Eukaryotic Gene Expression Practice Problems Class Work 1
... occurs when different nucleotide base is substituted for original nucleotide. b. Deletion: a deletion mutation occurs when a nucleotide is deleted from the original sequence. c. Insertion: an insertion mutation occurs when a nucleotide is inserted into the original sequence. 36. Insertions and delet ...
... occurs when different nucleotide base is substituted for original nucleotide. b. Deletion: a deletion mutation occurs when a nucleotide is deleted from the original sequence. c. Insertion: an insertion mutation occurs when a nucleotide is inserted into the original sequence. 36. Insertions and delet ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression Practice Problems Class Work 1
... occurs when different nucleotide base is substituted for original nucleotide. b. Deletion: a deletion mutation occurs when a nucleotide is deleted from the original sequence. c. Insertion: an insertion mutation occurs when a nucleotide is inserted into the original sequence. 36. Insertions and delet ...
... occurs when different nucleotide base is substituted for original nucleotide. b. Deletion: a deletion mutation occurs when a nucleotide is deleted from the original sequence. c. Insertion: an insertion mutation occurs when a nucleotide is inserted into the original sequence. 36. Insertions and delet ...
Genetic Disorders
... PKU is a metabolic disorder that results when the PKU gene is inherited from both parents (recessive or dominant? Monogenic or ...
... PKU is a metabolic disorder that results when the PKU gene is inherited from both parents (recessive or dominant? Monogenic or ...
CHAPTER 19 DNA Mutation and Repair
... 1. Chemical mutagens may be naturally occurring, or synthetic. They form different groups based on their mechanism of action: a. Base analogs depend upon replication, which incorpocates a base with alternate states (tautomers) that allow it to base pair in alternate ways, depending on its state. i. ...
... 1. Chemical mutagens may be naturally occurring, or synthetic. They form different groups based on their mechanism of action: a. Base analogs depend upon replication, which incorpocates a base with alternate states (tautomers) that allow it to base pair in alternate ways, depending on its state. i. ...
CHIMERISM. Principles and practise.
... Hemoglobin H-Constant Spring disease is a more severe form of this hemolytic disorder. Most severe form is a thalassemia major, in which fetus produces no a globins, which is generally incompatible with life. ...
... Hemoglobin H-Constant Spring disease is a more severe form of this hemolytic disorder. Most severe form is a thalassemia major, in which fetus produces no a globins, which is generally incompatible with life. ...
as a PDF
... In recent times it has been repeatedly observed that haplotypes surrounding rare alleles of a gene are quite large [1-9]. Sharing of large genomic areas can be used as a method to map disease genes: Identity By Descent (IBD) Mapping [4,10]. An empirical question is whether haplotype sharing can be o ...
... In recent times it has been repeatedly observed that haplotypes surrounding rare alleles of a gene are quite large [1-9]. Sharing of large genomic areas can be used as a method to map disease genes: Identity By Descent (IBD) Mapping [4,10]. An empirical question is whether haplotype sharing can be o ...
Mader/Biology, 13/e – Chapter Outline
... molecule that controls whether the operon is active or not. 2) A promotor is the sequence of DNA where RNA polymerase attaches when a gene is to be transcribed. 3) An operator is a short sequence of DNA where an active repressor binds, preventing RNA polymerase from attaching to the promotor—transcr ...
... molecule that controls whether the operon is active or not. 2) A promotor is the sequence of DNA where RNA polymerase attaches when a gene is to be transcribed. 3) An operator is a short sequence of DNA where an active repressor binds, preventing RNA polymerase from attaching to the promotor—transcr ...
Mechanisms Powerpoint
... beetles happened to have four offspring survive to reproduce. Several green beetles were killed when someone stepped on them and had no offspring. The next generation would have a few more brown beetles than the previous generation—but just by chance. These chance changes from generation to generati ...
... beetles happened to have four offspring survive to reproduce. Several green beetles were killed when someone stepped on them and had no offspring. The next generation would have a few more brown beetles than the previous generation—but just by chance. These chance changes from generation to generati ...
Genetic disorders
... synthesis of the receptor protein. Class II mutations - common, they encode receptor proteins that accumulate in the endoplasmic reticulum because they cannot be transported to the Golgi complex. Class III mutations - affect the LDL-binding domain of the receptor. Class IV mutations - encode protein ...
... synthesis of the receptor protein. Class II mutations - common, they encode receptor proteins that accumulate in the endoplasmic reticulum because they cannot be transported to the Golgi complex. Class III mutations - affect the LDL-binding domain of the receptor. Class IV mutations - encode protein ...
MCB 421 HOMEWORK #4 ANSWERS FALL 2006 Page 1 of 3
... ANSWER: sup-1 and sup-2 are both amber suppressors -- due to a mutation in the gene encoding a tRNA which allows recognition of the UAG codon. However these two mutations affect two different tRNA genes such that, although both mutant tRNAs recognise amber codons, they insert different amino acids ( ...
... ANSWER: sup-1 and sup-2 are both amber suppressors -- due to a mutation in the gene encoding a tRNA which allows recognition of the UAG codon. However these two mutations affect two different tRNA genes such that, although both mutant tRNAs recognise amber codons, they insert different amino acids ( ...
Gene Section SDHD (succinate dehydrogenase complex II, subunit D, integral membrane protein)
... the SDHD gene in hereditary paraganglioma abolishes the enzymatic activity of complex II in the mitochondrial respiratory chain and activates the hypoxia pathway. Am J Hum Genet. ...
... the SDHD gene in hereditary paraganglioma abolishes the enzymatic activity of complex II in the mitochondrial respiratory chain and activates the hypoxia pathway. Am J Hum Genet. ...
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology
... prevalence (35.3%), in contrast to 0.5–13.8% described in other series. Incidence of other mutations does not differ, as previously described: large deletions (19.6%), mutation in intron 2 (17.6%), and I172N (10.8%). Four novel mutations were found in four patients with the salt-wasting form. These ...
... prevalence (35.3%), in contrast to 0.5–13.8% described in other series. Incidence of other mutations does not differ, as previously described: large deletions (19.6%), mutation in intron 2 (17.6%), and I172N (10.8%). Four novel mutations were found in four patients with the salt-wasting form. These ...
A1978FE76900002
... development than were sea urchins or frogs, favorites of embryologists. "But the genetics of eye pigments in Drosophila did offer promise of bringing the two approaches together. By devising techniques of transplanting larval embryonic eye-buds we did identify two enzymatic steps in brown eye-pigmen ...
... development than were sea urchins or frogs, favorites of embryologists. "But the genetics of eye pigments in Drosophila did offer promise of bringing the two approaches together. By devising techniques of transplanting larval embryonic eye-buds we did identify two enzymatic steps in brown eye-pigmen ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... Neurospora that are all able to grow on compound R. The mutants are then grown on minimal media supplemented with one of 6 chemicals all known to be precursors to R. A summary of the ability of the mutants to grow on media containing these chemicals is indicated below, where a “+” sign indicates gro ...
... Neurospora that are all able to grow on compound R. The mutants are then grown on minimal media supplemented with one of 6 chemicals all known to be precursors to R. A summary of the ability of the mutants to grow on media containing these chemicals is indicated below, where a “+” sign indicates gro ...
BBHH BBHh
... • Example: In rabbits black coat (B) is dominant over brown (b) and straight hair (H) is dominant to curly (h). Cross a rabbit that is homozygous dominant for both traits with a rabbit that is homozygous dominant for black coat and heterozygous for straight hair. Then give the phenotypic ratio for ...
... • Example: In rabbits black coat (B) is dominant over brown (b) and straight hair (H) is dominant to curly (h). Cross a rabbit that is homozygous dominant for both traits with a rabbit that is homozygous dominant for black coat and heterozygous for straight hair. Then give the phenotypic ratio for ...
DNA notes - Chapel Hill
... will share the same DNA nucleotide sequence. Comparing DNA base pairs of two species will show their evolutionary history. ...
... will share the same DNA nucleotide sequence. Comparing DNA base pairs of two species will show their evolutionary history. ...
EVOLVING STILL S STILL STI
... mutations gives us a tremendous power to observe evolution over hundreds of generations but can obscure the complex interactions of environment, survival and fertility that unfolded in the past. We see the long-term winners, such as lactase persistence, but may miss the short-term dy namics. Human ...
... mutations gives us a tremendous power to observe evolution over hundreds of generations but can obscure the complex interactions of environment, survival and fertility that unfolded in the past. We see the long-term winners, such as lactase persistence, but may miss the short-term dy namics. Human ...
Presentation - College of American Pathologists
... inhibiting free speech and access to information. ...
... inhibiting free speech and access to information. ...
Module name Genetics - a basic course Module code B
... genetics) and molecular genetics, genetic mapping, mitosis and meiosis, DNA replication and recombination, gene transcription and regulation of gene expression, connection of genotype and phenotype. SKILLS -Understanding the logic and core concepts of classical and molecular genetics, including: pre ...
... genetics) and molecular genetics, genetic mapping, mitosis and meiosis, DNA replication and recombination, gene transcription and regulation of gene expression, connection of genotype and phenotype. SKILLS -Understanding the logic and core concepts of classical and molecular genetics, including: pre ...
Adaptation, natural selection and evolution
... • Give examples of adaptations which allow a species to survive. • State that adaptation may be structural, physiological or behavioural. • Describe examples of behaviours which allow a species to survive. • State that variation within a population makes it possible for a population to evolve over t ...
... • Give examples of adaptations which allow a species to survive. • State that adaptation may be structural, physiological or behavioural. • Describe examples of behaviours which allow a species to survive. • State that variation within a population makes it possible for a population to evolve over t ...
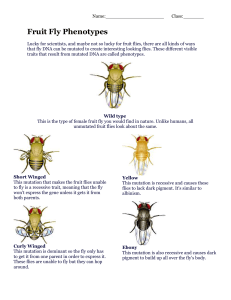
Fruit Fly Phenotypes
... Antennapedia This mutation is dominant and may not be obvious at first. Look closely, those are not antennae, those are an extra set of legs coming out of the fly's head. These fruit flies have a mutation that tells the body to turn the antenna into legs during development. ...
... Antennapedia This mutation is dominant and may not be obvious at first. Look closely, those are not antennae, those are an extra set of legs coming out of the fly's head. These fruit flies have a mutation that tells the body to turn the antenna into legs during development. ...
Audit
... Lynch Syndrome/HNPCC Update of Genetics of Lynch Syndrome/HNPCC Results of Northern Genetics Service audit of screening in patients with known MMR ...
... Lynch Syndrome/HNPCC Update of Genetics of Lynch Syndrome/HNPCC Results of Northern Genetics Service audit of screening in patients with known MMR ...
Introductory Biological Sequence Analysis Through Spreadsheets
... structure of DNA, RNA, and proteins are sequences of letters -- 4 letters in the case of DNA (ATGC) and RNA (AUGC) and 20 letters representing the sequence of amino acids which makes up a protein Secondary and Tertiary structures (bending, folding and twisting) of structures determines function -- ...
... structure of DNA, RNA, and proteins are sequences of letters -- 4 letters in the case of DNA (ATGC) and RNA (AUGC) and 20 letters representing the sequence of amino acids which makes up a protein Secondary and Tertiary structures (bending, folding and twisting) of structures determines function -- ...
Genetics
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
Frameshift mutation

A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon (""UAA"", ""UGA"" or ""UAG"") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likely not be functional.Frameshift mutations are apparent in severe genetic diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Cystic Fibrosis; they increase susceptibility to certain cancers and classes of familial hypercholesterolaemia; in 1997, a frameshift mutation was linked to resistance to infection by the HIV retrovirus. Frameshift mutations have been proposed as a source of biological novelty, as with the alleged creation of nylonase, however, this interpretation is controversial. A study by Negoro et al (2006) found that a frameshift mutation was unlikely to have been the cause and that rather a two amino acid substitution in the catalytic cleft of an ancestral esterase amplified Ald-hydrolytic activity.