ANSWER KEY Practice Free Response
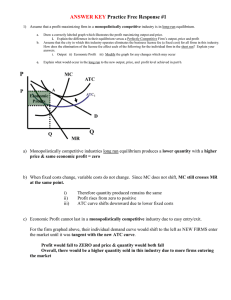
... Draw a correctly labeled graph which illustrates the profit maximizing output and price. i. Explain the difference in their equilibrium versus a Perfectly Competitive Firm’s output, price and profit Assume that the city in which this industry operates eliminates the business license fee (a fixed cos ...
... Draw a correctly labeled graph which illustrates the profit maximizing output and price. i. Explain the difference in their equilibrium versus a Perfectly Competitive Firm’s output, price and profit Assume that the city in which this industry operates eliminates the business license fee (a fixed cos ...
332excel assignment e+
... A. Copy this table of data into an excel spreadsheet. Run a regression using quantity as the dependent variable. B. (We haven’t covered everything on statistics yet….so don’t worry about any of the output other than the variable coefficients . Also, don’t worry about the statistical significance of ...
... A. Copy this table of data into an excel spreadsheet. Run a regression using quantity as the dependent variable. B. (We haven’t covered everything on statistics yet….so don’t worry about any of the output other than the variable coefficients . Also, don’t worry about the statistical significance of ...
Supply and Demand
... d. Supply of private college education would increase e. Supply of public education by SUNY colleges would increase f. Both supply of and demand for private college education would increase ...
... d. Supply of private college education would increase e. Supply of public education by SUNY colleges would increase f. Both supply of and demand for private college education would increase ...
Economics - Spring Branch ISD
... During periods of inflation, the value of cash in a person’s pocket increases from day to day as prices rise. 19. True or false; A good will continue to hold its value, provided that it can be stored for a long period of time. 20. If more suppliers enter a market, what will be the affect upon the su ...
... During periods of inflation, the value of cash in a person’s pocket increases from day to day as prices rise. 19. True or false; A good will continue to hold its value, provided that it can be stored for a long period of time. 20. If more suppliers enter a market, what will be the affect upon the su ...
File
... 2. If the market equilibrium wage for low-skilled labor is $4.50 per hour, and the minimum wage is set at $5.15, the result is ...
... 2. If the market equilibrium wage for low-skilled labor is $4.50 per hour, and the minimum wage is set at $5.15, the result is ...
Chapter 12 - Pegasus @ UCF
... Note Figure 12.6 covers all possibilities by assuming 3 different market prices(P1, P2, P3) ...
... Note Figure 12.6 covers all possibilities by assuming 3 different market prices(P1, P2, P3) ...
Laws of Demand and Supply
... • Why do companies need to consider demand? – Demand determines total income • Will increasing prices result in increased income? – ONLY if it is an inelastic good! – If a good becomes elastic, raising prices may decrease a firms total income/revenue ...
... • Why do companies need to consider demand? – Demand determines total income • Will increasing prices result in increased income? – ONLY if it is an inelastic good! – If a good becomes elastic, raising prices may decrease a firms total income/revenue ...
Chapter 3 Demand, supply, and the market
... Price and quantity changes • In practice, we cannot plot ex ante demand curves and supply curves • So we use historical data and the supposition that the observed values are equilibrium ones • Since other things are often not constant, some detective work is required • This is where our theory come ...
... Price and quantity changes • In practice, we cannot plot ex ante demand curves and supply curves • So we use historical data and the supposition that the observed values are equilibrium ones • Since other things are often not constant, some detective work is required • This is where our theory come ...
QUIZ 2 (ON CHAPTER 4) ECO 12 SPRING 2005 UDAYAN ROY
... equal, we would expect the supply of a. crystal to be unaffected. b. crystal to decrease. c. crystal to increase. d. lead to increase. 10. An advance in production technology will a. increase a firm's costs. b. allow firms to raise the price of their product. c. shift the supply curve to the right. ...
... equal, we would expect the supply of a. crystal to be unaffected. b. crystal to decrease. c. crystal to increase. d. lead to increase. 10. An advance in production technology will a. increase a firm's costs. b. allow firms to raise the price of their product. c. shift the supply curve to the right. ...
Supply and Demand Together
... 2. The change: • Did it affect supply or demand first? • Which determinant caused the shift? • Draw increase or decrease ...
... 2. The change: • Did it affect supply or demand first? • Which determinant caused the shift? • Draw increase or decrease ...
home3a - Cal Poly Pomona
... Assume now that the government establishes a supported price of, say, $5.40 for wheat. Explain carefully the effects of this supported price. Demonstrate your answer graphically (use the graph in part B). What might prompt government to establish this price support? See graph in (b). At P = $5.40 a ...
... Assume now that the government establishes a supported price of, say, $5.40 for wheat. Explain carefully the effects of this supported price. Demonstrate your answer graphically (use the graph in part B). What might prompt government to establish this price support? See graph in (b). At P = $5.40 a ...
Unit 2
... and completely original. Photocopies and/or computer printouts will not be allowed. Do this by hand, and do your own work. Failure to follow these rules will result in an immediate, and non-negotiable, failure (ZERO) on this quiz. ALL NOTECARDS WILL BE COLLECTED AND STAPLED TO YOUR QUIZ. CONCEPTS AN ...
... and completely original. Photocopies and/or computer printouts will not be allowed. Do this by hand, and do your own work. Failure to follow these rules will result in an immediate, and non-negotiable, failure (ZERO) on this quiz. ALL NOTECARDS WILL BE COLLECTED AND STAPLED TO YOUR QUIZ. CONCEPTS AN ...
Topic Priority Checklist
... equilibria of the purely competitive firm. 33. In words and using graphical analysis, show the profit scenario of a single price monopolist and a perfectly price-discriminating monopolist. 34. Identify the government policies employed when a firm exercises monopoly power or is a natural monopoly. 35 ...
... equilibria of the purely competitive firm. 33. In words and using graphical analysis, show the profit scenario of a single price monopolist and a perfectly price-discriminating monopolist. 34. Identify the government policies employed when a firm exercises monopoly power or is a natural monopoly. 35 ...
Quiz1
... b) [1 mark] Suppose K suddenly increases to 40. How does it affect the market equilibrium calculated in part a)? (Calculate new equilibrium). Answer: Qs now is given by: Qs = 175 + 10 P. Solving as above, the new equilibrium price is: P*=21. Substitute P* for P in either the equation for the market ...
... b) [1 mark] Suppose K suddenly increases to 40. How does it affect the market equilibrium calculated in part a)? (Calculate new equilibrium). Answer: Qs now is given by: Qs = 175 + 10 P. Solving as above, the new equilibrium price is: P*=21. Substitute P* for P in either the equation for the market ...
Supply and Demand
... • Productivity (Improvements in machines and production processes of a good or service) • Inputs ( Change in the price of inputs required to produce the good or service.) • Government Actions (Subsidies, Taxes and Regulations) • Technology (Improvements in machines and production processes of a good ...
... • Productivity (Improvements in machines and production processes of a good or service) • Inputs ( Change in the price of inputs required to produce the good or service.) • Government Actions (Subsidies, Taxes and Regulations) • Technology (Improvements in machines and production processes of a good ...
Supply and Demand
... • Productivity (Improvements in machines and production processes of a good or service) • Inputs ( Change in the price of inputs required to produce the good or service.) • Government Actions (Subsidies, Taxes and Regulations) • Technology (Improvements in machines and production processes of a good ...
... • Productivity (Improvements in machines and production processes of a good or service) • Inputs ( Change in the price of inputs required to produce the good or service.) • Government Actions (Subsidies, Taxes and Regulations) • Technology (Improvements in machines and production processes of a good ...
demand - ssvos.cz
... price elasticities in real life, including analysis of historic sales data • price elasticity of demand (PED) was devised by Alfred Marshall • a demand curve is a graphical depiction, it shows how the quantity demanded of some product during a specified period of time will change as the price of tha ...
... price elasticities in real life, including analysis of historic sales data • price elasticity of demand (PED) was devised by Alfred Marshall • a demand curve is a graphical depiction, it shows how the quantity demanded of some product during a specified period of time will change as the price of tha ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.