Introduction-1
... an organism consists of a very long sequence of four different nucleotides with bases A, C, G, T. Genomic DNA is a double-stranded helix comprised of two complementary strands, held together by A-T and C-G base pairs. The entire genome is replicated by DNA polymerases (a protein) and passed on to da ...
... an organism consists of a very long sequence of four different nucleotides with bases A, C, G, T. Genomic DNA is a double-stranded helix comprised of two complementary strands, held together by A-T and C-G base pairs. The entire genome is replicated by DNA polymerases (a protein) and passed on to da ...
Exemplar exam questions – Chapter 7
... polypeptide. DNA is transcribed into mRNA and protein is synthesized by ribosomes, which translate the mRNA. Ribosomes and tRNA bring the correct amino acid into position in the polypeptide as they move along the mRNA molecule. mRNA contains sequences that do not code for the polypeptide – these are ...
... polypeptide. DNA is transcribed into mRNA and protein is synthesized by ribosomes, which translate the mRNA. Ribosomes and tRNA bring the correct amino acid into position in the polypeptide as they move along the mRNA molecule. mRNA contains sequences that do not code for the polypeptide – these are ...
Exemplar exam questions – Chapter 7, Nucleic acids and proteins
... polypeptide. DNA is transcribed into mRNA and protein is synthesized by ribosomes, which translate the mRNA. Ribosomes and tRNA bring the correct amino acid into position in the polypeptide as they move along the mRNA molecule. mRNA contains sequences that do not code for the polypeptide – these are ...
... polypeptide. DNA is transcribed into mRNA and protein is synthesized by ribosomes, which translate the mRNA. Ribosomes and tRNA bring the correct amino acid into position in the polypeptide as they move along the mRNA molecule. mRNA contains sequences that do not code for the polypeptide – these are ...
Ch. 11
... the form of a ____________________________ B. Replication of DNA a. ____________________________ ______ – the copying of DNA chromosomes. Occurs in interphase 1. DNA Synthesis (replication) a. _______________(DNA Polymerase) unzip the DNA strand b. Free ____________________________ bond w/ open base ...
... the form of a ____________________________ B. Replication of DNA a. ____________________________ ______ – the copying of DNA chromosomes. Occurs in interphase 1. DNA Synthesis (replication) a. _______________(DNA Polymerase) unzip the DNA strand b. Free ____________________________ bond w/ open base ...
Bio 262- Genetics Study Guide
... Recessive: Moving back and out of view. In genetics, a recessive gene is a gene that does not express its instructions when paired with a dominant gene. Recombination: The process by which progeny derive a combination of genes different from that of either parent. In higher organisms, this can occur ...
... Recessive: Moving back and out of view. In genetics, a recessive gene is a gene that does not express its instructions when paired with a dominant gene. Recombination: The process by which progeny derive a combination of genes different from that of either parent. In higher organisms, this can occur ...
Recombination between homologous chromosomes
... processing, created during transcription RNA = nucleic acid present in all living cells, acts as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins Ribosomes = bind to mRNA and transfer RNA to synthesize polypeptides and ...
... processing, created during transcription RNA = nucleic acid present in all living cells, acts as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins Ribosomes = bind to mRNA and transfer RNA to synthesize polypeptides and ...
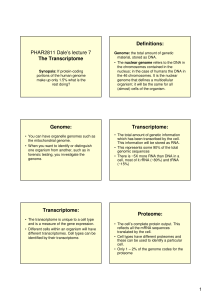
PHAR2811 Dale`s lecture 7 The Transcriptome Definitions: Genome
... • The rRNA is then modified by methylation at some sites. • There are many copies of the ribosomal RNA sequences in the genome (as well as the histone proteins). • Some sequences are required by all cells in such large quantities that they have multiple copies in the genome. ...
... • The rRNA is then modified by methylation at some sites. • There are many copies of the ribosomal RNA sequences in the genome (as well as the histone proteins). • Some sequences are required by all cells in such large quantities that they have multiple copies in the genome. ...
Transcription and Translation
... ATP, CTP, GTP, and UTP. It’s the same ATP as is used for energy in the cell. As with DNA replication, transcription proceeds 5- to 3’: new bases are added to the free 3’ OH group. Unlike replication, transcription does not need to build on a primer. Instead, transcription starts at a region of DNA c ...
... ATP, CTP, GTP, and UTP. It’s the same ATP as is used for energy in the cell. As with DNA replication, transcription proceeds 5- to 3’: new bases are added to the free 3’ OH group. Unlike replication, transcription does not need to build on a primer. Instead, transcription starts at a region of DNA c ...
Transcription and Translation
... ATP, CTP, GTP, and UTP. It’s the same ATP as is used for energy in the cell. As with DNA replication, transcription proceeds 5- to 3’: new bases are added to the free 3’ OH group. Unlike replication, transcription does not need to build on a primer. Instead, transcription starts at a region of DNA c ...
... ATP, CTP, GTP, and UTP. It’s the same ATP as is used for energy in the cell. As with DNA replication, transcription proceeds 5- to 3’: new bases are added to the free 3’ OH group. Unlike replication, transcription does not need to build on a primer. Instead, transcription starts at a region of DNA c ...
Slides PPT
... material, stored as DNA. • The nuclear genome refers to the DNA in the chromosomes contained in the nucleus; in the case of humans the DNA in the 46 chromosomes. It is the nuclear genome that defines a multicellular organism; it will be the same for all (almost) cells of the organism. ...
... material, stored as DNA. • The nuclear genome refers to the DNA in the chromosomes contained in the nucleus; in the case of humans the DNA in the 46 chromosomes. It is the nuclear genome that defines a multicellular organism; it will be the same for all (almost) cells of the organism. ...
THE DEVELOPMENT OF AN RNA BASED ASSAY SYSTEM TO
... multiplex (i.e. parallel) analysis procedures for body fluid identification, we have considered assays based upon protein and messenger RNA (mRNA) since both are expressed in a tissue type specific manner. Multiplex analysis of complex protein mixtures such as those present in body fluids awaits fur ...
... multiplex (i.e. parallel) analysis procedures for body fluid identification, we have considered assays based upon protein and messenger RNA (mRNA) since both are expressed in a tissue type specific manner. Multiplex analysis of complex protein mixtures such as those present in body fluids awaits fur ...
Chemical basis of Inheritance Review KEY - Pelletier Pages
... Leading strand? Strand of DNA synthesized continuously in the 5’-3’ direction. 13. What role do DNA polymerase and DNA ligase play in gene replication? DNA polymerase adds DNA nucleotides to the 3’ end of the growing DNA molecule. DNA ligase forms the phosphodiester bonds between the okazaki fragmen ...
... Leading strand? Strand of DNA synthesized continuously in the 5’-3’ direction. 13. What role do DNA polymerase and DNA ligase play in gene replication? DNA polymerase adds DNA nucleotides to the 3’ end of the growing DNA molecule. DNA ligase forms the phosphodiester bonds between the okazaki fragmen ...
Release of Human Genome Project
... RNA folding problem is easier because secondary structure separates from tertiary structure more easily - But it is still a complex problem. RNA model has real parameters therefore you can say something about real molecules. RNA folding algorithm is simple enough to be able to do statistical ...
... RNA folding problem is easier because secondary structure separates from tertiary structure more easily - But it is still a complex problem. RNA model has real parameters therefore you can say something about real molecules. RNA folding algorithm is simple enough to be able to do statistical ...
CHAPTER 3 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... – Determine what activities will occur in a protein. – Enzymes and hormones Carrier proteins – Transport molecules from one place to another. – Lipoproteins ...
... – Determine what activities will occur in a protein. – Enzymes and hormones Carrier proteins – Transport molecules from one place to another. – Lipoproteins ...
What is Biology? The word biology is 1………………………. from the
... https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SMtWvDbfHLo&index=2&list=PL72461B60C870CBC4 The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: "DNA makes RNA makes protein". Here the process begins. Transcription factors 1…………………………….. at a specific promoter region along the DNA. The length of DNA following the promoter is a ...
... https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SMtWvDbfHLo&index=2&list=PL72461B60C870CBC4 The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: "DNA makes RNA makes protein". Here the process begins. Transcription factors 1…………………………….. at a specific promoter region along the DNA. The length of DNA following the promoter is a ...
Heredity and Meiosis - Chaparral Star Academy
... As one tRNA adds its amino acid to the chain, a peptide bond occurs between amino acids to hold the chain together. When a bond has been made the ribosome will then move on down the mRNA to the next active site and continue the process. The used tRNA then returns to the cytoplasm ...
... As one tRNA adds its amino acid to the chain, a peptide bond occurs between amino acids to hold the chain together. When a bond has been made the ribosome will then move on down the mRNA to the next active site and continue the process. The used tRNA then returns to the cytoplasm ...
Unit 11 web
... = ~2 meters ! When cells divide one strand from each ‘double thread/helix ’ goes to each new cell thus carrying the identical sequence/information. ...
... = ~2 meters ! When cells divide one strand from each ‘double thread/helix ’ goes to each new cell thus carrying the identical sequence/information. ...
File - Mr Murphy`s Science Blog
... 1. What is a species? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ...
... 1. What is a species? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ...
THE NUCLEIC ACIDS
... messenger RNA and brings specific amino acids to the ribosome for protein synthesis • Each amino acid is recognized by one or more specific tRNA • tRNA has a tertiary structure that is L-shaped - one end attaches to the amino acid and the other binds to the mRNA by a 3-base complimentary sequence ...
... messenger RNA and brings specific amino acids to the ribosome for protein synthesis • Each amino acid is recognized by one or more specific tRNA • tRNA has a tertiary structure that is L-shaped - one end attaches to the amino acid and the other binds to the mRNA by a 3-base complimentary sequence ...
chapter_3_2007
... – Determine what activities will occur in a protein. – Enzymes and hormones Carrier proteins – Transport molecules from one place to another. – Lipoproteins ...
... – Determine what activities will occur in a protein. – Enzymes and hormones Carrier proteins – Transport molecules from one place to another. – Lipoproteins ...
Biochemistry: the chemical makeup of living things
... the shape of a protein a. Primary Structure – amino acid sequence **This is what determines the 3D conformation b. Secondary Structure – coils and folds made by polypeptide chain **Coils caused by hydrogen bonds at regular intervals along the polypeptide chain **Alpha helix – coil held together by H ...
... the shape of a protein a. Primary Structure – amino acid sequence **This is what determines the 3D conformation b. Secondary Structure – coils and folds made by polypeptide chain **Coils caused by hydrogen bonds at regular intervals along the polypeptide chain **Alpha helix – coil held together by H ...
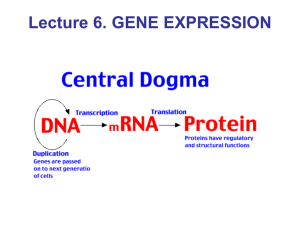
Gene Expression
... molecules are long double-stranded chains; 4 types of bases are attached to the backbone: adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), and guanine (G) with cytosine (C). A gene is a segment of DNA that specifies how to make a protein. Proteins are large molecules are essential to the structure, function, ...
... molecules are long double-stranded chains; 4 types of bases are attached to the backbone: adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), and guanine (G) with cytosine (C). A gene is a segment of DNA that specifies how to make a protein. Proteins are large molecules are essential to the structure, function, ...
Microbial Genetics
... assembled into proteins. 2. DNA directs its own replication by giving rise to two complete, identical DNA ...
... assembled into proteins. 2. DNA directs its own replication by giving rise to two complete, identical DNA ...
Nucleic acid tertiary structure

The tertiary structure of a nucleic acid is its precise three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates. RNA and DNA molecules are capable of diverse functions ranging from molecular recognition to catalysis. Such functions require a precise three-dimensional tertiary structure. While such structures are diverse and seemingly complex, they are composed of recurring, easily recognizable tertiary structure motifs that serve as molecular building blocks. Some of the most common motifs for RNA and DNA tertiary structure are described below, but this information is based on a limited number of solved structures. Many more tertiary structural motifs will be revealed as new RNA and DNA molecules are structurally characterized.