ch 12 quick check answers
... DNA profiling of a cat was critical evidence in one case in Canada (see page 451). Cat hairs were found on a bloodstained jacket found near a crime scene and the blood matched that of the victim. The estranged husband of the victim was a suspect and so the cat hairs on this jacket were tested to s ...
... DNA profiling of a cat was critical evidence in one case in Canada (see page 451). Cat hairs were found on a bloodstained jacket found near a crime scene and the blood matched that of the victim. The estranged husband of the victim was a suspect and so the cat hairs on this jacket were tested to s ...
Chapter 12: Genetic Engineering
... genes that might predispose individuals to other medical problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer If ...
... genes that might predispose individuals to other medical problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer If ...
Q3 - Franklin County Community School Corporation
... List the correct base pairs of DNA Explain how and why the genetic code is universal Describe the structure and function of DNA Differentiate between replication, transcription, and translation. Draw and label the parts of DNA Replication Draw and explain transcription and translation Describe how g ...
... List the correct base pairs of DNA Explain how and why the genetic code is universal Describe the structure and function of DNA Differentiate between replication, transcription, and translation. Draw and label the parts of DNA Replication Draw and explain transcription and translation Describe how g ...
Recombinant DNA Simulation
... Investigation 6: Recombinant DNA Simulation Introduction: One of the most important processes developed by biotechnologists was the procedure where a gene is removed from the DNA of one organism and inserted into the DNA of another organism. This technique is called Recombinant DNA. The entire proce ...
... Investigation 6: Recombinant DNA Simulation Introduction: One of the most important processes developed by biotechnologists was the procedure where a gene is removed from the DNA of one organism and inserted into the DNA of another organism. This technique is called Recombinant DNA. The entire proce ...
DNA is - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... bonds, double helix, phosphate groups, 5 carbon sugar, base pairing ...
... bonds, double helix, phosphate groups, 5 carbon sugar, base pairing ...
AIPL Update - John B. Cole`s Website
... retained, and >15,000 SNP were added from the GeneSeek high-density ...
... retained, and >15,000 SNP were added from the GeneSeek high-density ...
Georgia Department of Education Study Guide Domain III Genetic
... Describe the meaning of haploid. Are 2n cells diploid or haploid? Are 1n cells diploid or haploid? Meiosis provides the opportunity for what? Explain the different kinds of genetic combination a person can produce. Another source of genetic variation during meiosis is what? Crossing over occurs when ...
... Describe the meaning of haploid. Are 2n cells diploid or haploid? Are 1n cells diploid or haploid? Meiosis provides the opportunity for what? Explain the different kinds of genetic combination a person can produce. Another source of genetic variation during meiosis is what? Crossing over occurs when ...
Mitochondrial DNA Analysis
... • Rather than genotyping STRs or SNPs • mtDNA profile is determined by sequencing both hypervariable regions • mtDNA is a haploid genome • Determining the mitochondria’s haplotype ...
... • Rather than genotyping STRs or SNPs • mtDNA profile is determined by sequencing both hypervariable regions • mtDNA is a haploid genome • Determining the mitochondria’s haplotype ...
Mutations Activity
... small subunits called nucleotides. There are four possible nitrogen bases in DNA—adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). The nitrogen bases will preferentially bond with only one other nitrogenous base–adenine with thynine and guanine with cytosine. The bonded nitrogen bases are cal ...
... small subunits called nucleotides. There are four possible nitrogen bases in DNA—adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). The nitrogen bases will preferentially bond with only one other nitrogenous base–adenine with thynine and guanine with cytosine. The bonded nitrogen bases are cal ...
Plasmid Isolation Using Alkaline Lysis
... free the plasmid DNA from the cell, leaving behind the E. coli chromosomal DNA with cell wall debris. The protocol described involves three basic steps: growth of bacteria and amplification of the plasmid; harvesting and lysis of the bacteria; and purification of the plasmid DNA. These purification ...
... free the plasmid DNA from the cell, leaving behind the E. coli chromosomal DNA with cell wall debris. The protocol described involves three basic steps: growth of bacteria and amplification of the plasmid; harvesting and lysis of the bacteria; and purification of the plasmid DNA. These purification ...
Biology 155 Practice Exam 3 Name
... recessive trait. If a man who is noncolorblind marries a noncolorblind woman whose father was colorblind, what proportion of their sons and daughters should be colorblind? a. all sons, 1/2 daughters b. no sons, 1/2 daughters c. 1/2 sons, no daughters d. 1/2 sons, 1/2 daughters 12. For a single trait ...
... recessive trait. If a man who is noncolorblind marries a noncolorblind woman whose father was colorblind, what proportion of their sons and daughters should be colorblind? a. all sons, 1/2 daughters b. no sons, 1/2 daughters c. 1/2 sons, no daughters d. 1/2 sons, 1/2 daughters 12. For a single trait ...
Unit 4 Review
... ____ 46. An organism with a dominant allele for a particular form of a trait will sometimes exhibit that trait. _________________________ ____ 47. If an organism has 16 chromosomes in each of its egg cells, the organism’s diploid number is 32. _________________________ ____ 48. Mitosis results in tw ...
... ____ 46. An organism with a dominant allele for a particular form of a trait will sometimes exhibit that trait. _________________________ ____ 47. If an organism has 16 chromosomes in each of its egg cells, the organism’s diploid number is 32. _________________________ ____ 48. Mitosis results in tw ...
Galter Health Sciences Library
... Very few polymorphisms show direct impact by creating deleterious phenotypes. However, non-disease-causing polymorphisms, when mapped to the genome, may serve as markers to identify and map other genes that do cause disease when mutated. If these non-disease-causing variations are found to be inheri ...
... Very few polymorphisms show direct impact by creating deleterious phenotypes. However, non-disease-causing polymorphisms, when mapped to the genome, may serve as markers to identify and map other genes that do cause disease when mutated. If these non-disease-causing variations are found to be inheri ...
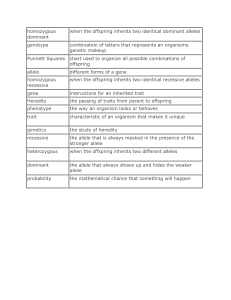
homozygous dominant when the offspring inherits two identical
... the allele that is always masked in the presence of the stronger allele ...
... the allele that is always masked in the presence of the stronger allele ...
BTCH Reg Course Rev Sem2
... Explain Mendel’s three Laws (Principles) of Dominance, Segregation and Independent Assortment. Describe how dominant and recessive traits are inherited. Describe the non-Mendelian inheritance patterns of codominance, incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, polygenic inheritance, and sex-linked trait ...
... Explain Mendel’s three Laws (Principles) of Dominance, Segregation and Independent Assortment. Describe how dominant and recessive traits are inherited. Describe the non-Mendelian inheritance patterns of codominance, incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, polygenic inheritance, and sex-linked trait ...
Tool 1
... DNA, where such repeats are know to be present. The result of the analysis is simply these lengths. It could for instance be, if a MLVA method was measuring lengths at, say, five such DNA locations (called loci in DNA jargon): 5, 10, 18, 7 and 0. To measure the number of repeats, the DNA areas under ...
... DNA, where such repeats are know to be present. The result of the analysis is simply these lengths. It could for instance be, if a MLVA method was measuring lengths at, say, five such DNA locations (called loci in DNA jargon): 5, 10, 18, 7 and 0. To measure the number of repeats, the DNA areas under ...
Biology- Semester 2 Final Exam Review 2012
... State two laws of heredity that were developed from Mendel’s work. Differentiate genes from alleles. How did Mendel’s F1 generation plants differ from his F2 generation plants? Many inherited disorders of humans appear in children of parents who do not have the disorder. How can you explain this? 6. ...
... State two laws of heredity that were developed from Mendel’s work. Differentiate genes from alleles. How did Mendel’s F1 generation plants differ from his F2 generation plants? Many inherited disorders of humans appear in children of parents who do not have the disorder. How can you explain this? 6. ...
A simple set of rules for primer sequence design is as follows
... association of a greater-than-17-base oligonucleotide with its target sequence is an extremely sequence-specific process. Consequently, 17-mer or longer primers are routinely used for amplification from genomic DNA of animals and plants. Elongation Temperature and Time This is normally 70 - 72oC, fo ...
... association of a greater-than-17-base oligonucleotide with its target sequence is an extremely sequence-specific process. Consequently, 17-mer or longer primers are routinely used for amplification from genomic DNA of animals and plants. Elongation Temperature and Time This is normally 70 - 72oC, fo ...
Chapter 13: Genetic Technology
... For forensic scientists they offer a means of distinguishing one individual from another through DNA fingerprinting _______ of human genome is composed of tandem repeats. Tandem repeats seem to act as filler or spacers between the gene regions of DNA ...
... For forensic scientists they offer a means of distinguishing one individual from another through DNA fingerprinting _______ of human genome is composed of tandem repeats. Tandem repeats seem to act as filler or spacers between the gene regions of DNA ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.