Functions of DNA methylation: islands, start sites, gene bodies and
... at TSSs cannot initiate transcription after the DNA has been assembled into nucleosomes37–39. However, the issue of whether silencing or methylation comes first has long been a discussion in the field. Early experiments by Lock et al.40 clearly showed that methylation of the Hprt gene on the inactiv ...
... at TSSs cannot initiate transcription after the DNA has been assembled into nucleosomes37–39. However, the issue of whether silencing or methylation comes first has long been a discussion in the field. Early experiments by Lock et al.40 clearly showed that methylation of the Hprt gene on the inactiv ...
Chpt8_RecombineDNA.doc
... number of common enzymatic pathways. This chapter will be concerned almost entirely with general recombination. Illegitimate or nonhomologous recombination occurs in regions where no large-scale sequence similarity is apparent, e.g. translocations between different chromosomes or deletions that remo ...
... number of common enzymatic pathways. This chapter will be concerned almost entirely with general recombination. Illegitimate or nonhomologous recombination occurs in regions where no large-scale sequence similarity is apparent, e.g. translocations between different chromosomes or deletions that remo ...
Introduction to Molecular Diagnostics
... and other types of infections. There are records of the study of gross anatomy and pathology (organs and tissues) dating back to at least the ancient Greeks. It was the advent of modern microscopy and histopathology, or cellular pathology, in the nineteenth century, however, which enabled a tremendo ...
... and other types of infections. There are records of the study of gross anatomy and pathology (organs and tissues) dating back to at least the ancient Greeks. It was the advent of modern microscopy and histopathology, or cellular pathology, in the nineteenth century, however, which enabled a tremendo ...
Slide 1
... Many mutations are produced by errors in genetic processes. For example, some point mutations are caused by errors during DNA replication. The cellular machinery that replicates DNA inserts an incorrect base roughly once in every 10 million bases. Small changes in genes can gradually accumulate over ...
... Many mutations are produced by errors in genetic processes. For example, some point mutations are caused by errors during DNA replication. The cellular machinery that replicates DNA inserts an incorrect base roughly once in every 10 million bases. Small changes in genes can gradually accumulate over ...
SNP
... alleles (0.1% of total SNPs is tri-allelic markers in TSC data). SNPs has lower mutation rate than do repeat sequences, but not as informative as microsatellite markers. detection methods for SNPs are potentially more suitable for genetic screening in automated and large-scale. the SNPs are likely b ...
... alleles (0.1% of total SNPs is tri-allelic markers in TSC data). SNPs has lower mutation rate than do repeat sequences, but not as informative as microsatellite markers. detection methods for SNPs are potentially more suitable for genetic screening in automated and large-scale. the SNPs are likely b ...
The case for transgenerational epigenetic inheritance in humans
... sensitive to environmental influences. Moreover, in some cases the epigenetic state at these alleles can survive across generations, termed transgenerational epigenetic inheritance. Together these findings raise the spectre of Lamarckism and epigenetics is now being touted as an explanation for some ...
... sensitive to environmental influences. Moreover, in some cases the epigenetic state at these alleles can survive across generations, termed transgenerational epigenetic inheritance. Together these findings raise the spectre of Lamarckism and epigenetics is now being touted as an explanation for some ...
Harvey ras (H-ras) Point Mutations Are Induced by 4
... DMBA, and the promoter, TPA (12, 13). Continuous exposure of squamous cells to DMBA and TPA induced H-ras mutations on chromosome 7 in greater than 90% of mice (14). H-ras appeared to be activated by specific mutations which can be affected by the initiating carcinogen (15). Since tumors do not deve ...
... DMBA, and the promoter, TPA (12, 13). Continuous exposure of squamous cells to DMBA and TPA induced H-ras mutations on chromosome 7 in greater than 90% of mice (14). H-ras appeared to be activated by specific mutations which can be affected by the initiating carcinogen (15). Since tumors do not deve ...
Genetic Analyses of Schizosaccharomyces pombe dna2
... Kim et al. 1998; Gary et al. 1999a; Wu et al. 1999). These results deemphasize the only known role of Fen-1 for DNA replication and strongly argue for the existence of an alternative enzymatic system that allows cells to endure the loss of Fen-1/RNase HI functions. Genetic studies in S. cerevisiae u ...
... Kim et al. 1998; Gary et al. 1999a; Wu et al. 1999). These results deemphasize the only known role of Fen-1 for DNA replication and strongly argue for the existence of an alternative enzymatic system that allows cells to endure the loss of Fen-1/RNase HI functions. Genetic studies in S. cerevisiae u ...
Amplification of 16S rRNA Genes from Frankia Strains in Root
... demonstrating that amplification of contaminants was not occurring. In each case, the sum of the fragment sizes in the restriction pattern was greater than the value expected from a single band of 16S rDNA (1,500 bp), suggesting that more than one gene was being amplified. Given the lack of bacteria ...
... demonstrating that amplification of contaminants was not occurring. In each case, the sum of the fragment sizes in the restriction pattern was greater than the value expected from a single band of 16S rDNA (1,500 bp), suggesting that more than one gene was being amplified. Given the lack of bacteria ...
Use of a novel cassette to label phenotypically a cryptic plasmid of
... to allow easy screening for the presence of plasmids in B. subtilis. In addition we flanked the cassette with transcriptional terminators to ensure that insertion of the cassette had no deleterious effect other than that due to its disruption of the continuity of the plasmid backbone. The terminator ...
... to allow easy screening for the presence of plasmids in B. subtilis. In addition we flanked the cassette with transcriptional terminators to ensure that insertion of the cassette had no deleterious effect other than that due to its disruption of the continuity of the plasmid backbone. The terminator ...
2- pcr primer design and reaction optimisation
... partly why one should not do more than about 30 amplification cycles: however, it is possible to reduce the denaturation temperature after about 10 rounds of amplification, as the mean length of target DNA is decreased: for templates of 300bp or less, denaturation temperature may be reduced to as lo ...
... partly why one should not do more than about 30 amplification cycles: however, it is possible to reduce the denaturation temperature after about 10 rounds of amplification, as the mean length of target DNA is decreased: for templates of 300bp or less, denaturation temperature may be reduced to as lo ...
Unit 30C Cell Division, Genetics, and Molecular
... division. Organisms that reproduce asexually produce offspring that are identical to the parents. Sexually reproducing organisms exchange genetic information, so that the offspring have a unique combination of traits. The genetic material determines the proteins that make up cells, which ultimately ...
... division. Organisms that reproduce asexually produce offspring that are identical to the parents. Sexually reproducing organisms exchange genetic information, so that the offspring have a unique combination of traits. The genetic material determines the proteins that make up cells, which ultimately ...
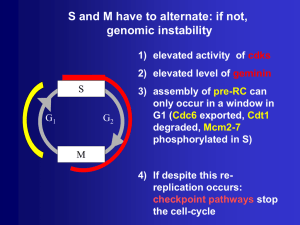
No Slide Title
... • Use in prognosis: e.g. tumors with high S phase fraction detected by flow cytometry have poorer prognosis • Use in predicting responsiveness to a particular type of therapy: e.g. high S phase fraction and loss of p53 will make cells more suceptible to DNA damaging agents ...
... • Use in prognosis: e.g. tumors with high S phase fraction detected by flow cytometry have poorer prognosis • Use in predicting responsiveness to a particular type of therapy: e.g. high S phase fraction and loss of p53 will make cells more suceptible to DNA damaging agents ...
Analysis and nucleotide sequence of an origin of DNA replication in
... Restreaking on minimal plates with Ap yielded 16 candidates. From these the plasmid DNA was prepared from 3 ml overnight cultures and retransformed to A. calcoaceticus BD413 trpE. The transformants were plated on LB-Ap plates and minimal medium Ap plates. Four plasmids yielded roughly the same numbe ...
... Restreaking on minimal plates with Ap yielded 16 candidates. From these the plasmid DNA was prepared from 3 ml overnight cultures and retransformed to A. calcoaceticus BD413 trpE. The transformants were plated on LB-Ap plates and minimal medium Ap plates. Four plasmids yielded roughly the same numbe ...
Origins of DNA Replication - DNA Replication and Human Disease
... lines, but only rarely are genes amplified during normal animal development (Tlsty 1990). In contrast, replication of mtDNA and large viral DNA genomes such as herpes and vaccinia is not dependent on the cell entering S phase. mtDNA replicates randomly throughout the cell division cycle, and large v ...
... lines, but only rarely are genes amplified during normal animal development (Tlsty 1990). In contrast, replication of mtDNA and large viral DNA genomes such as herpes and vaccinia is not dependent on the cell entering S phase. mtDNA replicates randomly throughout the cell division cycle, and large v ...
Creating conditional dual fluorescence labelled transgenic animals
... In addition to messenger RNA that encodes proteins, non-coding RNAs, including microRNA (miRNA) and long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) have been shown to be involved in gene regulation at post-transcriptional and translational levels. For example, microRNAs, about 22 nucleotide long, are among the largest ...
... In addition to messenger RNA that encodes proteins, non-coding RNAs, including microRNA (miRNA) and long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) have been shown to be involved in gene regulation at post-transcriptional and translational levels. For example, microRNAs, about 22 nucleotide long, are among the largest ...
Sequence Information Encoded in DNA that May Influence Long
... continuous chromatin organizing signals than in control regions. We also found a relationship between the meiotic recombination frequency and the presence of strong VWG chromatin organizing signals. Large ($300 kb) genomic DNA regions having low average recombination frequency are enriched in chroma ...
... continuous chromatin organizing signals than in control regions. We also found a relationship between the meiotic recombination frequency and the presence of strong VWG chromatin organizing signals. Large ($300 kb) genomic DNA regions having low average recombination frequency are enriched in chroma ...
Separation of DNA Restriction Fragments by Ion
... plays a central role in DNA research. However, when used for preparative purposes electrophoresis has two particularly serious drawbacks: (A) Extraction of the purified material out of the gel is tedious and difficult to accomplish with high yields (1). (B) The purified DNA is often contaminated wit ...
... plays a central role in DNA research. However, when used for preparative purposes electrophoresis has two particularly serious drawbacks: (A) Extraction of the purified material out of the gel is tedious and difficult to accomplish with high yields (1). (B) The purified DNA is often contaminated wit ...