APEconHW#3aFall2014
... This homework is due on Tuesday, September 30th at the beginning of class. Late homework will be accepted at a cost of 10% per day until they are graded and handed back (2 days after the due date). At that point, I will not accept your homework and you will receive a zero. Please be as neat as possi ...
... This homework is due on Tuesday, September 30th at the beginning of class. Late homework will be accepted at a cost of 10% per day until they are graded and handed back (2 days after the due date). At that point, I will not accept your homework and you will receive a zero. Please be as neat as possi ...
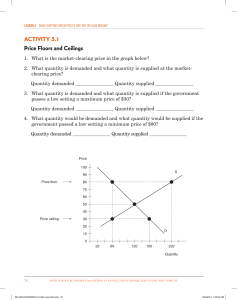
Price ceiling
... equals the number of units sold. There is neither a surplus nor a shortage of the product in the market. ...
... equals the number of units sold. There is neither a surplus nor a shortage of the product in the market. ...
Answer to Quiz #2
... c. Suppose this economy opens to trade and the world price of this good is $80. Describe what happens in this market when this economy opens to trade. In your answer identify 1) whether this country imports or exports the good; 2) the numeric level of imports or exports; 3) who benefits from this ec ...
... c. Suppose this economy opens to trade and the world price of this good is $80. Describe what happens in this market when this economy opens to trade. In your answer identify 1) whether this country imports or exports the good; 2) the numeric level of imports or exports; 3) who benefits from this ec ...
Practice Questions #3 Principles of Microeconomics
... 2. What happens to producer surplus when a price ceiling (below the equilibrium price) is enacted? What happens to consumer surplus? Will there be a shortage or a surplus in the new equilibrium? ...
... 2. What happens to producer surplus when a price ceiling (below the equilibrium price) is enacted? What happens to consumer surplus? Will there be a shortage or a surplus in the new equilibrium? ...
Task 1: Sample multiple choice and data interpretation questions
... insufficient money to buy essential goods and services. insufficient food to keep the population at a reasonable level of health. insufficient resources to satisfy all wants in an economy. insufficient capital goods to produce essential services. ...
... insufficient money to buy essential goods and services. insufficient food to keep the population at a reasonable level of health. insufficient resources to satisfy all wants in an economy. insufficient capital goods to produce essential services. ...
Goal 8: Analyze features of the economic system of the US
... 22. Which best defines an oligopoly? A. When a market is dominated by a single seller of a good. B. When a market is dominated by a few large sellers of a good. C. When a market is dominated by a large number of sellers of a good. D. When a market is dominated by the government. 23. If prices are se ...
... 22. Which best defines an oligopoly? A. When a market is dominated by a single seller of a good. B. When a market is dominated by a few large sellers of a good. C. When a market is dominated by a large number of sellers of a good. D. When a market is dominated by the government. 23. If prices are se ...
The Law of Supply - The Big L | James 1:2-4
... could not produce our maximum of 50 CD players, but we could only produce 45 CD players. However, we had to leave the prices the same. Which way would the supply curve shift? ...
... could not produce our maximum of 50 CD players, but we could only produce 45 CD players. However, we had to leave the prices the same. Which way would the supply curve shift? ...
Changes in Price due to Change in Supply and Demand
... Changes in Demand Fad- sudden and dramatic increase in demand ...
... Changes in Demand Fad- sudden and dramatic increase in demand ...
Supply and Demand
... -the fact that there are no barriers to entry and exit, firms in the long run may enjoy supernormal profits -the firms may engage in non-price competition and likely price competition among themselves Oligopoly: dominated by a few firms (3-8) so that there is a high concentration of sales. (see pg 2 ...
... -the fact that there are no barriers to entry and exit, firms in the long run may enjoy supernormal profits -the firms may engage in non-price competition and likely price competition among themselves Oligopoly: dominated by a few firms (3-8) so that there is a high concentration of sales. (see pg 2 ...
UNIT 2: Chapter 6: PRICES: Section 1: Combining Supply and
... Graphing Equilibrium---the market supply curve and the market demand curve are plotted on same graph. Equilibrium price and quantity can be found where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded, or the point where the supply curve crosses the demand curve. Disequilibrium---if the market price or qu ...
... Graphing Equilibrium---the market supply curve and the market demand curve are plotted on same graph. Equilibrium price and quantity can be found where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded, or the point where the supply curve crosses the demand curve. Disequilibrium---if the market price or qu ...
Chapter 10: Monopoly and Monopsony • Objectives – By the end of
... o Understand the relationship between marginal and average revenue and a monopolistic market demand curve. o Calculate total, marginal, and average revenue at a particular quantity if given either a monopoly demand curve or a table with a demand schedule. o Find profit-maximizing quantity, market pr ...
... o Understand the relationship between marginal and average revenue and a monopolistic market demand curve. o Calculate total, marginal, and average revenue at a particular quantity if given either a monopoly demand curve or a table with a demand schedule. o Find profit-maximizing quantity, market pr ...
Essential graphs for AP Microeconomics
... Long run equilibrium for the market and firm-price takers Allocative and productive efficiency at P=MR=MC=min ATC P ...
... Long run equilibrium for the market and firm-price takers Allocative and productive efficiency at P=MR=MC=min ATC P ...
Practice Questions on Perfect Competition
... Consider a perfectly competitive market in the short run. Assume that market demand is P 100 4QD and market supply is P=Qs. Denoting firm level quantity by q, assume TC=50+4q+2q2 so that MC=4+4q. a) What is the market equilibrium price and quantity? b) How many firms are in the industry in the s ...
... Consider a perfectly competitive market in the short run. Assume that market demand is P 100 4QD and market supply is P=Qs. Denoting firm level quantity by q, assume TC=50+4q+2q2 so that MC=4+4q. a) What is the market equilibrium price and quantity? b) How many firms are in the industry in the s ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.