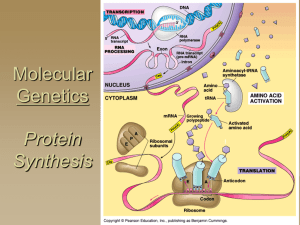
CHEM 482
... 1. What is the polypeptide specified by the following DNA antisense strand? Assume translation starts after the first initiation codon and continues until a stop. 5’-TCTGACTATTGAGCTCTCTGGCACATAGCA-3’ ...
... 1. What is the polypeptide specified by the following DNA antisense strand? Assume translation starts after the first initiation codon and continues until a stop. 5’-TCTGACTATTGAGCTCTCTGGCACATAGCA-3’ ...
1 - TESTBANKcorner.EU
... recombinational analysis is that two genes that are far apart on a chromosome will have a higher frequency of recombination than two genes that are close together. Thus, if recombination between the gene of interest and a marker is very low, then the gene is likely located near that marker gene. ...
... recombinational analysis is that two genes that are far apart on a chromosome will have a higher frequency of recombination than two genes that are close together. Thus, if recombination between the gene of interest and a marker is very low, then the gene is likely located near that marker gene. ...
Teacher notes and student sheets
... Cystic Fibrosis is one of the commonest inherited diseases in the UK. It is caused by mutations in the CTFR gene. These mutated alleles are recessive. (a) Before the faulty gene was identified affected families had no way of preventing the birth of children with the disease, except by not having chi ...
... Cystic Fibrosis is one of the commonest inherited diseases in the UK. It is caused by mutations in the CTFR gene. These mutated alleles are recessive. (a) Before the faulty gene was identified affected families had no way of preventing the birth of children with the disease, except by not having chi ...
Sex linked inheritance, sex linkage in Drosophila and man, XO, XY
... stacked at the center of the DNA molecule. This occurrence can lead to single-nucleotide-pair insertions and deletions. ...
... stacked at the center of the DNA molecule. This occurrence can lead to single-nucleotide-pair insertions and deletions. ...
Chapter 15 - ShoultzScience
... Researchers have identified many proto-oncogenes whose mutation to an oncogene cause increased growth and lead to a tumor. The ras family of genes are the most common oncogenes implicated in human cancers. Alteration of one nucleotide pair converts a normal functioning ras proto-oncogene to an oncog ...
... Researchers have identified many proto-oncogenes whose mutation to an oncogene cause increased growth and lead to a tumor. The ras family of genes are the most common oncogenes implicated in human cancers. Alteration of one nucleotide pair converts a normal functioning ras proto-oncogene to an oncog ...
Update on Boxer Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
... disease in humans may be applicable to the dog In humans there are 8 different genes that can cause the development of ARVC. Each one, all by itself can lead to the development of ARVC. There are 141 DIFFERENT mutations in these 8 genes. Therefore, it is very likely that there is more than one mutat ...
... disease in humans may be applicable to the dog In humans there are 8 different genes that can cause the development of ARVC. Each one, all by itself can lead to the development of ARVC. There are 141 DIFFERENT mutations in these 8 genes. Therefore, it is very likely that there is more than one mutat ...
Proteins-and-Mutations
... Gene mutations may lead to the production of different proteins. Mutation may occur spontaneously but can be made to occur more often by radiation or chemicals. Mutations are often harmful but may be beneficial or have no effect. Only some of the full set of genes is used in any one cell; some genes ...
... Gene mutations may lead to the production of different proteins. Mutation may occur spontaneously but can be made to occur more often by radiation or chemicals. Mutations are often harmful but may be beneficial or have no effect. Only some of the full set of genes is used in any one cell; some genes ...
Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3)
... Gene mutations may lead to the production of different proteins. Mutation may occur spontaneously but can be made to occur more often by radiation or chemicals. Mutations are often harmful but may be beneficial or have no effect. Only some of the full set of genes is used in any one cell; some genes ...
... Gene mutations may lead to the production of different proteins. Mutation may occur spontaneously but can be made to occur more often by radiation or chemicals. Mutations are often harmful but may be beneficial or have no effect. Only some of the full set of genes is used in any one cell; some genes ...
DNA- The Genetic Material
... Gene Mutations A Mutation is a change in the sequence of bases within a gene Causes: • Mutations can be spontaneous or caused by environmental influences called mutagens. • Mutagens include radiation (X-rays, UV radiation), and organic chemicals (in cigarette smoke and pesticides). ...
... Gene Mutations A Mutation is a change in the sequence of bases within a gene Causes: • Mutations can be spontaneous or caused by environmental influences called mutagens. • Mutagens include radiation (X-rays, UV radiation), and organic chemicals (in cigarette smoke and pesticides). ...
Chapter 10 The Code of Life Test Review Name
... 20. The order of base pairs along a gene is called its _base sequence. 21. The base pair cytosine only pairs with the base pair guanine in DNA sequencing 22. DNA replication ensures that each daughter cell has an exact copy of the DNA from the parent cell. 23. DNA molecules are in the shape of a dou ...
... 20. The order of base pairs along a gene is called its _base sequence. 21. The base pair cytosine only pairs with the base pair guanine in DNA sequencing 22. DNA replication ensures that each daughter cell has an exact copy of the DNA from the parent cell. 23. DNA molecules are in the shape of a dou ...
Educational Items Section population Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... To pass of q0 = 0.51 to qn = 0.71 and qe = 0. 91 Mutations can produce equilibrium states, but they will be reached very slowly through the time. The mutation process does not have major effect on the genetic structure of populations; the variation of allele frequencies is very low through the time. ...
... To pass of q0 = 0.51 to qn = 0.71 and qe = 0. 91 Mutations can produce equilibrium states, but they will be reached very slowly through the time. The mutation process does not have major effect on the genetic structure of populations; the variation of allele frequencies is very low through the time. ...
Semiconservative
... • Transfer of plasmid DNA from a F+ (F factor) cell to a F- cell • An F+ bacterium possesses a pilus • Pilus attaches to the recipient cell and creates pore for the transfer DNA ...
... • Transfer of plasmid DNA from a F+ (F factor) cell to a F- cell • An F+ bacterium possesses a pilus • Pilus attaches to the recipient cell and creates pore for the transfer DNA ...
12GeneEvol
... A. an extended sequence that lacks stop codons. B. a sequence downstream from a known promoter sequence. C. a sequence from which a meaningful protein can be deduced. D. a sequence with close homology to that of a gene in another organism. 11. A retrotransposon would be best described as A. a mobile ...
... A. an extended sequence that lacks stop codons. B. a sequence downstream from a known promoter sequence. C. a sequence from which a meaningful protein can be deduced. D. a sequence with close homology to that of a gene in another organism. 11. A retrotransposon would be best described as A. a mobile ...
2015/5/13 9:24 AM
... 12. DNA controls the tertiary structure of proteins because DNA is directly responsible for transcription of RNA and nucleotide sequence. 13. Messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA are involved in protein synthesis. 14. RNA polymerase is a type of RNA that functions as a “blueprint” for prot ...
... 12. DNA controls the tertiary structure of proteins because DNA is directly responsible for transcription of RNA and nucleotide sequence. 13. Messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA are involved in protein synthesis. 14. RNA polymerase is a type of RNA that functions as a “blueprint” for prot ...
That Come Close to the Bone - Max-Planck
... marked with different fluorescent dyes. The fluorescent signals are then identified with the aid of a scanner. Depending on how strong a given fluorescent signal is, it is possible to establish whether both DNA samples have bound equally or whether one has bound more and the other less. ...
... marked with different fluorescent dyes. The fluorescent signals are then identified with the aid of a scanner. Depending on how strong a given fluorescent signal is, it is possible to establish whether both DNA samples have bound equally or whether one has bound more and the other less. ...
detection and pathogenetic role of mmr missense mutations
... To address a pathogenic significance to these mutations, functional studies dealing with expression level, interaction and localization analysis were developed and performed. The expression levels of the MLH1 and MSH2 mutated proteins were investigated by transfecting an human MMR(-) expression syst ...
... To address a pathogenic significance to these mutations, functional studies dealing with expression level, interaction and localization analysis were developed and performed. The expression levels of the MLH1 and MSH2 mutated proteins were investigated by transfecting an human MMR(-) expression syst ...
Gene Section PHOX2B (paired-like homeobox 2b) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... NB cell lines and NB tumor samples as reported in the Table 1. Note There is a clear correlation between types of PHOX2B mutations and clinical manifestations. Indeed, while the vast majority of PHOX2B mutations identified in isolated Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome (CCHS) are PARMs (Pol ...
... NB cell lines and NB tumor samples as reported in the Table 1. Note There is a clear correlation between types of PHOX2B mutations and clinical manifestations. Indeed, while the vast majority of PHOX2B mutations identified in isolated Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome (CCHS) are PARMs (Pol ...
Progressive Retinal Atrophy, (PAP1_PRA)
... Progressive Retinal Atrophy, (PAP1_PRA) In brief Progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) comprises a group of genetically inherited diseases affecting dogs of various breeds. PRA is characterised by retinal degeneration and progressive loss of vision culminating in blindness. PR ...
... Progressive Retinal Atrophy, (PAP1_PRA) In brief Progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) comprises a group of genetically inherited diseases affecting dogs of various breeds. PRA is characterised by retinal degeneration and progressive loss of vision culminating in blindness. PR ...
HIV Resistant Mutation
... HIV a person can live many years without developing AIDS. After a person is infected with HIV, the virus seeks out the body's immune cells and attaches itself to them in the hopes of producing more virus particles. HIV's "main target" are CD4 immune cells. In the acute stages of infection the virus ...
... HIV a person can live many years without developing AIDS. After a person is infected with HIV, the virus seeks out the body's immune cells and attaches itself to them in the hopes of producing more virus particles. HIV's "main target" are CD4 immune cells. In the acute stages of infection the virus ...
Lec3-Molecular-Aspects-of-Lymphocyte-Transformation
... syndrome is a common example of a chromosomal disorder where translocation (an abnormality in chromosome structure) has taken place on Chromosome 21. Single-Gene Disorders: Also referred to as monogenic or Mendelian disorders, single-gene disorders are caused by mutations that occur in the nucleotid ...
... syndrome is a common example of a chromosomal disorder where translocation (an abnormality in chromosome structure) has taken place on Chromosome 21. Single-Gene Disorders: Also referred to as monogenic or Mendelian disorders, single-gene disorders are caused by mutations that occur in the nucleotid ...
Chapter 3- Section 4 The DNA Connection
... The DNA molecule “unzips” and the messenger RNA strand (which is responsible for copying the coded messages from the DNA in the nucleus and carrying them to the cytoplasm.) base pairs with the DNA strand and copies the coded messages. Once in the cytoplasm, messenger RNA attaches to a ribosome and t ...
... The DNA molecule “unzips” and the messenger RNA strand (which is responsible for copying the coded messages from the DNA in the nucleus and carrying them to the cytoplasm.) base pairs with the DNA strand and copies the coded messages. Once in the cytoplasm, messenger RNA attaches to a ribosome and t ...
ch14_sec1 NOTES
... • DNA and chromosomes are involved in many processes, so there are many kinds of mutations. • Most mutations involve a misplacement of a nucleotide in a DNA segment. • A mutation may change the results of a gene (when the gene is translated and transcribed), but not all mutations ...
... • DNA and chromosomes are involved in many processes, so there are many kinds of mutations. • Most mutations involve a misplacement of a nucleotide in a DNA segment. • A mutation may change the results of a gene (when the gene is translated and transcribed), but not all mutations ...
Clinical Exome Sequencing at GeneDx Cheryl Scacheri, MS, LGC Licensed Genetic Counselor
... May need follow up with different test method ...
... May need follow up with different test method ...
Gene to Protein
... anticodons on the surface of the tRNA • 10. peptide bonds can be formed between the two adjacent amino acids • 11. the ribosome can progress along the mRNA to the next codon ...
... anticodons on the surface of the tRNA • 10. peptide bonds can be formed between the two adjacent amino acids • 11. the ribosome can progress along the mRNA to the next codon ...
Frameshift mutation

A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon (""UAA"", ""UGA"" or ""UAG"") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likely not be functional.Frameshift mutations are apparent in severe genetic diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Cystic Fibrosis; they increase susceptibility to certain cancers and classes of familial hypercholesterolaemia; in 1997, a frameshift mutation was linked to resistance to infection by the HIV retrovirus. Frameshift mutations have been proposed as a source of biological novelty, as with the alleged creation of nylonase, however, this interpretation is controversial. A study by Negoro et al (2006) found that a frameshift mutation was unlikely to have been the cause and that rather a two amino acid substitution in the catalytic cleft of an ancestral esterase amplified Ald-hydrolytic activity.