End-products, Fermentation Balances and Molar
... Each of the five species of Lactobacillus studied autolysed after attaining maximum growth on limiting amounts of glucose in the defined medium. Lactobacillum plantarum, however, did not lyse if galactose replaced glucose, suggesting that this species, similar to certain streptococci (Moustafa & Col ...
... Each of the five species of Lactobacillus studied autolysed after attaining maximum growth on limiting amounts of glucose in the defined medium. Lactobacillum plantarum, however, did not lyse if galactose replaced glucose, suggesting that this species, similar to certain streptococci (Moustafa & Col ...
Path of Glucose Breakdown and Cell Yields of a
... conversion of ribose 5-phosphate to glucose 6-phosphate. The mechanism by which COz was incorporated into the carboxyl carbons of succinate by Actinomyces naeslundii was not determined unequivocally. However, a low but significant exchange reaction between 14C02and the /3-carboxyl carbon of oxaloace ...
... conversion of ribose 5-phosphate to glucose 6-phosphate. The mechanism by which COz was incorporated into the carboxyl carbons of succinate by Actinomyces naeslundii was not determined unequivocally. However, a low but significant exchange reaction between 14C02and the /3-carboxyl carbon of oxaloace ...
Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and other Energy
... 1- Plants make ATP during photosynthesis. 2- All other organisms, including plants, must produce ATP by breaking down molecules such as glucose. Aerobic respiration : the process by which a cell uses O2 to "burn" molecules and release energy. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O Note: this reaction is the o ...
... 1- Plants make ATP during photosynthesis. 2- All other organisms, including plants, must produce ATP by breaking down molecules such as glucose. Aerobic respiration : the process by which a cell uses O2 to "burn" molecules and release energy. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O Note: this reaction is the o ...
Succinate Dehydrogenase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... forms; however, the localization and distribution of fumarase appears to be unique because there is only one translation product, which is targeted to mitochondria [3]. Malate dehydrogenase (7) catalyzes the last step of the TCA and leads to the oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate. There are three i ...
... forms; however, the localization and distribution of fumarase appears to be unique because there is only one translation product, which is targeted to mitochondria [3]. Malate dehydrogenase (7) catalyzes the last step of the TCA and leads to the oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate. There are three i ...
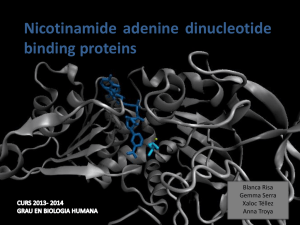
NAD - SBI
... b) There are two different classes of NAD: A and B c) The two forms of NAD differ by a flip of the nicotinamide ring, 180º around the glycosilic bond that links it to the ribose d) What defines the two different classes is the concavity that makes the protein and the interactions with NAD. e) all th ...
... b) There are two different classes of NAD: A and B c) The two forms of NAD differ by a flip of the nicotinamide ring, 180º around the glycosilic bond that links it to the ribose d) What defines the two different classes is the concavity that makes the protein and the interactions with NAD. e) all th ...
Role of NAD+-Dependent Malate Dehydrogenase in the Metabolism
... NAD(P)+/NAD(P)H-dependent interconversion of L-malate to oxaloacetic acid (OAA) is widespread in the three domains of life. It plays crucial roles in many metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, energy generation and the formation of metabolites for biosynthesis. Aerobic ba ...
... NAD(P)+/NAD(P)H-dependent interconversion of L-malate to oxaloacetic acid (OAA) is widespread in the three domains of life. It plays crucial roles in many metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, energy generation and the formation of metabolites for biosynthesis. Aerobic ba ...
Respiratory enzyme activity and regulation of respiration pathway in
... activity of seashore mallow seedlings was not significant (Fig. 1-a). However, the difference between each treatment and the control increased with the duration of waterlogging. On 20th and 30th d, the PDH activity of the adventitious root-retained seedlings decreased by 22.7% and 11.4%, respectivel ...
... activity of seashore mallow seedlings was not significant (Fig. 1-a). However, the difference between each treatment and the control increased with the duration of waterlogging. On 20th and 30th d, the PDH activity of the adventitious root-retained seedlings decreased by 22.7% and 11.4%, respectivel ...
Citrate Cycle
... Reaction 6: Oxidation of succinate by succinate dehydrogenase to form fumarate This coupled redox reaction directly links the citrate cycle to the electron transport system through the redox conjugate pair FAD/FADH2 which is covalently linked to the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase, an inner mitochond ...
... Reaction 6: Oxidation of succinate by succinate dehydrogenase to form fumarate This coupled redox reaction directly links the citrate cycle to the electron transport system through the redox conjugate pair FAD/FADH2 which is covalently linked to the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase, an inner mitochond ...
The Effect of Temperature on the Metabolism of
... found to differ in several respects (Table 2). The yield of organisms was greater at the lower growth temperature and slightly more nitrogen was utilized. In contrast, the ethanol production was less than half that observed with cultures grown at 38", despite the complete utilization of glucose. A f ...
... found to differ in several respects (Table 2). The yield of organisms was greater at the lower growth temperature and slightly more nitrogen was utilized. In contrast, the ethanol production was less than half that observed with cultures grown at 38", despite the complete utilization of glucose. A f ...
C nuclear magnetic resonance studies of anaerobic
... the apparently greater rate of alanine production compared with that of p y r u v a t e simply r e f l e c t s the longer T t for C-3 of pyruvate compared with T I for C-3 of alanine. The remaining 13C-NMR signals in Fig. 2 are due to 2,2-dihydroxypropionate (C 1 d, 6179.8 3C1_C2 = 60 Hz; C2 dd, 695 ...
... the apparently greater rate of alanine production compared with that of p y r u v a t e simply r e f l e c t s the longer T t for C-3 of pyruvate compared with T I for C-3 of alanine. The remaining 13C-NMR signals in Fig. 2 are due to 2,2-dihydroxypropionate (C 1 d, 6179.8 3C1_C2 = 60 Hz; C2 dd, 695 ...
You Light Up My Life - Hillsborough Community College
... • Electron transfer chain is in bacterial plasma membrane • Final electron acceptor is compound from environment (such as nitrate), not oxygen • ATP yield is low ...
... • Electron transfer chain is in bacterial plasma membrane • Final electron acceptor is compound from environment (such as nitrate), not oxygen • ATP yield is low ...
Chapter 23 Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis, con`t.
... pyruvate. When acetyl-CoA is low, pyruvate is broken down by pyruvate dehydrogenase. High levels of acetyl-CoA signal the need for more OAA to run the citric acid cycle, or to be converted to glucose. ...
... pyruvate. When acetyl-CoA is low, pyruvate is broken down by pyruvate dehydrogenase. High levels of acetyl-CoA signal the need for more OAA to run the citric acid cycle, or to be converted to glucose. ...
Muscle Energetics and Fatigue - Dr. Feher
... originates from liver and extrahepatic tissues either through glycolysis (liver) or gluconeogenesis (liver, kidneys, intestine). Fatty acids form acetylCoA through beta oxidation and the acetyl CoA is then completely oxidized, in the presence of adequate oxygen, in the mitochondria. These fatty acid ...
... originates from liver and extrahepatic tissues either through glycolysis (liver) or gluconeogenesis (liver, kidneys, intestine). Fatty acids form acetylCoA through beta oxidation and the acetyl CoA is then completely oxidized, in the presence of adequate oxygen, in the mitochondria. These fatty acid ...
Structure
... With any form of exercise a small amount of anaerobic metabolism occurs, but at submaximal speeds the majority of energy is produced by aerobic metabolism. As the speed of exercise increases so does the energy demand placed on the muscle. More muscle fibers are recruited including type 2B fibers and ...
... With any form of exercise a small amount of anaerobic metabolism occurs, but at submaximal speeds the majority of energy is produced by aerobic metabolism. As the speed of exercise increases so does the energy demand placed on the muscle. More muscle fibers are recruited including type 2B fibers and ...
Biochemistry review-ppt
... 4. Which is required for the conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate (in gluconeogenesis) 5. Which is required for the action of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (in gluconeogenesis) 6. Which is an END product formed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (pick 2) ...
... 4. Which is required for the conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate (in gluconeogenesis) 5. Which is required for the action of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (in gluconeogenesis) 6. Which is an END product formed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (pick 2) ...
the significance of serum s100, mia and ldh in cutaneous malignant
... Melanoma inhibitory activity (MIA) was purified in 1989 (36, 37) and cloned in 1994 (38, 39). Its discovery is linked to the search for autocrine growth factors in malignant melanoma. Initially, it was considered that MIA has a tumor suppressor activity, hence the name (38, 39). In vitro, MIA alters ...
... Melanoma inhibitory activity (MIA) was purified in 1989 (36, 37) and cloned in 1994 (38, 39). Its discovery is linked to the search for autocrine growth factors in malignant melanoma. Initially, it was considered that MIA has a tumor suppressor activity, hence the name (38, 39). In vitro, MIA alters ...
Document
... now been recovered. E Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each of two intermediates to ADP. Two more ATP have formed by substrate-level phosphorylation. Two molecules of pyruvate form at this last reaction step. F Summing up, glycolysis yields two NADH, two ATP (net), and two pyruvate for each g ...
... now been recovered. E Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each of two intermediates to ADP. Two more ATP have formed by substrate-level phosphorylation. Two molecules of pyruvate form at this last reaction step. F Summing up, glycolysis yields two NADH, two ATP (net), and two pyruvate for each g ...
respiration revision quiz
... When there is insufficient …………………….., it is important that the reduced NAD (……………) is …………………….. back to NAD+ so that the energy yielding phase of glycolysis can continue. In yeast, p ...
... When there is insufficient …………………….., it is important that the reduced NAD (……………) is …………………….. back to NAD+ so that the energy yielding phase of glycolysis can continue. In yeast, p ...
How Cells Release Chemical Energy
... now been recovered. E Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each of two intermediates to ADP. Two more ATP have formed by substrate-level phosphorylation. Two molecules of pyruvate form at this last reaction step. F Summing up, glycolysis yields two NADH, two ATP (net), and two pyruvate for each g ...
... now been recovered. E Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each of two intermediates to ADP. Two more ATP have formed by substrate-level phosphorylation. Two molecules of pyruvate form at this last reaction step. F Summing up, glycolysis yields two NADH, two ATP (net), and two pyruvate for each g ...
Mini-Series: Modern Metabolic Concepts The Biochemistry of the
... the principal product of carbohydrate digestion, passes through a series of enzymatic steps first in the non-oxidative glycolytic pathway (from glucose to pyruvate) followed by efficient oxidative metabolism via the tricarboxylic acid cycle (from acetyl-CoA to CO2 and H2O) to harness a portion of it ...
... the principal product of carbohydrate digestion, passes through a series of enzymatic steps first in the non-oxidative glycolytic pathway (from glucose to pyruvate) followed by efficient oxidative metabolism via the tricarboxylic acid cycle (from acetyl-CoA to CO2 and H2O) to harness a portion of it ...
Cellular Respiration (Text Book)
... • Without O2, the electron transport chain will cease to operate • In that case, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produce ATP ...
... • Without O2, the electron transport chain will cease to operate • In that case, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produce ATP ...
NIH Public Access
... syndrome (KSS) is defined by the obligate triad of onset before age 20, extraocular muscle weakness (ptosis and ophthalmoparesis), and pigmentary retinopathy, plus one of the following: ataxia, cerebrospinal fluid protein level greater than 100 mg/dL, or cardiac conduction block. The vast majority ( ...
... syndrome (KSS) is defined by the obligate triad of onset before age 20, extraocular muscle weakness (ptosis and ophthalmoparesis), and pigmentary retinopathy, plus one of the following: ataxia, cerebrospinal fluid protein level greater than 100 mg/dL, or cardiac conduction block. The vast majority ( ...
L26_Adv06
... B liver glycolysis lactate is a product of rapid glycolysis C muscle glycolysis D muscle PDH activity lactate is a substrate E All of the above ...
... B liver glycolysis lactate is a product of rapid glycolysis C muscle glycolysis D muscle PDH activity lactate is a substrate E All of the above ...
Lactic Acid and Exercise Performance | SpringerLink
... to be extruded via lactate-proton transporter proteins in the cell membrane.[27] This leads to the lactic acid hypothesis for muscle fatigue which is ‘accumulation of lactate or an acidosis in working muscle causes inhibition of contractile processes, either directly or via metabolism, resulting in ...
... to be extruded via lactate-proton transporter proteins in the cell membrane.[27] This leads to the lactic acid hypothesis for muscle fatigue which is ‘accumulation of lactate or an acidosis in working muscle causes inhibition of contractile processes, either directly or via metabolism, resulting in ...
Lactate dehydrogenase

A lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells (animals, plants, and prokaryotes). LDH catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate and back, as it converts NADH to NAD+ and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from one molecule to another.LDH exist in four distinct enzyme classes. This article is about the common NAD(P)-dependent L-lactate dehydrogenase. Other LDHs act on D-lactate and/or are dependent on cytochrome c: D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)) and L-lactate (L-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome)). LDH has been of medical significance because it is found extensively in body tissues, such as blood cells and heart muscle. Because it is released during tissue damage, it is a marker of common injuries and disease such as heart failure.