ECON 1: PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS
... D. Shifting the supply curve B. Change in production cost E. Change in price C. Change in supply F. Movement along the supply curve 17. True or False, and explain: An increase in the wage of computer workers will shift the supply curve for computers to the left. 18. From the variables, quantity of h ...
... D. Shifting the supply curve B. Change in production cost E. Change in price C. Change in supply F. Movement along the supply curve 17. True or False, and explain: An increase in the wage of computer workers will shift the supply curve for computers to the left. 18. From the variables, quantity of h ...
Unit 2 Fundamental Concept Review Guide
... 1. A place where people come together to buy and sell goods or services is called a(n) ___________. 2. The _________________ states that as a person consumes additional units of a good, eventually the utility gained from each additional unit of the good decreases. 3. Goods consumed jointly are _____ ...
... 1. A place where people come together to buy and sell goods or services is called a(n) ___________. 2. The _________________ states that as a person consumes additional units of a good, eventually the utility gained from each additional unit of the good decreases. 3. Goods consumed jointly are _____ ...
Econ 370
... What is the cost function for this firm? If the factor prices are equal to 1, what is the marginal cost of producing y units of output? How many units of output would be supplied at price p? What would be the cost per unit of output? Suppose the producer is in a competitive market where p=48 and fac ...
... What is the cost function for this firm? If the factor prices are equal to 1, what is the marginal cost of producing y units of output? How many units of output would be supplied at price p? What would be the cost per unit of output? Suppose the producer is in a competitive market where p=48 and fac ...
The Demand Curve and The Demand Schedule
... A table showing how much of a good or service consumers will want to buy at different prices See pg. 50; Figure 5.1 ...
... A table showing how much of a good or service consumers will want to buy at different prices See pg. 50; Figure 5.1 ...
Consumer and Producer Surplus
... To calculate CS or PS, use the formula for area of a triangle: Example 1: ...
... To calculate CS or PS, use the formula for area of a triangle: Example 1: ...
Chapter 6 Section Main Menu Combining Supply and Demand How
... Think of prices as a traffic light. A relatively high price is a green light telling producers to make more. A relatively low price is a red light telling producers to make less. 3. Flexibility In many markets, prices are much more flexible than production levels. They can be easily increased or dec ...
... Think of prices as a traffic light. A relatively high price is a green light telling producers to make more. A relatively low price is a red light telling producers to make less. 3. Flexibility In many markets, prices are much more flexible than production levels. They can be easily increased or dec ...
Chapter 4 Test
... A measure of the way a quantity supplied reacts to a change in price. A chart that lists how much of a good a supplier will offer at various prices. A graph of the quantity supplied of a good by all suppliers at different prices. Level where marginal product goes up with a new investment. Level wher ...
... A measure of the way a quantity supplied reacts to a change in price. A chart that lists how much of a good a supplier will offer at various prices. A graph of the quantity supplied of a good by all suppliers at different prices. Level where marginal product goes up with a new investment. Level wher ...
ECON460: Answer Key to Problem Set 1
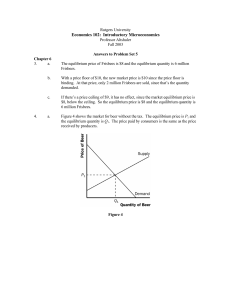
... d. Solve for the short-run perfectly competitive equilibrium levels of price and output in which there are two firms.What are profits of each firm in this short-run equilibrium? Answer: need to find the intersection of the industry demand curve and the 2-firm supply curve above: Q = 100 − p = 4p − 4 ...
... d. Solve for the short-run perfectly competitive equilibrium levels of price and output in which there are two firms.What are profits of each firm in this short-run equilibrium? Answer: need to find the intersection of the industry demand curve and the 2-firm supply curve above: Q = 100 − p = 4p − 4 ...
Shortages and Surpluses
... 2.d.3. According to the graph above, the market equilibrium is when the price is $10 and the quantity demanded is 3. However, at a price of $14, the quantity of pizza supplied is 4 and the quantity of pizza demanded is only 2. This means that the suppliers are willing to supply more pizza and the bu ...
... 2.d.3. According to the graph above, the market equilibrium is when the price is $10 and the quantity demanded is 3. However, at a price of $14, the quantity of pizza supplied is 4 and the quantity of pizza demanded is only 2. This means that the suppliers are willing to supply more pizza and the bu ...
Powerpoint Presenation of Notes
... The Clayton Antitrust Act (1914) clarified and strengthened the Sherman Act by prohibiting price discrimination, local price cutting, mergers that reduce competition, and exclusive sales contracts. The Federal Trade Commission Act (1914) created the Federal Trade Commission to investigate charges o ...
... The Clayton Antitrust Act (1914) clarified and strengthened the Sherman Act by prohibiting price discrimination, local price cutting, mergers that reduce competition, and exclusive sales contracts. The Federal Trade Commission Act (1914) created the Federal Trade Commission to investigate charges o ...
Exchange rates - Business-TES
... Linked to this is the important fact that cost does not change only price. (Look at how you labelled your y axis.) ...
... Linked to this is the important fact that cost does not change only price. (Look at how you labelled your y axis.) ...
Economics Cumulative Problem Sets
... what will happen to price and output of apples? 3 If there is a signify increase in the export of apples to other countries what will be the change in the price of apples and output? 4. If the price of pears and other fruits fall in price what is likely to happen in the apple market? 5. If a major s ...
... what will happen to price and output of apples? 3 If there is a signify increase in the export of apples to other countries what will be the change in the price of apples and output? 4. If the price of pears and other fruits fall in price what is likely to happen in the apple market? 5. If a major s ...
P2 - BrainMass
... A. Determine the supply curve for each firm. Express price as a function of quantity and quantity as a function of price. (Hint: Set P = MR = MC to find each firm's supply curve.) B. Calculate the quantity supplied by each firm at prices of $325, $350, and $375. What is the minimum price necessary f ...
... A. Determine the supply curve for each firm. Express price as a function of quantity and quantity as a function of price. (Hint: Set P = MR = MC to find each firm's supply curve.) B. Calculate the quantity supplied by each firm at prices of $325, $350, and $375. What is the minimum price necessary f ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.