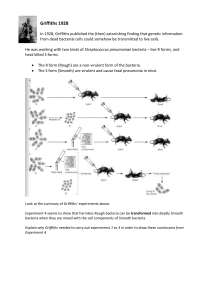
Name - EdWeb
... 16. Each gene in DNA encodes information on how to make an _________________________________ 17. Once in the cytoplasm, the _______________ reads the message. What is Heredity? 18. The passing of traits from parents to a child is the basis of _______________________________ 19. Every child receives ...
... 16. Each gene in DNA encodes information on how to make an _________________________________ 17. Once in the cytoplasm, the _______________ reads the message. What is Heredity? 18. The passing of traits from parents to a child is the basis of _______________________________ 19. Every child receives ...
DNA Technology
... 2. Research an example of how the technique has been used by humans. You can use one of the examples listed above or find your own. Be specific in explaining how the technique was used. Cite your sources – not the textbook. This is the major part of your report. DO NOT USE INSULIN or INDENTIFYING CR ...
... 2. Research an example of how the technique has been used by humans. You can use one of the examples listed above or find your own. Be specific in explaining how the technique was used. Cite your sources – not the textbook. This is the major part of your report. DO NOT USE INSULIN or INDENTIFYING CR ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... o On vs. off o What types of cells have this? o Role of lactose (or allolactose) Lac operon vs. trp operon Genetic Engineering (5 m/c + plasmid mapping) Restriction Enyzmes Sticky ends Hydrogen bonds DNA charge Direction DNA migrates in gel electrophoresis Which sized DNA fragments mov ...
... o On vs. off o What types of cells have this? o Role of lactose (or allolactose) Lac operon vs. trp operon Genetic Engineering (5 m/c + plasmid mapping) Restriction Enyzmes Sticky ends Hydrogen bonds DNA charge Direction DNA migrates in gel electrophoresis Which sized DNA fragments mov ...
COA: phiX174 DNA/BsuRI (HaeIII) Marker, 9, ready-to
... • Following electrophoretic separation on gel, visualize the DNA bands by ethidium bromide staining. ...
... • Following electrophoretic separation on gel, visualize the DNA bands by ethidium bromide staining. ...
What`s the Big Deal About DNA?
... 5. Describe why scientists would want to change how fast (or slow) organisms like salmon or grass grow. Do you think this should be done? Defend your answer. ...
... 5. Describe why scientists would want to change how fast (or slow) organisms like salmon or grass grow. Do you think this should be done? Defend your answer. ...
Study Guide for LS
... molecules. When DNA copies itself it splits down the middle where the two bases meet. The bases on each side of the molecule can be used as a pattern for a new complementary side. ...
... molecules. When DNA copies itself it splits down the middle where the two bases meet. The bases on each side of the molecule can be used as a pattern for a new complementary side. ...
DNA info
... chromosome in males), and each pair is made up of a single molecule of double-stranded DNA tightly coiled many times around a protein called a histone that supports its structure. If you imagine this strand of DNA being uncoiled and stretched out, it might look like a long ladder. The sides of the l ...
... chromosome in males), and each pair is made up of a single molecule of double-stranded DNA tightly coiled many times around a protein called a histone that supports its structure. If you imagine this strand of DNA being uncoiled and stretched out, it might look like a long ladder. The sides of the l ...
DNA experiments exercise
... What do these data reveal about the ratios different bases? Watson and Crick used this information as one of their key insights into the double helix structure of DNA. ...
... What do these data reveal about the ratios different bases? Watson and Crick used this information as one of their key insights into the double helix structure of DNA. ...
Hypercholesterolemia Questions KEY
... It is found on chromosome 19 and only one copy must be present for a person to have the disease. Both homozygous dominant as well as heterozygous individuals will have the disease. However, a person that is homozygous dominant will have a worse case of the disease. ...
... It is found on chromosome 19 and only one copy must be present for a person to have the disease. Both homozygous dominant as well as heterozygous individuals will have the disease. However, a person that is homozygous dominant will have a worse case of the disease. ...
Genetics review sheet VOCABULARY- on the test, the vocabulary
... VOCABULARY- on the test, the vocabulary section will be fill in the blank with a word bank 1. gene ...
... VOCABULARY- on the test, the vocabulary section will be fill in the blank with a word bank 1. gene ...
Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
... DNA samples for denaturing gel electrophoresis must be denatured prior to loading, to avoid time dependent denaturation artifacts on the gel. This is usually carried out by diluting the sample into 95% formamide and heating to 95°C, see the Dideoxy Sequencing (Taq Polymerase) Protocol for a formula ...
... DNA samples for denaturing gel electrophoresis must be denatured prior to loading, to avoid time dependent denaturation artifacts on the gel. This is usually carried out by diluting the sample into 95% formamide and heating to 95°C, see the Dideoxy Sequencing (Taq Polymerase) Protocol for a formula ...
DNA Structure, Replication and Protein Synthesis
... Name the part of a double stranded chromosome to which spindle fibres attach during cell division ...
... Name the part of a double stranded chromosome to which spindle fibres attach during cell division ...
Additional Slides Ch Biotech Dr Violet
... the disease is actually one and the same as the mutation that gives rise to the polymorphism. Direct detection by RFLPs of diseases that result from point mutations is at present limited to only a few genetic diseases. • Sickle cell anemia is caused by a point mutation. The sequence altered by the m ...
... the disease is actually one and the same as the mutation that gives rise to the polymorphism. Direct detection by RFLPs of diseases that result from point mutations is at present limited to only a few genetic diseases. • Sickle cell anemia is caused by a point mutation. The sequence altered by the m ...
RODENT GENOTYPING The proper identification of transgenic
... The proper identification of transgenic animals in a litter is critical to the efficient pursuit of research and in reducing the number of animals involved in a research project. Most often the genotype is determined by analysis of DNA extracted from tissues of young mice. Analysis by the Polymerase ...
... The proper identification of transgenic animals in a litter is critical to the efficient pursuit of research and in reducing the number of animals involved in a research project. Most often the genotype is determined by analysis of DNA extracted from tissues of young mice. Analysis by the Polymerase ...
Biology Study Guide CH 12 Part I DNA-RNA
... 7. DNA is copied during a process called __________________. 8. DNA _____________ results in 2 DNA molecules, each consisting of one new strand & one original strand. 9. Be sure that you understand base pairing and can give the sequence of a complementary DNA strand. 10. Where is DNA located in a eu ...
... 7. DNA is copied during a process called __________________. 8. DNA _____________ results in 2 DNA molecules, each consisting of one new strand & one original strand. 9. Be sure that you understand base pairing and can give the sequence of a complementary DNA strand. 10. Where is DNA located in a eu ...
Lab 1 - DNA Isolation from Drosophila melanogaster (Fly DNA Mini
... Use a different pipette tip for each component of the reaction so as to NOT contaminate the stock solutions. As usual, it is very important that you employ sterile technique to avoid contamination. Only remove the enzyme from the freezer or from the ice when you are prepared to add it. When any enzy ...
... Use a different pipette tip for each component of the reaction so as to NOT contaminate the stock solutions. As usual, it is very important that you employ sterile technique to avoid contamination. Only remove the enzyme from the freezer or from the ice when you are prepared to add it. When any enzy ...
PPT
... for 10~20 min at RT Fragments of 10~50 bp were purified from 2% low meltin point agarose gels ...
... for 10~20 min at RT Fragments of 10~50 bp were purified from 2% low meltin point agarose gels ...
Test Study Guide
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.