DNA Structure Worksheet
... 5. These bases are of two different types of molecules: purines and pyrimidines. Purines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure, and pyrimidines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure. 6. The two bases that are purines are _____________________ and _________________ ...
... 5. These bases are of two different types of molecules: purines and pyrimidines. Purines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure, and pyrimidines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure. 6. The two bases that are purines are _____________________ and _________________ ...
STSE Power point
... volunteers’ DNA for similar studies later All participants must be volunteers as it is considered unethical to purchase bodily fluids in this country ...
... volunteers’ DNA for similar studies later All participants must be volunteers as it is considered unethical to purchase bodily fluids in this country ...
Polymerase Chain Reaction and DNA Sequencing
... • In this procedure, known as RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase is used to copy all of the mRNAs in ...
... • In this procedure, known as RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase is used to copy all of the mRNAs in ...
DNA
... Complimentary sequences of ssDNA will bind together to form dsDNA Temperature at which dsDNA remains together depends on percent of matching and GC content Does not yield the DNA sequence of organisms, just the sequence similarity between organisms Total genomic hybridization can be used to estimate ...
... Complimentary sequences of ssDNA will bind together to form dsDNA Temperature at which dsDNA remains together depends on percent of matching and GC content Does not yield the DNA sequence of organisms, just the sequence similarity between organisms Total genomic hybridization can be used to estimate ...
Gene Technology - Manasquan Public Schools
... Comparison of DNA found in blood samples, tissue samples, etc. to identify individuals for classification, criminology, paternity suits, etc. Can determine diseases & genetic defects Tracing family history & evolution ...
... Comparison of DNA found in blood samples, tissue samples, etc. to identify individuals for classification, criminology, paternity suits, etc. Can determine diseases & genetic defects Tracing family history & evolution ...
Study Guide Unit 4 - Mrs. Wolodkowicz`s Biological Realm
... write the definitions for DNA & RNA, transcription & translation, autosome, & sex linkage. the components of DNA the nitrogen bases & their complementary base pairs in DNA & RNA functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, geno ...
... write the definitions for DNA & RNA, transcription & translation, autosome, & sex linkage. the components of DNA the nitrogen bases & their complementary base pairs in DNA & RNA functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, geno ...
DNA/RNA Worksheet TACGGCACCGTTAGGATT
... Is DNA double-stranded or single-stranded? ________________________________________ ...
... Is DNA double-stranded or single-stranded? ________________________________________ ...
Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering, Chapter Summary Date
... 6. a techniques scientist used to make many copies of a certain gene. 8. produced by combining DNA from different species or different sources. 14. a technique that breed specific animals and plants with desired traits. This technique takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in a gro ...
... 6. a techniques scientist used to make many copies of a certain gene. 8. produced by combining DNA from different species or different sources. 14. a technique that breed specific animals and plants with desired traits. This technique takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in a gro ...
Chapter 10 Study Guide Know the definitions for: Cross
... Within the DNA ladder; Adenine always pairs with _?_ , and Cytosine always pairs with _?_ Be able to describe the process of DNA replication (DNA making exact copy of itself). Be able to put the following in order of size (DNA, cell, nucleotide, nucleus, chromosome). RNA (like DNA) is also composed ...
... Within the DNA ladder; Adenine always pairs with _?_ , and Cytosine always pairs with _?_ Be able to describe the process of DNA replication (DNA making exact copy of itself). Be able to put the following in order of size (DNA, cell, nucleotide, nucleus, chromosome). RNA (like DNA) is also composed ...
How many fragments of DNA can be assembled in one reaction
... NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly: Bridging dsDNA with a ssDNA Oligo Learn how NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly bridges dsDNA with a ssDNA oligo. ...
... NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly: Bridging dsDNA with a ssDNA Oligo Learn how NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly bridges dsDNA with a ssDNA oligo. ...
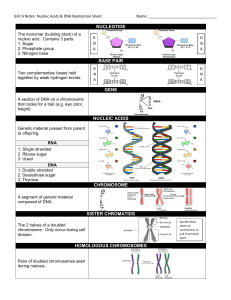
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... CHROMOSOME A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
... CHROMOSOME A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
Life Science Vocabulary.xlsx
... an allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present recessive an allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present co-dominance a condition in which neither of the two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive genotype an organism's genetic make up or allele combi ...
... an allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present recessive an allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present co-dominance a condition in which neither of the two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive genotype an organism's genetic make up or allele combi ...
Word Definition Synonym 1 DNA replication the
... an allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present recessive an allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present co-dominance a condition in which neither of the two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive genotype an organism's genetic make up or allele combi ...
... an allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present recessive an allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present co-dominance a condition in which neither of the two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive genotype an organism's genetic make up or allele combi ...
Polymerase Chain Reaction
... hot springs where the bacterium was discovered), the temperature of the vial is raised to 72-75 Degrees Celsius The DNA polymerase recognizes the primer and makes a complementary copy of the template which is now single stranded. Approximately 150 nucleotides/sec ...
... hot springs where the bacterium was discovered), the temperature of the vial is raised to 72-75 Degrees Celsius The DNA polymerase recognizes the primer and makes a complementary copy of the template which is now single stranded. Approximately 150 nucleotides/sec ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation STUDY GUIDE
... What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid? How many amino acids are used to make up the all of the proteins in the human body? A tRNA that carries the amino acid methionine pairs with ...
... What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid? How many amino acids are used to make up the all of the proteins in the human body? A tRNA that carries the amino acid methionine pairs with ...
The Effects of Predictive Genetic Testing on the - Antioch Co-op
... - Carriers and non-carriers of the colon cancer gene will be screened again after they have received their results ...
... - Carriers and non-carriers of the colon cancer gene will be screened again after they have received their results ...
HomeworkCh7
... d. What are the three main phases of RNA synthesis? e. Can more than one copy of the gene be copied at the same time? 6. Translation a. What is translation? Why do you think it’s called that? b. How many different codons are possible for providing a three nucleotide code for the amino acids? Take a ...
... d. What are the three main phases of RNA synthesis? e. Can more than one copy of the gene be copied at the same time? 6. Translation a. What is translation? Why do you think it’s called that? b. How many different codons are possible for providing a three nucleotide code for the amino acids? Take a ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.