CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR RESPIRATION: HARVESTING CHEMICAL
... • During lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced directly by NADH to form lactate (ionized form of lactic acid). • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt. • Muscle cells switch from aerobic respiration to lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP ...
... • During lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced directly by NADH to form lactate (ionized form of lactic acid). • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt. • Muscle cells switch from aerobic respiration to lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP ...
ASSESSMENt Of ANAErObIC ENDurANCE bASED ON
... work, expressed as the maximum level of physical capabilities and rapid restitution processes (Kubica, 1995). Among the factors determining physical endurance, there are: aerobic energetic potential (aerobic endurance), anaerobic energetic potential (anaerobic endurance), anthropological and biomech ...
... work, expressed as the maximum level of physical capabilities and rapid restitution processes (Kubica, 1995). Among the factors determining physical endurance, there are: aerobic energetic potential (aerobic endurance), anaerobic energetic potential (anaerobic endurance), anthropological and biomech ...
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle
... $”) and reducing power, as NADH and FADH2 • It is at the hub of metabolism, because its intermediates can be end-products of catabolism as well as precursors for anabolism • It is also coordinately regulated with other pathways (as we’ll see later on) Chapter 16 ...
... $”) and reducing power, as NADH and FADH2 • It is at the hub of metabolism, because its intermediates can be end-products of catabolism as well as precursors for anabolism • It is also coordinately regulated with other pathways (as we’ll see later on) Chapter 16 ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... • Enzyme structures may also contain allosteric sites where the binding of a small molecule causes a conformational changes that increases or decreases activity. • Mechanism: • Substrate binding • Enzymes must bind their substrates before they can catalyse any chemical reaction. Enzymes are usually ...
... • Enzyme structures may also contain allosteric sites where the binding of a small molecule causes a conformational changes that increases or decreases activity. • Mechanism: • Substrate binding • Enzymes must bind their substrates before they can catalyse any chemical reaction. Enzymes are usually ...
Pyruvate and Acetate Metabolism in the Photosynthetic Bacterium
... * Kmr, kanamycin resistance ;pyc/Pyc, pyruvate carboxylase activity; Pyu, utilization of pyruvate and related substrates; rif, rifampicin; Str', streptomycin resistance; Tc', tetracycline resistance. curves obtained by measuring the ODb6, of cultures directly in a Bausch and Lomb Spectronic spectrop ...
... * Kmr, kanamycin resistance ;pyc/Pyc, pyruvate carboxylase activity; Pyu, utilization of pyruvate and related substrates; rif, rifampicin; Str', streptomycin resistance; Tc', tetracycline resistance. curves obtained by measuring the ODb6, of cultures directly in a Bausch and Lomb Spectronic spectrop ...
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
... pathway occurring in plants and several bacteria, but not animals. . The glyoxylate cycle allows these organisms to use fats for the synthesis of carbohydrates, a task which vertebrates, including humans, cannot perform. Isocitrate --> succinate + glyoxylate (O=CH-COO-)+acetyl-CoA--> malate-->> gluc ...
... pathway occurring in plants and several bacteria, but not animals. . The glyoxylate cycle allows these organisms to use fats for the synthesis of carbohydrates, a task which vertebrates, including humans, cannot perform. Isocitrate --> succinate + glyoxylate (O=CH-COO-)+acetyl-CoA--> malate-->> gluc ...
October 26 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... A) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it does not require oxygen. B) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it is not located in a membrane-bound organelle. C) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it occu ...
... A) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it does not require oxygen. B) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it is not located in a membrane-bound organelle. C) Glycolysis is considered to be an ancient metabolic system because it occu ...
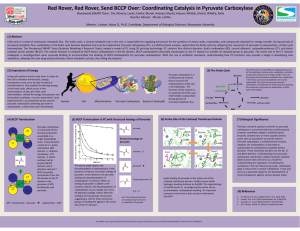
Poster
... The basic research question centered on pyruvate carboxylase is concerned with how multifunctional enzymes coordinate catalysis. Multifunctional enzymes combine two or more spatially distinct active sites to accomplish an overall reaction. Pyruvate carboxylase, a multifunctional enzyme, catalyzes th ...
... The basic research question centered on pyruvate carboxylase is concerned with how multifunctional enzymes coordinate catalysis. Multifunctional enzymes combine two or more spatially distinct active sites to accomplish an overall reaction. Pyruvate carboxylase, a multifunctional enzyme, catalyzes th ...
α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit
... α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (α-KGDH) (EC 1.2.4.2) is a key enzyme in the citric acid cycle. It forms an enzyme complex with dihydrolipoamide succinyl transferase (E2) and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (E3). α-KGDH converts α-ketoglutarate into succinylCoA in the presence of NAD and CoA. It is hig ...
... α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (α-KGDH) (EC 1.2.4.2) is a key enzyme in the citric acid cycle. It forms an enzyme complex with dihydrolipoamide succinyl transferase (E2) and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (E3). α-KGDH converts α-ketoglutarate into succinylCoA in the presence of NAD and CoA. It is hig ...
Dear Notetaker:
... The enzyme fructose 1,6 biphosphotase removes the phosphate Conversion using mutase to get glucose 1,6 phosphate from fructose 1,6 phosphate Glucose 6 phosphotase removes phosphate group to end up with glucose Energy o Takes 6 ATPs to make glucose Regulation ...
... The enzyme fructose 1,6 biphosphotase removes the phosphate Conversion using mutase to get glucose 1,6 phosphate from fructose 1,6 phosphate Glucose 6 phosphotase removes phosphate group to end up with glucose Energy o Takes 6 ATPs to make glucose Regulation ...
Chapter 1
... Begins with D-glucose as the substrate All organisms can use glucose as an energy source Requires no oxygen Occurs free in the cytoplasm Ten step pathway catalyzed by enzymes ...
... Begins with D-glucose as the substrate All organisms can use glucose as an energy source Requires no oxygen Occurs free in the cytoplasm Ten step pathway catalyzed by enzymes ...
L22_GlngBox
... Hydrogenation is a chemical process – using strange temperatures, pressures and catalysts Creates some strangly positioned and configured double bonds ...
... Hydrogenation is a chemical process – using strange temperatures, pressures and catalysts Creates some strangly positioned and configured double bonds ...
Citrate cycle - 3.LF UK 2015
... ATP / ADP NADH / NAD+ ATP / ADP GTP succinyl-CoA ...
... ATP / ADP NADH / NAD+ ATP / ADP GTP succinyl-CoA ...
Work and Energy in Muscles
... Another 50% cut can be seen when we examine the rate of aerobic glycolysis starting with glucose from the circulation. And, once again, there is another 50 % reduction in the rate of ATP synthesis if we begin with fatty acids from adipocytes. Physical activity lasting over many minutes and hours can ...
... Another 50% cut can be seen when we examine the rate of aerobic glycolysis starting with glucose from the circulation. And, once again, there is another 50 % reduction in the rate of ATP synthesis if we begin with fatty acids from adipocytes. Physical activity lasting over many minutes and hours can ...
Short-term regulation of the mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase
... et al., 1976; Sumegi & Alkonyi, 1983). The measurements were based on the initial rate of the reaction catalyzed by PDHC. However, a far higher PDC activity was observed when the reaction rate was measured for a longer period, because in the absence of added TDP the maximum rate was achieved only a� ...
... et al., 1976; Sumegi & Alkonyi, 1983). The measurements were based on the initial rate of the reaction catalyzed by PDHC. However, a far higher PDC activity was observed when the reaction rate was measured for a longer period, because in the absence of added TDP the maximum rate was achieved only a� ...
biochem 33 [3-24
... b. Leptin and glucagonlike peptide 1 (GLP-1) 42. 2 ways that nonesterified fatty acids (NEFA) can lead to insulin resistance? a. Elevated free FA in blood used by muscle leading to buildup of Acetyl CoA in mitochondria that is exported as citrate and inhibits PFK-1; this inhibits glucose metab in mu ...
... b. Leptin and glucagonlike peptide 1 (GLP-1) 42. 2 ways that nonesterified fatty acids (NEFA) can lead to insulin resistance? a. Elevated free FA in blood used by muscle leading to buildup of Acetyl CoA in mitochondria that is exported as citrate and inhibits PFK-1; this inhibits glucose metab in mu ...
Glucose Metabolism Glycolysis Expectations
... • Previous concepts: Standard free energy is +23kJ, but it is a near equilibrium reaction ...
... • Previous concepts: Standard free energy is +23kJ, but it is a near equilibrium reaction ...
Decreased Concentration of Xanthine
... Immunodiffusion disc was from Miles Laboratories, Inc., Naperville, IL. All other chemicals were also of analytical grade. Tissues. Chemically induced transplantable hepatomas were main tained as described previously (9). Hepatoma 20 was transplanted in male Buffalo strain rats, and hepatoma 3924A w ...
... Immunodiffusion disc was from Miles Laboratories, Inc., Naperville, IL. All other chemicals were also of analytical grade. Tissues. Chemically induced transplantable hepatomas were main tained as described previously (9). Hepatoma 20 was transplanted in male Buffalo strain rats, and hepatoma 3924A w ...
Problem-Set Solutions
... glycolytic pathway. Glycogenolysis in muscle and brain cells produces glucose 6-phosphate, which can enter the glycolytic pathway as the first intermediate in that pathway. Since brain and muscle cells do not produce glucose, these cells can use glycogen for energy production only. 24.64 It enters a ...
... glycolytic pathway. Glycogenolysis in muscle and brain cells produces glucose 6-phosphate, which can enter the glycolytic pathway as the first intermediate in that pathway. Since brain and muscle cells do not produce glucose, these cells can use glycogen for energy production only. 24.64 It enters a ...
Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy
... Where did the glucose come from? Where did the O2 come from? Where did the CO2 come from? Where did the CO2 go? Where did the H2O come from? Where did the ATP come from? What else is produced that is not listed in this equation? Why do we breathe? ...
... Where did the glucose come from? Where did the O2 come from? Where did the CO2 come from? Where did the CO2 go? Where did the H2O come from? Where did the ATP come from? What else is produced that is not listed in this equation? Why do we breathe? ...
IEMs Emergency Management
... elicited by tapping the tip of the nose. – SIDS has been reported. – Intellect is usually normal. ...
... elicited by tapping the tip of the nose. – SIDS has been reported. – Intellect is usually normal. ...
Lactate dehydrogenase

A lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells (animals, plants, and prokaryotes). LDH catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate and back, as it converts NADH to NAD+ and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from one molecule to another.LDH exist in four distinct enzyme classes. This article is about the common NAD(P)-dependent L-lactate dehydrogenase. Other LDHs act on D-lactate and/or are dependent on cytochrome c: D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)) and L-lactate (L-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)). LDH has been of medical significance because it is found extensively in body tissues, such as blood cells and heart muscle. Because it is released during tissue damage, it is a marker of common injuries and disease such as heart failure.