Focus points chapters 6
... What kinds of things cause mutations? Which nucleotide base is only found in RNA? What is the product of transcription? What is “reverse transcription” ...
... What kinds of things cause mutations? Which nucleotide base is only found in RNA? What is the product of transcription? What is “reverse transcription” ...
Chromosomal Rearrangements I
... (multigenic). Deletions can arise from DNA damage (X-rays or chemical agents that break chromosomes), or from mistakes during recombination or replication. If the deleted region does not contain any genes essential for survival, an individual homozygous for a deletion (Del/Del) will live. An example ...
... (multigenic). Deletions can arise from DNA damage (X-rays or chemical agents that break chromosomes), or from mistakes during recombination or replication. If the deleted region does not contain any genes essential for survival, an individual homozygous for a deletion (Del/Del) will live. An example ...
Karotype Chromosomal Abnormalities
... CAUSE: Chromosomes don’t separate correctly during anaphase ...
... CAUSE: Chromosomes don’t separate correctly during anaphase ...
Microevolution
... Acts against extreme phenotypes Favors the more common intermediate variants Maintains the “status quo” Example: ...
... Acts against extreme phenotypes Favors the more common intermediate variants Maintains the “status quo” Example: ...
Things to Know for the Test – Honors
... hormones such as insulin, etc. DNA is so important to an organism that it can’t get damaged. So, it must be copied in a process called transcription. This process takes place in the nucleus. It is done by an enzyme, RNA polymerase, that breaks the H-bonds between the bases and makes a complementary ...
... hormones such as insulin, etc. DNA is so important to an organism that it can’t get damaged. So, it must be copied in a process called transcription. This process takes place in the nucleus. It is done by an enzyme, RNA polymerase, that breaks the H-bonds between the bases and makes a complementary ...
PopGen 5: Mutation pressure
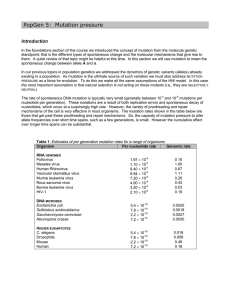
... the most important assumption is that natural selection is not acting on these mutants (i.e., they are SELECTIVELY NEUTRAL). The rate of spontaneous DNA mutation is typically very small (generally between 10-4 and 10-6 mutations per nucleotide per generation). These mutations are a result of both re ...
... the most important assumption is that natural selection is not acting on these mutants (i.e., they are SELECTIVELY NEUTRAL). The rate of spontaneous DNA mutation is typically very small (generally between 10-4 and 10-6 mutations per nucleotide per generation). These mutations are a result of both re ...
Basic Laws of Chemistry that Drive Protein Folding: Stably
... Cysteine amino acid-often interact with each other to form covalent disulfide bonds that stabilize protein structure. ...
... Cysteine amino acid-often interact with each other to form covalent disulfide bonds that stabilize protein structure. ...
Study Guide Game - Campbell County Schools
... Mutations have what type of affects on organisms? 1. Harmful 2. Beneficial 3. No Affects 4. All the above ...
... Mutations have what type of affects on organisms? 1. Harmful 2. Beneficial 3. No Affects 4. All the above ...
Evidence that a Safe Dose of Mutagen Does Not Exist
... 1. The physical principle of molecular mass action dictates that even the best DNA repair system in the most healthy person can not detect and repair all premutational lesions prior to DNA replication. Assuming it were true, many people are "repair compromised" because of their genotype or due to th ...
... 1. The physical principle of molecular mass action dictates that even the best DNA repair system in the most healthy person can not detect and repair all premutational lesions prior to DNA replication. Assuming it were true, many people are "repair compromised" because of their genotype or due to th ...
Clicker Review-DNAProtein Syn Mutation
... not double stranded Contains ribose and not deoxyribose Contains thymine and not uracil 1 and 2 are correct All are correct ...
... not double stranded Contains ribose and not deoxyribose Contains thymine and not uracil 1 and 2 are correct All are correct ...
Predisposition of genetic disease by modestly decreased
... Recently it was shown that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can explain individual variation because of the small changes of the gene expression level and that the 50% decreased expression of an allele might even lead to predisposition to cancer. In this study, we found that a decreased expres ...
... Recently it was shown that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can explain individual variation because of the small changes of the gene expression level and that the 50% decreased expression of an allele might even lead to predisposition to cancer. In this study, we found that a decreased expres ...
Genetic Algorithms
... • Genotype (genome) – population of abstract representations of candidate solutions. • Phenotype – the candidate solution. • Fitness function – particular type of objective function that quantifies the optimality of the solution. ...
... • Genotype (genome) – population of abstract representations of candidate solutions. • Phenotype – the candidate solution. • Fitness function – particular type of objective function that quantifies the optimality of the solution. ...
View Full Text-PDF
... The study confirms a heterogeneity of βthalassemia mutations within different districts of Basrah. In addition the frequency of these mutations differ from those detected in other parts of Iraq and neighboring countries and signifies the need for future studies to detect mutations that were not iden ...
... The study confirms a heterogeneity of βthalassemia mutations within different districts of Basrah. In addition the frequency of these mutations differ from those detected in other parts of Iraq and neighboring countries and signifies the need for future studies to detect mutations that were not iden ...
Mrs. Paparella/ Living Environment Genetics Essential Questions
... base order: AAGTTCAGAAT (for example) which determines the order of amino acids that will be brought to the ribosome to make the protein in the process of protein synthesis. 11. What are the steps to protein synthesis? 1. DNA is transcribed into mRNA (messenger RNA) in the nucleus. A-->U; G-->C; T-- ...
... base order: AAGTTCAGAAT (for example) which determines the order of amino acids that will be brought to the ribosome to make the protein in the process of protein synthesis. 11. What are the steps to protein synthesis? 1. DNA is transcribed into mRNA (messenger RNA) in the nucleus. A-->U; G-->C; T-- ...
From Genetic Code to Protein Structure Worksheet
... In this activity you will explore the relationship between the codons and the shape of the protein. It is important to think about what this model shows, as well as what of the translation and transcription process it is not representing when answering the questions. 1. Open the From Genetic Code to ...
... In this activity you will explore the relationship between the codons and the shape of the protein. It is important to think about what this model shows, as well as what of the translation and transcription process it is not representing when answering the questions. 1. Open the From Genetic Code to ...
High carriers frequency of an apparently ancient founder mutation p
... mutation (p.TyrY322X) was detected in carriers in Christian Arabs from all over the Northern part of Israel. Moreover, the same mutation was detected in two CS Australian patients originally from Lebanon [Laugel et al., 2010]. The Israeli Christian Arab community originated, in part from Lebanon, an ...
... mutation (p.TyrY322X) was detected in carriers in Christian Arabs from all over the Northern part of Israel. Moreover, the same mutation was detected in two CS Australian patients originally from Lebanon [Laugel et al., 2010]. The Israeli Christian Arab community originated, in part from Lebanon, an ...
NCEA Level 2 Biology (91159) 2015
... Phenotype is the observable physical / characteristics of an organism. Genotype is the set of alleles in our DNA, which is responsible for a particular trait an individual possesses. Biologists use yarrow plants that have identical genotypes because if there are any changes to their phenotype, it ca ...
... Phenotype is the observable physical / characteristics of an organism. Genotype is the set of alleles in our DNA, which is responsible for a particular trait an individual possesses. Biologists use yarrow plants that have identical genotypes because if there are any changes to their phenotype, it ca ...
Genetics Review Sheet
... Resources: Class notes, Flow Chart, practice notes from sentence activity. Outline the process of protein synthesis- what are the steps that occur? 1. DNA “unzips” in the nucleus. 2. mRNA copies the DNA code into its own unique language (U’s instead of T’s). It then takes that “message” out of the n ...
... Resources: Class notes, Flow Chart, practice notes from sentence activity. Outline the process of protein synthesis- what are the steps that occur? 1. DNA “unzips” in the nucleus. 2. mRNA copies the DNA code into its own unique language (U’s instead of T’s). It then takes that “message” out of the n ...
Document
... (1) There is more polymorphism in introns than in exons. (2) In the exons, there is much more polymorphism in DNA sequence than in amino acid sequence. (4) The left end of exon 4 is an exception. The F/S site is polymorphic, and regions close to it on both sides have a higher polymorphism than other ...
... (1) There is more polymorphism in introns than in exons. (2) In the exons, there is much more polymorphism in DNA sequence than in amino acid sequence. (4) The left end of exon 4 is an exception. The F/S site is polymorphic, and regions close to it on both sides have a higher polymorphism than other ...
Somatic point mutations in the p53 gene of human tumors and cell
... Mutations that are single base transitions at CpG dinucleotides, i.e. CpG→TpG or CpG→CpA are designated by ‘yes’. If there is no entry the mutation does not fall into this category. Column L Chain terminating mutations due to single base substitutions are designated by ‘(three letter amino acid abbr ...
... Mutations that are single base transitions at CpG dinucleotides, i.e. CpG→TpG or CpG→CpA are designated by ‘yes’. If there is no entry the mutation does not fall into this category. Column L Chain terminating mutations due to single base substitutions are designated by ‘(three letter amino acid abbr ...
Inheritance - Perth Grammar
... Genetic information is passed on to offspring by sex cells produced by the parents. Sex cells are also called gametes. State the difference in chromosome sets between a gamete and a ‘normal’ body cell. Gamete=____ set(s) ‘Normal’ body cell _____ set(s) Draw what happens at fertilisation in terms of ...
... Genetic information is passed on to offspring by sex cells produced by the parents. Sex cells are also called gametes. State the difference in chromosome sets between a gamete and a ‘normal’ body cell. Gamete=____ set(s) ‘Normal’ body cell _____ set(s) Draw what happens at fertilisation in terms of ...
DNA Mismatch Repair in Endometrial Cancers
... MSI Target Genes (where is the meat?) • MMR defects in colorectal cancer are associated with mutations in “driver” genes – strand slippage mutation in TGFRB2 are common in MSI+ colorectal cancers – TGFRB2 mutations seen in tumors with normal MMR (MSS) – germline mutation associated with risk for co ...
... MSI Target Genes (where is the meat?) • MMR defects in colorectal cancer are associated with mutations in “driver” genes – strand slippage mutation in TGFRB2 are common in MSI+ colorectal cancers – TGFRB2 mutations seen in tumors with normal MMR (MSS) – germline mutation associated with risk for co ...
CP Biology Chapter 8 Structure of DNA notes
... DNA double helix, and both involve large enzymes called polymerases. But the end results of the two processes are very different. Replication makes a copy of DNA and transcription makes RNA molecules. Another difference is that replication happens only once during the cell cycle. Transcription can h ...
... DNA double helix, and both involve large enzymes called polymerases. But the end results of the two processes are very different. Replication makes a copy of DNA and transcription makes RNA molecules. Another difference is that replication happens only once during the cell cycle. Transcription can h ...
mutation - UMDBIO101SUMMER2012
... • in some cases, particular mutant alleles have become more common in human populations and produce harmful effects called genetic disorders ...
... • in some cases, particular mutant alleles have become more common in human populations and produce harmful effects called genetic disorders ...
Nonsense-suppressing mutation causes addition of amino acid at
... All living organisms use same basic genetic code Translational systems can use mRNA from another organism to generate protein Comparisons of DNA and protein sequence reveal perfect correspondence between codons and amino acids among all organisms ...
... All living organisms use same basic genetic code Translational systems can use mRNA from another organism to generate protein Comparisons of DNA and protein sequence reveal perfect correspondence between codons and amino acids among all organisms ...
Frameshift mutation

A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon (""UAA"", ""UGA"" or ""UAG"") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likely not be functional.Frameshift mutations are apparent in severe genetic diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Cystic Fibrosis; they increase susceptibility to certain cancers and classes of familial hypercholesterolaemia; in 1997, a frameshift mutation was linked to resistance to infection by the HIV retrovirus. Frameshift mutations have been proposed as a source of biological novelty, as with the alleged creation of nylonase, however, this interpretation is controversial. A study by Negoro et al (2006) found that a frameshift mutation was unlikely to have been the cause and that rather a two amino acid substitution in the catalytic cleft of an ancestral esterase amplified Ald-hydrolytic activity.