* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Essential graphs for AP Microeconomics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
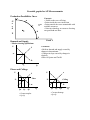
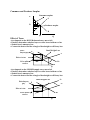
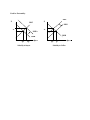
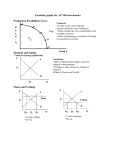
Essential graphs for AP Microeconomics Production Possibilities Curve A B G o o d W C D F X Concepts: • Points on the curve-efficient • Points inside the curve-inefficient • Points outside the curve-unattainable with available resources • Gains in technology or resources favoring one good both not other. E Good Y Demand and Supply √ Market clearing equilibrium P S Variations: • Shifts in demand and supply caused by changes in determinants • Changes in slope caused by changes in elasticity •Effect of Quotas and Tariffs Pe D Qe Q Floors and Ceilings P P S Floor Pe S Pe Ceiling D D QD Qe QS • Creates surplus • Qd<Qs Q QS Qe QD • Creates shortage • Qd>Qs Q Consumer and Producer Surplus Consumer surplus S P Pe Producer surplus D Qe Effect of Taxes Q A tax imposed on the BUYER-demand curve moves left • Elasticity determines whether buyer or seller bears incidence of tax • Shaded area is amount of tax • Connect the dots to find the triangle of deadweight or efficiency loss. Price buyers pay P Dead Weight Loss S Price w/o tax Price sellers receive D1 D2 Q A tax imposed on the SELLER-supply curve moves left • Elasticity determines whether buyer or seller bears incidence of tax • Shaded area is amount of tax • Connect the dots to find the triangle of deadweight or efficiency loss. Price buyers pay S2 Dead Weight Loss P S1 Price w/o tax Price sellers receive D1 Q Purely Competitive Product Market Structure Long run equilibrium for the market and firm-price takers Allocative and productive efficiency at P=MR=MC=min ATC P MC P S Pe AC MR=D=AR=P Pe D Qe Q Qe Q Variations: • Short run profits, losses and shutdown cases caused by shifts in market demand and supply. Imperfectly Competitive Product Market Structure Monopoly Market Structure Single price monopolist-price maker Earning economic profit P Natural Regulated Monopoly Selling at Fair return ( Qfr at Pfr) Dead Weight Loss MC P MC ATC P Pm ATC PFR D Ec Profit Q PSO D QFR QSO Qm Q MR Q MR Monopolistically Competitive Market structure Long run equilibrium where P=AC at MR=MC output MC P Variations: • Short run profits, losses and shutdown cases caused by shifts in market demand and supply. ATC PMC D Qmc MR Q Pure Competition Resource Market Structure Perfectly competitive Labor Market-Wage takers Firm wage comes from market so changes in labor demand do not raise wages. S Wage Rate Wage Rate Wc S=MRC Wc D= ∑ mrp’s DL=mrp Qc Labor Market Quantity Quantity qc Individual Firm Variations: • Changes in market demand and supply factors can influence the firm’s wage and number of workers hired. Imperfectly competitive market structure-Wage makers Quantity derived from MRC=MRP (Qm Wage (Wm) comes from that point downward to Supply curve. MRC Wage Rate S b Wc a Wm Qm Externalities No Externality P MRP c Qc Q Negative Externality MPC 2 MSC P Pe MSC Pe MSB Qo MSB Q Qo Qe Q Tax, direct controls, lawsuits, Coase theorem, market for externalities Positive Externality P MSC Pe MPC P MSC2 MSB 2 Pe MSB MPB Qe Qo Subsidy to buyer Q Qe Qo Subsidy to Seller Q