Supply, Demand, and Equilibrium
... 2. The change: • Did it affect supply or demand first? • Which determinant caused the shift? • Draw increase or decrease ...
... 2. The change: • Did it affect supply or demand first? • Which determinant caused the shift? • Draw increase or decrease ...
The law of Supply
... The law of Supply When the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied will also rise ...
... The law of Supply When the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied will also rise ...
here - mrrobinson.org
... 3. New vs Old firms have no advantages over each other 4. Seller/Buyer informed about price ...
... 3. New vs Old firms have no advantages over each other 4. Seller/Buyer informed about price ...
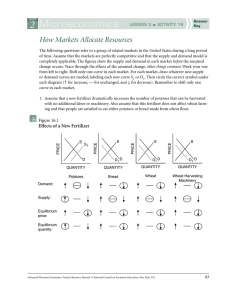
How Markets Allocate Resources
... completely applicable. The figures show the supply and demand in each market before the assumed change occurs. Trace through the effects of the assumed change, other things constant. Work your way from left to right. Shift only one curve in each market. For each market, draw whatever new supply or d ...
... completely applicable. The figures show the supply and demand in each market before the assumed change occurs. Trace through the effects of the assumed change, other things constant. Work your way from left to right. Shift only one curve in each market. For each market, draw whatever new supply or d ...
uwcmaastricht-econ
... Allocative efficiency occurs when the economy produces the combination of goods that are mostly wanted by society. That is, when the ‘what to produce’ question is answered in the best possible way. In a competitive market, allocative efficiency is achieved at the equilibrium point, where quantity de ...
... Allocative efficiency occurs when the economy produces the combination of goods that are mostly wanted by society. That is, when the ‘what to produce’ question is answered in the best possible way. In a competitive market, allocative efficiency is achieved at the equilibrium point, where quantity de ...
Chapter 4 AP Econ
... An increase in the price of marshmallows will decrease the demand for this good An increase in consumer incomes will decrease the demand for this good A decrease in consumer incomes will decrease the demand for this good An increase in consumer incomes will increase the quantity demanded of this goo ...
... An increase in the price of marshmallows will decrease the demand for this good An increase in consumer incomes will decrease the demand for this good A decrease in consumer incomes will decrease the demand for this good An increase in consumer incomes will increase the quantity demanded of this goo ...
Answers
... The coefficient on the related good’s price (Pr) is -32, which means for every dollar increase in the price of the related good production of the good we are interested in decreases by 32 units. Logically, the two goods must be substitutes in production. D. 19 = intercept term: quantity supplied if ...
... The coefficient on the related good’s price (Pr) is -32, which means for every dollar increase in the price of the related good production of the good we are interested in decreases by 32 units. Logically, the two goods must be substitutes in production. D. 19 = intercept term: quantity supplied if ...
Chapter 3
... What is the law of supply? What influences the quantity supplied of a good? What are the features of a supply curve? How do supply curves illustrate the law of supply? What factors can cause the supply of a product to change and how are these changes reflected in the supply curve? ...
... What is the law of supply? What influences the quantity supplied of a good? What are the features of a supply curve? How do supply curves illustrate the law of supply? What factors can cause the supply of a product to change and how are these changes reflected in the supply curve? ...
Document
... Law of Demand Law of Demand People do less of what they want to do as the cost of doing it rises Recall the Cost-Benefit Principle Pursue an action if and only if its benefits are at least as great as its costs Recall the Reservation Price The highest price we’d be willing to pay ...
... Law of Demand Law of Demand People do less of what they want to do as the cost of doing it rises Recall the Cost-Benefit Principle Pursue an action if and only if its benefits are at least as great as its costs Recall the Reservation Price The highest price we’d be willing to pay ...
Chapter 6 Section Main Menu
... If the market price or quantity supplied is anywhere but at the equilibrium price, the market is in a state called disequilibrium. There are two causes for disequilibrium: Excess Demand ...
... If the market price or quantity supplied is anywhere but at the equilibrium price, the market is in a state called disequilibrium. There are two causes for disequilibrium: Excess Demand ...
Ch 3 Presentation 2
... Supply Curve • Upward sloping from left to right showing that as the price increases, companies are willing to provide more of good in order to increase profit • Remember--- “supply to the sky” • ***y-axis is price, x-axis is quantity supplied • Be sure to label supply curve S, S1, S2 etc. ...
... Supply Curve • Upward sloping from left to right showing that as the price increases, companies are willing to provide more of good in order to increase profit • Remember--- “supply to the sky” • ***y-axis is price, x-axis is quantity supplied • Be sure to label supply curve S, S1, S2 etc. ...
Chapter 09 Key Question Solutions
... units. Loss per unit = $1.14, or $8 per firm. The industry will contract in the long run. (Key Question) Using diagrams for both the industry and a representative firm, illustrate competitive long-run equilibrium. Assuming constant costs, employ these diagrams to show how (a) an increase and (b) a d ...
... units. Loss per unit = $1.14, or $8 per firm. The industry will contract in the long run. (Key Question) Using diagrams for both the industry and a representative firm, illustrate competitive long-run equilibrium. Assuming constant costs, employ these diagrams to show how (a) an increase and (b) a d ...
9‑3 (Key Question) Use the following demand schedule to determine
... (Key Question) In long-run equilibrium, P = minimum ATC = MC. Of what significance for economic efficiency is the equality of P and minimum ATC? The equality of P and MC? Distinguish between productive efficiency and allocative efficiency in your answer. The equality of P and minimum ATC means the f ...
... (Key Question) In long-run equilibrium, P = minimum ATC = MC. Of what significance for economic efficiency is the equality of P and minimum ATC? The equality of P and MC? Distinguish between productive efficiency and allocative efficiency in your answer. The equality of P and minimum ATC means the f ...
21‑3 (Key Question) Use the following demand schedule to
... (Key Question) In long-run equilibrium, P = minimum ATC = MC. Of what significance for economic efficiency is the equality of P and minimum ATC? The equality of P and MC? Distinguish between productive efficiency and allocative efficiency in your answer. The equality of P and minimum ATC means the f ...
... (Key Question) In long-run equilibrium, P = minimum ATC = MC. Of what significance for economic efficiency is the equality of P and minimum ATC? The equality of P and MC? Distinguish between productive efficiency and allocative efficiency in your answer. The equality of P and minimum ATC means the f ...
When a market achieves perfect equilibrium there is no excess
... consistently align with the quantity demanded. Market clearing requires a variety of assumptions whichsimplify the complexities of real markets to coincide with a more theoretical framework, most centrally the assumptions of perfect competition and Say's Law. While this concept of market clearing re ...
... consistently align with the quantity demanded. Market clearing requires a variety of assumptions whichsimplify the complexities of real markets to coincide with a more theoretical framework, most centrally the assumptions of perfect competition and Say's Law. While this concept of market clearing re ...
Answers to Problems
... 4. The demand for binoculars might increase, leading to an increase in the quantity of binoculars supplied, but no change in the supply of binoculars should occur. The UFO sighting does nothing to change the factors that govern the supply of binoculars. 5. An increase in the cost of an input used in ...
... 4. The demand for binoculars might increase, leading to an increase in the quantity of binoculars supplied, but no change in the supply of binoculars should occur. The UFO sighting does nothing to change the factors that govern the supply of binoculars. 5. An increase in the cost of an input used in ...
Chapter 3: Answers to Problems 1a. Substitutes b. Complements c
... 4. The demand for binoculars might increase, leading to an increase in the quantity of binoculars supplied, but no change in the supply of binoculars should occur. The UFO sighting does nothing to change the factors that govern the supply of binoculars. 5. An increase in the cost of an input used in ...
... 4. The demand for binoculars might increase, leading to an increase in the quantity of binoculars supplied, but no change in the supply of binoculars should occur. The UFO sighting does nothing to change the factors that govern the supply of binoculars. 5. An increase in the cost of an input used in ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.