Chapter 5: Digestive System - respiratorytherapyfiles.net
... is divided into a small upper pouch and a much larger lower "remnant" pouch and then the small intestine is rearranged to connect to both. ...
... is divided into a small upper pouch and a much larger lower "remnant" pouch and then the small intestine is rearranged to connect to both. ...
Anatomy For Reiki
... While an extensive understanding of anatomy is not necessary for Reiki practitioners, there are times when a basic knowledge of the major organs of the body is helpful, and even necessary. These include when the client has a condition or illness involving a specific organ(s) that needs treatment or ...
... While an extensive understanding of anatomy is not necessary for Reiki practitioners, there are times when a basic knowledge of the major organs of the body is helpful, and even necessary. These include when the client has a condition or illness involving a specific organ(s) that needs treatment or ...
The digestive system
... stomach you go down to the small intestine where it is 6 meters and 20 feet long. The food goes down to the large intestine where the colon is when you. ...
... stomach you go down to the small intestine where it is 6 meters and 20 feet long. The food goes down to the large intestine where the colon is when you. ...
Quiz #3 - Digestive Physiology
... 2. List the substances found in saliva that help protect/heal us. 3. List the 2 commonly ingested substances that can be absorbed directly from stomach into the blood. 4. Your large intestine bacteria produce vitamins ______ and ______ to help you. 5. Describe a cleft palate and the serious problems ...
... 2. List the substances found in saliva that help protect/heal us. 3. List the 2 commonly ingested substances that can be absorbed directly from stomach into the blood. 4. Your large intestine bacteria produce vitamins ______ and ______ to help you. 5. Describe a cleft palate and the serious problems ...
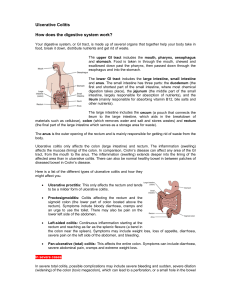
Ulcerative Colitis How does the digestive system work?
... the colon near the spleen). Symptoms may include weight loss, loss of appetite, diarrhoea, severe pain on the left side of the abdomen, and bleeding. ...
... the colon near the spleen). Symptoms may include weight loss, loss of appetite, diarrhoea, severe pain on the left side of the abdomen, and bleeding. ...
FIBERPLUS Dietary fiber and good health
... Inulin help in gastrointestinal function regulation. It help to proliferate bifidobacteria in the human body which can suppress the growth of intestinal salmonella and spoilage bacteria, promotes intestinal peristalsis, prevention and treatment of constipation. ...
... Inulin help in gastrointestinal function regulation. It help to proliferate bifidobacteria in the human body which can suppress the growth of intestinal salmonella and spoilage bacteria, promotes intestinal peristalsis, prevention and treatment of constipation. ...
Intestinal Obstruction
... • Def. :- It is a congenital agangliosis of the intestine which result of disordered emberyogenesis involving the myenteric nervous system . • Etiology :- Lack of migratory nerve cells to develop . • Esophagus 6th week . • Transverse colon 8th week . • Rectum 12th week . • Incidence :- 1 per 5000 li ...
... • Def. :- It is a congenital agangliosis of the intestine which result of disordered emberyogenesis involving the myenteric nervous system . • Etiology :- Lack of migratory nerve cells to develop . • Esophagus 6th week . • Transverse colon 8th week . • Rectum 12th week . • Incidence :- 1 per 5000 li ...
1. Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides. 2. 20
... 18. HCl, pepsin/pepsinogen, mucous 19. Pepsin 20. Duodenum, jejenum, illeum 21. Pancreatic, bile 22. villi 23. To increase surface area and absorption 24. Jujenum 25. 20 to 21 ft. 26. illeoceccal valve. 27. messentary 28. rectum 29. Chief 30. Lacteal 31. Cecum, ascending, transverse, descending, sig ...
... 18. HCl, pepsin/pepsinogen, mucous 19. Pepsin 20. Duodenum, jejenum, illeum 21. Pancreatic, bile 22. villi 23. To increase surface area and absorption 24. Jujenum 25. 20 to 21 ft. 26. illeoceccal valve. 27. messentary 28. rectum 29. Chief 30. Lacteal 31. Cecum, ascending, transverse, descending, sig ...
COMMON GASTROINTESTINAL PROBLEMS
... most are not. However, almost all colon cancer does begin as a polyp. Therefore, by removing polyps early the chances of it growing into colon cancer are eliminated. People with a higher risk for developing polyps are anyone over age 50, those who have had polyps previously or those who have a famil ...
... most are not. However, almost all colon cancer does begin as a polyp. Therefore, by removing polyps early the chances of it growing into colon cancer are eliminated. People with a higher risk for developing polyps are anyone over age 50, those who have had polyps previously or those who have a famil ...
Dr. Hendershot OMM Lecture – Abdominal Exam Objectives: Describe
... bright red blood (hematochezia) – tumors, diverticular disease, ulcerative colitis. ...
... bright red blood (hematochezia) – tumors, diverticular disease, ulcerative colitis. ...
File
... Fistula- an abnormal opening or passage between two internal organs or from an internal organ to the surface of the body Gastritis/gastroenteritis- inflammation of the gastric mucosa Hematic coma- coma that can occur in severe cases of liver disease Hiatal hernia- protrusion of part of the stomach t ...
... Fistula- an abnormal opening or passage between two internal organs or from an internal organ to the surface of the body Gastritis/gastroenteritis- inflammation of the gastric mucosa Hematic coma- coma that can occur in severe cases of liver disease Hiatal hernia- protrusion of part of the stomach t ...
Common GI Problems - Mercer County Surgery Center
... most are not. However, almost all colon cancer does begin as a polyp. Therefore, by removing polyps early the chances of it growing into colon cancer are eliminated. People with a higher risk for developing polyps are anyone over age 50, those who have had polyps previously or those who have a famil ...
... most are not. However, almost all colon cancer does begin as a polyp. Therefore, by removing polyps early the chances of it growing into colon cancer are eliminated. People with a higher risk for developing polyps are anyone over age 50, those who have had polyps previously or those who have a famil ...
File #: Information on Preparing for a Colonoscopy Last Name: First
... Colonoscopies and polyp removal are safe procedures. There can, however, be complications. Bleeding: Bleeding may occur after a biopsy or polyp removal (1 or 2 possible cases/100). Bleeding will generally be mild and stop on its own. Heavy bleeding is rare. It if does occur, cauterization may be u ...
... Colonoscopies and polyp removal are safe procedures. There can, however, be complications. Bleeding: Bleeding may occur after a biopsy or polyp removal (1 or 2 possible cases/100). Bleeding will generally be mild and stop on its own. Heavy bleeding is rare. It if does occur, cauterization may be u ...
Chapter 37 Notes Pages
... stomach, and upper duodenum through an optic scope. A sigmoidoscopy examines the distal sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal through a flexible or rigid sigmoidoscope. UGI series involves fluoroscopic examination of the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine after ingestion of barium sulfate. • In ...
... stomach, and upper duodenum through an optic scope. A sigmoidoscopy examines the distal sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal through a flexible or rigid sigmoidoscope. UGI series involves fluoroscopic examination of the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine after ingestion of barium sulfate. • In ...
in-depth article about APC I1307K
... Many patients with colorectal cancer experience no symptoms in the early stage of their disease. In fact, many people have no symptoms until the disease is quite advanced. Therefore, routine colorectal screening and an appreciation of risk factors are extremely important. Since many of the symptoms ...
... Many patients with colorectal cancer experience no symptoms in the early stage of their disease. In fact, many people have no symptoms until the disease is quite advanced. Therefore, routine colorectal screening and an appreciation of risk factors are extremely important. Since many of the symptoms ...
Document
... Benign – adenomas, adenomatous polyps Malignant – adenocarcinoma, carcinoid tumor Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) – benign to ...
... Benign – adenomas, adenomatous polyps Malignant – adenocarcinoma, carcinoid tumor Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) – benign to ...
File - Jillian M. O`Neil
... Fistula- an abnormal opening or passage between two internal organs or from an internal organ to the surface of the body Gastritis/gastroenteritis- inflammation of the gastric mucosa Hematic coma- coma that can occur in severe cases of liver disease Hiatal hernia- protrusion of part of the stomach t ...
... Fistula- an abnormal opening or passage between two internal organs or from an internal organ to the surface of the body Gastritis/gastroenteritis- inflammation of the gastric mucosa Hematic coma- coma that can occur in severe cases of liver disease Hiatal hernia- protrusion of part of the stomach t ...
The Digestive System
... which stool (feces) leaves the body. It is formed from surface areas of the surface of the body. This includes skin and part of the intestine. The anus is lined with an external skin and a muscular ring called the anal sphincter keeps it closed. ...
... which stool (feces) leaves the body. It is formed from surface areas of the surface of the body. This includes skin and part of the intestine. The anus is lined with an external skin and a muscular ring called the anal sphincter keeps it closed. ...
NewYork-Presbyterian Digestive Disease Services
... image processing and enhanced optics. It is improving the outcomes of GI surgical patients and speeding their recovery from conditions such as GERD, gallbladder disease, and benign and malignant colon and rectal disease. • Our surgeons also perform endoscopic sewing (endocinch) and radiofrequency tr ...
... image processing and enhanced optics. It is improving the outcomes of GI surgical patients and speeding their recovery from conditions such as GERD, gallbladder disease, and benign and malignant colon and rectal disease. • Our surgeons also perform endoscopic sewing (endocinch) and radiofrequency tr ...
Colon cancer: should I be screened?
... You'll be sent for a colonoscopy if you get a positive result from any of the other screening tests. Colonoscopy is a very thorough test for cancer, because it can see the full length of the colon and rectum. If the colonoscopy finds any polyps, these can be removed during the colonoscopy. If the co ...
... You'll be sent for a colonoscopy if you get a positive result from any of the other screening tests. Colonoscopy is a very thorough test for cancer, because it can see the full length of the colon and rectum. If the colonoscopy finds any polyps, these can be removed during the colonoscopy. If the co ...
Conditions presenting with abdominal pain (2)
... and tenesmus (painful straining at stool). The clinical course is marked by exacerbations and remissions, which may occur spontaneously or in response to treatment changes or intercurrent illnesses. ...
... and tenesmus (painful straining at stool). The clinical course is marked by exacerbations and remissions, which may occur spontaneously or in response to treatment changes or intercurrent illnesses. ...
Colonoscopy

Colonoscopy or coloscopy is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It can provide a visual diagnosis (e.g. ulceration, polyps) and grants the opportunity for biopsy or removal of suspected colorectal cancer lesions. Colonoscopy can remove polyps as small as one millimetre or less. Once polyps are removed, they can be studied with the aid of a microscope to determine if they are precancerous or not. It takes 15 years or fewer for a polyp to turn cancerous.Colonoscopy is similar to sigmoidoscopy—the difference being related to which parts of the colon each can examine. A colonoscopy allows an examination of the entire colon (1200–1500 mm in length). A sigmoidoscopy allows an examination of the distal portion (about 600 mm) of the colon, which may be sufficient because benefits to cancer survival of colonoscopy have been limited to the detection of lesions in the distal portion of the colon.A sigmoidoscopy is often used as a screening procedure for a full colonoscopy, often done in conjunction with a fecal occult blood test (FOBT). About 5% of these screened patients are referred to colonoscopy.Virtual colonoscopy, which uses 2D and 3D imagery reconstructed from computed tomography (CT) scans or from nuclear magnetic resonance (MR) scans, is also possible, as a totally non-invasive medical test, although it is not standard and still under investigation regarding its diagnostic abilities. Furthermore, virtual colonoscopy does not allow for therapeutic maneuvers such as polyp/tumour removal or biopsy nor visualization of lesions smaller than 5 millimeters. If a growth or polyp is detected using CT colonography, a standard colonoscopy would still need to be performed. Additionally, surgeons have lately been using the term pouchoscopy to refer to a colonoscopy of the ileo-anal pouch.