarily in interest rates. In contrast, Keynes believed that investment spending depended on expected profits. Interest rates and technological change can spur and incr ...
... by businesses on new equipment, new factories, and new buildings. Classical economists believed that investment spending depended primarily in interest rates. In contrast, Keynes believed that investment spending depended on expected profits. Interest rates and technological change can spur and incr ...
creation of money
... fraction of their customers’ deposits as readily available reserves (i.e. cash in vaults and deposits at the central bank). They are not required to maintain 100% backing for all deposits. This practice is safe in general, as depositors generally do not all demand payment at the same time. However, ...
... fraction of their customers’ deposits as readily available reserves (i.e. cash in vaults and deposits at the central bank). They are not required to maintain 100% backing for all deposits. This practice is safe in general, as depositors generally do not all demand payment at the same time. However, ...
creation of money
... fraction of their customers’ deposits as readily available reserves (i.e. cash in vaults and deposits at the central bank). They are not required to maintain 100% backing for all deposits. This practice is safe in general, as depositors generally do not all demand payment at the same time. However, ...
... fraction of their customers’ deposits as readily available reserves (i.e. cash in vaults and deposits at the central bank). They are not required to maintain 100% backing for all deposits. This practice is safe in general, as depositors generally do not all demand payment at the same time. However, ...
Essential Understandings Economic Philosophies Basic concepts of
... Discuss the impact of interest rates on the demand for money (Theory of liquidity preference) Impact of interest rates on Money Supply? ...
... Discuss the impact of interest rates on the demand for money (Theory of liquidity preference) Impact of interest rates on Money Supply? ...
The Panic of 1857 in the absence of a National Bank Peter Kostadinov
... US but have international implications because they take place in a world of interconnected trade. Yet, these crises are different in their length, severity and the way they were handled by the authorities. The two longest and most severe develop in the context of a central bank having the control o ...
... US but have international implications because they take place in a world of interconnected trade. Yet, these crises are different in their length, severity and the way they were handled by the authorities. The two longest and most severe develop in the context of a central bank having the control o ...
Business Cycle Facts and Standard RBC Theory
... The relative labor supply in the two periods responds to relative wage. If w1 is larger than w2 (household expects that future productivity will be lower than the current productivity), household supplies more labor today than in the next period. In other words, household has a stronger incentive to ...
... The relative labor supply in the two periods responds to relative wage. If w1 is larger than w2 (household expects that future productivity will be lower than the current productivity), household supplies more labor today than in the next period. In other words, household has a stronger incentive to ...
BOOK ONE
... 15. When a J-Curve situation exists, a depreciation of the US dollar relative to the yen causes a prompt improvement in nominal US net exports, but a delayed, more gradual improvement in real US net exports. ...
... 15. When a J-Curve situation exists, a depreciation of the US dollar relative to the yen causes a prompt improvement in nominal US net exports, but a delayed, more gradual improvement in real US net exports. ...
Marxism and the Uno School
... skilled labor (when compared to simple labor) and the compatibility of the labor theory of value with the reality ofjoint-production (when a single production process like raising cattle produces two products-beef and hide). I t is here, in relation to this second, deeper plane of discussion, that I ...
... skilled labor (when compared to simple labor) and the compatibility of the labor theory of value with the reality ofjoint-production (when a single production process like raising cattle produces two products-beef and hide). I t is here, in relation to this second, deeper plane of discussion, that I ...
Misunderstanding the Great Depression, making the next one
... – “Given both the prominence of debt in popular discussion of our current economic difficulties …, one might have expected debt to be at the heart of most mainstream macroeconomic models… – Perhaps somewhat surprisingly, however, it is quite common to abstract altogether from this…” (p. 2) • But ret ...
... – “Given both the prominence of debt in popular discussion of our current economic difficulties …, one might have expected debt to be at the heart of most mainstream macroeconomic models… – Perhaps somewhat surprisingly, however, it is quite common to abstract altogether from this…” (p. 2) • But ret ...
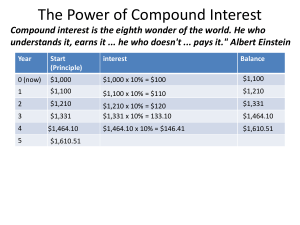
The Power of Compound Interest
... •If your growth slips to 2%, it will double in 36 years. If growth increases to 4%, the economy doubles in 18 years. •Given the speed at which technology develops, shaving years off your growth time could be very important ...
... •If your growth slips to 2%, it will double in 36 years. If growth increases to 4%, the economy doubles in 18 years. •Given the speed at which technology develops, shaving years off your growth time could be very important ...
Three Items for the Macroeconomic Agenda
... I. Ricardo's Farm Macroeconomics is still dominated by the image of the Ricardian farm: constant returns when both land and labor can be varied; smoothly diminishing returns when labor is varied, land held constant. Increasing returns have finally come onto the theoretical agenda in the recently bur ...
... I. Ricardo's Farm Macroeconomics is still dominated by the image of the Ricardian farm: constant returns when both land and labor can be varied; smoothly diminishing returns when labor is varied, land held constant. Increasing returns have finally come onto the theoretical agenda in the recently bur ...
Vienna vs. Chicago on Monetary Issues
... One is from Vienna, the other is from Chicago. The Viennese investigator asks, “Where in the world did this hideous thing come from?” [Here, I seemed to have stacked the cards against the Austrian. It’s hard even to imagine an insightful answer to this question—unless, of course, the monster turns o ...
... One is from Vienna, the other is from Chicago. The Viennese investigator asks, “Where in the world did this hideous thing come from?” [Here, I seemed to have stacked the cards against the Austrian. It’s hard even to imagine an insightful answer to this question—unless, of course, the monster turns o ...
Document
... perfect information on prices. If a certain general price increase (inflation) is perceived by the agents as an increase in the relative price of the commodity they are producing, then their immediate rational reaction would be to increase the production and supply of the commodity. Once the agents ...
... perfect information on prices. If a certain general price increase (inflation) is perceived by the agents as an increase in the relative price of the commodity they are producing, then their immediate rational reaction would be to increase the production and supply of the commodity. Once the agents ...
View/Open
... without a tax cut. Nevertheless, a tax cut is desirable for several reasons regardless of its effects on final demand. First, our tax system is in serious need of revision for the purpose of increasing incentives and thereby increasing the capacity of our economy to grow. Many tax laws were adopted ...
... without a tax cut. Nevertheless, a tax cut is desirable for several reasons regardless of its effects on final demand. First, our tax system is in serious need of revision for the purpose of increasing incentives and thereby increasing the capacity of our economy to grow. Many tax laws were adopted ...
CH 18-Monetary and Fiscal Policy
... “The Federal Reserve, through its power to raise and lower interest rates, exercises more influence over economic growth and the level of employment than any other government entity. That unusual role dates from the 1970s, when the executive branch and Congress pulled back from the use of fiscal too ...
... “The Federal Reserve, through its power to raise and lower interest rates, exercises more influence over economic growth and the level of employment than any other government entity. That unusual role dates from the 1970s, when the executive branch and Congress pulled back from the use of fiscal too ...
The Fed and The Interest Rates
... Monetary Policy, this will lead to decline in interest rate, this lead to increase components of AD and finally this leads to pushing the economy (Unless it is in a liquidity trap) • both schools about how CB should try to effect on real sector ...
... Monetary Policy, this will lead to decline in interest rate, this lead to increase components of AD and finally this leads to pushing the economy (Unless it is in a liquidity trap) • both schools about how CB should try to effect on real sector ...
ECON 3080-004 Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory
... models, that yield policy implications. Moreover, we wish to place great emphasis on these policy implications, whether they be fiscal policies, monetary policies, or policies of other types. As I see it, we are concerned with understanding how policy makers can make society a better place for us to ...
... models, that yield policy implications. Moreover, we wish to place great emphasis on these policy implications, whether they be fiscal policies, monetary policies, or policies of other types. As I see it, we are concerned with understanding how policy makers can make society a better place for us to ...
Inflation, Unemployment, and Stabilization Policies: Macroeconomic
... be used to fight recessions. Keynesian economists didn’t oppose discretionary monetary policy, but they were skeptical about its effectiveness. Monetarists argued that discretionary monetary policy was doing ...
... be used to fight recessions. Keynesian economists didn’t oppose discretionary monetary policy, but they were skeptical about its effectiveness. Monetarists argued that discretionary monetary policy was doing ...
1 The Insufficiency of Economics Dan Hammond
... economics. It also comes from my personal intellectual migration from economics and history of economics to “philosophy, politics, and economics.” In a nutshell, the argument that I will develop is that economics needs to be in “philosophy, politics, and economics.” Economics has been deracinated ...
... economics. It also comes from my personal intellectual migration from economics and history of economics to “philosophy, politics, and economics.” In a nutshell, the argument that I will develop is that economics needs to be in “philosophy, politics, and economics.” Economics has been deracinated ...
Statistics/Data - Dana Investment Advisors
... statistics or you can end up with paralysis by analysis and be too fearful to make any investment decisions. So review the statistic, listen to the Fed and use some common sense. Look at the current direction of interest rates and the economy. Remember that the “trend is your friend.” Sometimes an ...
... statistics or you can end up with paralysis by analysis and be too fearful to make any investment decisions. So review the statistic, listen to the Fed and use some common sense. Look at the current direction of interest rates and the economy. Remember that the “trend is your friend.” Sometimes an ...
Test#1
... The QTM disequilibrium changes are, of course, short-run adjustment processes in moving to the new long-run equilibrium. These disequilibrium adjustments are also consistent with the neoclassical approach, as well as being a fundamental aspect of Keynesian ideas. Wicksell shifted the transmission me ...
... The QTM disequilibrium changes are, of course, short-run adjustment processes in moving to the new long-run equilibrium. These disequilibrium adjustments are also consistent with the neoclassical approach, as well as being a fundamental aspect of Keynesian ideas. Wicksell shifted the transmission me ...
Lecture 4 Business Cycles and Aggregate Supply and
... Principles of Macroeconomics Lecture 4 BUSINESS CYCLES AND AGGREGATE DEMAND ...
... Principles of Macroeconomics Lecture 4 BUSINESS CYCLES AND AGGREGATE DEMAND ...
Power Point - U of T : Economics
... • M = stock of money in coin, notes, bank deposits (‘high-powered’) • V = the velocity of circulation; the rate at which a unit of money circulates in effecting transactions in course of one year (average turnover) – difficult to measure: only as V = T/M (see below) • P = measure of the price level; ...
... • M = stock of money in coin, notes, bank deposits (‘high-powered’) • V = the velocity of circulation; the rate at which a unit of money circulates in effecting transactions in course of one year (average turnover) – difficult to measure: only as V = T/M (see below) • P = measure of the price level; ...