Genetic Mutations
... If a point mutation occurs in a proto-oncogene it can form an oncogene. This can stimulate excessive cell division, leading to the formation of a tumor. If a point mutation occurs in a tumor suppressor gene it can become inactivated. This allows the rate of cell division to increase unregulated. ...
... If a point mutation occurs in a proto-oncogene it can form an oncogene. This can stimulate excessive cell division, leading to the formation of a tumor. If a point mutation occurs in a tumor suppressor gene it can become inactivated. This allows the rate of cell division to increase unregulated. ...
CHAPTER 14: Genes in Action Essential Ideas
... Mutagens cause mutations, include environmental factors ike chemicals, X-rays, and UV light Genetic Mutations – single or small changes to individual genes DNA sequence Point mutations include; silent, missense and nonsense SILENT mutation - the change in the codon results in the same amino acid- UA ...
... Mutagens cause mutations, include environmental factors ike chemicals, X-rays, and UV light Genetic Mutations – single or small changes to individual genes DNA sequence Point mutations include; silent, missense and nonsense SILENT mutation - the change in the codon results in the same amino acid- UA ...
Mutations
... 5. Translocation = occurs when part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome. ...
... 5. Translocation = occurs when part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome. ...
Gene Mutations
... The Pat Hid And The Cat Sat And Got Fat Adding or deleting a letter is worse because ALL words change The Rat Hix Dan Dth Eca Tsa Tan Dgo Tfa T The Rah Ida Ndt Hec Ats Atat Ndg Otf At ...
... The Pat Hid And The Cat Sat And Got Fat Adding or deleting a letter is worse because ALL words change The Rat Hix Dan Dth Eca Tsa Tan Dgo Tfa T The Rah Ida Ndt Hec Ats Atat Ndg Otf At ...
Mutations & Genetic Engineering
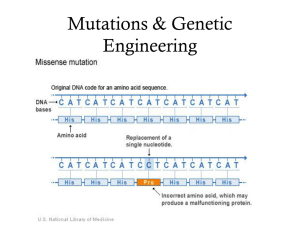
... – New codon codes for the same amino acid – silent – New codon changes the amino acid – missense • Sickle cell anemia ...
... – New codon codes for the same amino acid – silent – New codon changes the amino acid – missense • Sickle cell anemia ...
lecture 2: biological diversity in organisms
... it from the external environment; nuclear membrane protects the DNA…. • Adaptability: is essential to survival and creating the diversity of life that exists occur via mutations: • A mutation is a change, mostly permanent, to the DNA and can be classified into 2 types chromosomal mutation and point ...
... it from the external environment; nuclear membrane protects the DNA…. • Adaptability: is essential to survival and creating the diversity of life that exists occur via mutations: • A mutation is a change, mostly permanent, to the DNA and can be classified into 2 types chromosomal mutation and point ...
Mutation Study Guide
... abnormal regulation of genes. 6. What is translocation? The attachment of a piece of one chromosome to a non-homologous chromosome 7. In a frameshift mutation, what is the “frame” that is being shifted? This mutation involves the insertion or deletion of a nucleotide in a DNA sequence, which shifts ...
... abnormal regulation of genes. 6. What is translocation? The attachment of a piece of one chromosome to a non-homologous chromosome 7. In a frameshift mutation, what is the “frame” that is being shifted? This mutation involves the insertion or deletion of a nucleotide in a DNA sequence, which shifts ...
Review for Molecular Genetics Quest
... 5. Where does this happen? Make sure to label location and type of cell. There are two answers for this!! ...
... 5. Where does this happen? Make sure to label location and type of cell. There are two answers for this!! ...
DNA and Mutations Webquest
... 1. What is sickle-cell anemia? 2. People with _________ copies of the gene have the disease. 3. What are the effects of the sickle cell gene? ...
... 1. What is sickle-cell anemia? 2. People with _________ copies of the gene have the disease. 3. What are the effects of the sickle cell gene? ...
DNA and Mutations Webquest
... 1. What is sickle-cell anemia? 2. People with _________ copies of the gene have the disease. 3. What are the effects of the sickle cell gene? ...
... 1. What is sickle-cell anemia? 2. People with _________ copies of the gene have the disease. 3. What are the effects of the sickle cell gene? ...
Genetics Guided Notes Use Chapter 12
... Define Polyploidy and provide two examples of these types of organisms from the text: ...
... Define Polyploidy and provide two examples of these types of organisms from the text: ...
Part 3 - Alexander Local Schools
... I can… describe how DNA becomes the traits using RNA I can… define mutations and give 3 types I can… describe some harmful mutations in humans I can… explain the three possible outcomes of mutations. ...
... I can… describe how DNA becomes the traits using RNA I can… define mutations and give 3 types I can… describe some harmful mutations in humans I can… explain the three possible outcomes of mutations. ...
Ch 13 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Small mutations in DNA can cause huge changes in the proteins that are synthesized. Similarly, small changes in a word can dramatically alter its ...
... Small mutations in DNA can cause huge changes in the proteins that are synthesized. Similarly, small changes in a word can dramatically alter its ...
13.3_Mutations
... Small mutations in DNA can cause huge changes in the proteins that are synthesized. Similarly, small changes in a word can dramatically alter its ...
... Small mutations in DNA can cause huge changes in the proteins that are synthesized. Similarly, small changes in a word can dramatically alter its ...
DNA mutations 11.3 notes
... If the DNA is mutated, what will happen to the mRNA? It will take the changed info into the cytoplasm and the tRNA will bring the wrong amino acid to the rRNA. The protein will be based on the mutated ...
... If the DNA is mutated, what will happen to the mRNA? It will take the changed info into the cytoplasm and the tRNA will bring the wrong amino acid to the rRNA. The protein will be based on the mutated ...
Section 8.7 Mutations
... • Usually occur in DNA replication • Affect one gene and the protein made from it ...
... • Usually occur in DNA replication • Affect one gene and the protein made from it ...
Mutations Learning goals Mutation Where Mutations Occur
... Where Mutations Occur – Mutations occur in regular body cells • 1. Occurs during mitosis (cell division) • 2. Affects the person, not the offspring • 3. Affects the function of the cell – This may cause cancer ...
... Where Mutations Occur – Mutations occur in regular body cells • 1. Occurs during mitosis (cell division) • 2. Affects the person, not the offspring • 3. Affects the function of the cell – This may cause cancer ...
Transposons_&_DNA_Mutations
... Genetic characteristics of a population can change over time – “Evolution” ...
... Genetic characteristics of a population can change over time – “Evolution” ...
Chromosomal Mutations
... Insertions & Deletions! These mutations will always cause a frameshift mutation, which will change the reading frame & the amino acid sequence! This will give you a completely different protein! Substitutions could change the amino acid sequence, but it may ...
... Insertions & Deletions! These mutations will always cause a frameshift mutation, which will change the reading frame & the amino acid sequence! This will give you a completely different protein! Substitutions could change the amino acid sequence, but it may ...
Foundations of Biology
... Micro-mutations tend to have a dramatic effect on proteins as all codons down stream from the mutation are changed and thus code for different amino acids. As a result, the length of the polypeptide may also be changed as a stop codon will probably come at a different spot than the original stop cod ...
... Micro-mutations tend to have a dramatic effect on proteins as all codons down stream from the mutation are changed and thus code for different amino acids. As a result, the length of the polypeptide may also be changed as a stop codon will probably come at a different spot than the original stop cod ...
Gene Regulation and Mutation Notes and Questions
... • Insertion is the addition of one or more bases into a nucleotide sequence • This can change many amino acids in the polypeptide chain, thus changing the protein • It causes a “frameshift” in the mRNA bases, thus causing the wrong amino acid to be added to the polypeptide chain. • Crohn’s disease i ...
... • Insertion is the addition of one or more bases into a nucleotide sequence • This can change many amino acids in the polypeptide chain, thus changing the protein • It causes a “frameshift” in the mRNA bases, thus causing the wrong amino acid to be added to the polypeptide chain. • Crohn’s disease i ...
Frameshift mutation

A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon (""UAA"", ""UGA"" or ""UAG"") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likely not be functional.Frameshift mutations are apparent in severe genetic diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Cystic Fibrosis; they increase susceptibility to certain cancers and classes of familial hypercholesterolaemia; in 1997, a frameshift mutation was linked to resistance to infection by the HIV retrovirus. Frameshift mutations have been proposed as a source of biological novelty, as with the alleged creation of nylonase, however, this interpretation is controversial. A study by Negoro et al (2006) found that a frameshift mutation was unlikely to have been the cause and that rather a two amino acid substitution in the catalytic cleft of an ancestral esterase amplified Ald-hydrolytic activity.