blood
... •large acidophilic granules -appear pink (or red) •nucleus has two lobes connected by a band of nuclear material. (telephone receiver) •granules contain digestive enzymes that are particularly effective against parasitic worms in their larval form. •Phagocyte: antigen - antibody complexes. •These ce ...
... •large acidophilic granules -appear pink (or red) •nucleus has two lobes connected by a band of nuclear material. (telephone receiver) •granules contain digestive enzymes that are particularly effective against parasitic worms in their larval form. •Phagocyte: antigen - antibody complexes. •These ce ...
Cell Structure and Function - Red Clay Secondary Science Wiki
... 2. Use forceps to peel off a small section of the thin layer, and lay it flat on a microscope slide. Discard the rest of the onion piece. Trim the piece with a scalpel if necessary, and smooth any wrinkles. 3. Add 1 or 2 drops of Lugol’s iodine solution and a cover slip. 4. Examine the first slide w ...
... 2. Use forceps to peel off a small section of the thin layer, and lay it flat on a microscope slide. Discard the rest of the onion piece. Trim the piece with a scalpel if necessary, and smooth any wrinkles. 3. Add 1 or 2 drops of Lugol’s iodine solution and a cover slip. 4. Examine the first slide w ...
Name
... 9. What do you call an animal that lives off of another animal usually harming the animal it is living on? ________________________________ 10. What do you call the interaction where one organism kills and eats another organism for food? ________________________________ 11. What do you call the livi ...
... 9. What do you call an animal that lives off of another animal usually harming the animal it is living on? ________________________________ 10. What do you call the interaction where one organism kills and eats another organism for food? ________________________________ 11. What do you call the livi ...
No Slide Title - Effingham County Schools
... sponges – simplest of all animals A. Body Plan – asymmetrical, pores all over body with large hole on top called osculum where water is pumped through, Have no mouth or gut, Have no tissues or organ systems, Simple functions are carried out by a few specialized cells B. Protection: skeleton of spicu ...
... sponges – simplest of all animals A. Body Plan – asymmetrical, pores all over body with large hole on top called osculum where water is pumped through, Have no mouth or gut, Have no tissues or organ systems, Simple functions are carried out by a few specialized cells B. Protection: skeleton of spicu ...
- PlanbookConnect
... b. Frontal-along the long axis (anterior & posterior) c. Sagittal-runs along the long axis (mid & parasagittal) (right & left) 2. Body Cavities-protect internal organs and allow them to change shape. a. Dorsal Body Cavities-refers to the back 1. Cranial Cavity 2. Spinal Cavity b. Ventral Body Caviti ...
... b. Frontal-along the long axis (anterior & posterior) c. Sagittal-runs along the long axis (mid & parasagittal) (right & left) 2. Body Cavities-protect internal organs and allow them to change shape. a. Dorsal Body Cavities-refers to the back 1. Cranial Cavity 2. Spinal Cavity b. Ventral Body Caviti ...
Slide 1 - SFP Online!
... Earthworms, squids, octopuses, and all vertebrates have closed circulatory systems. ...
... Earthworms, squids, octopuses, and all vertebrates have closed circulatory systems. ...
3.4 Prenatal Development
... Eventually the plasma membrane becomes weak enough that one sperm can penetrate the egg. Immediately following this penetration, the egg forms a barrier to prevent other sperm from entering the now-fertilized egg. ...
... Eventually the plasma membrane becomes weak enough that one sperm can penetrate the egg. Immediately following this penetration, the egg forms a barrier to prevent other sperm from entering the now-fertilized egg. ...
Reproduction and Development - Mahopac Central School District
... a. this joining of sex cells is called fertilization b. a fertilized egg is called a zygote and contains a full set of genetic information c. fertilization in some animal species takes place outside the body – this is called external fertilization 1) salmon and frogs are examples d. fertilization is ...
... a. this joining of sex cells is called fertilization b. a fertilized egg is called a zygote and contains a full set of genetic information c. fertilization in some animal species takes place outside the body – this is called external fertilization 1) salmon and frogs are examples d. fertilization is ...
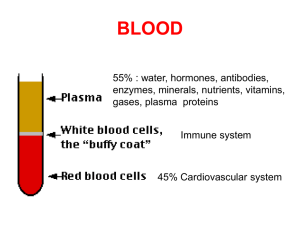
Function of the blood
... like erythropoietin, which are responsible for stimulating the production of erythrocytes, are transported in plasma. Other hormones like testosterone, oestrogen, ADH, thyroxin, adrenaline, insulin, FSH and LH are also transported in the plasma. The red blood cells are produced in a complex process ...
... like erythropoietin, which are responsible for stimulating the production of erythrocytes, are transported in plasma. Other hormones like testosterone, oestrogen, ADH, thyroxin, adrenaline, insulin, FSH and LH are also transported in the plasma. The red blood cells are produced in a complex process ...
Levels of Organization - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... body. Blood, fat, ligaments, cartilage, bones, and tendons are all connective tissues. ...
... body. Blood, fat, ligaments, cartilage, bones, and tendons are all connective tissues. ...
Review PPT – Life Science – Cells and Human
... Cells build together to make tissues • The process by which cells become different types of cells is called cell differentiation • In multicellular organisms, similar types of cells are organized together into groups. • Tissues are groups of similar types of cells that work together to carry out a ...
... Cells build together to make tissues • The process by which cells become different types of cells is called cell differentiation • In multicellular organisms, similar types of cells are organized together into groups. • Tissues are groups of similar types of cells that work together to carry out a ...
Architectural Pattern of an animal
... • Coelom - major innovation in bilaterally symmetric animals • Tube within a tube arrangement ...
... • Coelom - major innovation in bilaterally symmetric animals • Tube within a tube arrangement ...
Study Guide Cells Unit Test
... help prevent infection and further injury. But what if there were such a thing as a living bandage that actually helped your body heal? It sounds like science fiction, but it’s not! The Main Factor An injury to the skin, such as a scraped knee, triggers skin cells to produce and release a steady str ...
... help prevent infection and further injury. But what if there were such a thing as a living bandage that actually helped your body heal? It sounds like science fiction, but it’s not! The Main Factor An injury to the skin, such as a scraped knee, triggers skin cells to produce and release a steady str ...
Module 1 themes of life review
... hydrogen bond. In other words water likes to stick to itself. Water sticking to water is called cohesion. Water sticking to something else is called adhesion. 5. In the diagram to the right use dotted lines to draw in the bonds that form between water molecules. 6. What is the name of this type of b ...
... hydrogen bond. In other words water likes to stick to itself. Water sticking to water is called cohesion. Water sticking to something else is called adhesion. 5. In the diagram to the right use dotted lines to draw in the bonds that form between water molecules. 6. What is the name of this type of b ...
Bio01 Intro
... cells for tissue growth, repair, or replacement. The formation of new cells for the production of a new individual organism (i.e. through fertilization of an ovum by a sperm cell). ...
... cells for tissue growth, repair, or replacement. The formation of new cells for the production of a new individual organism (i.e. through fertilization of an ovum by a sperm cell). ...
Reproduction and Development
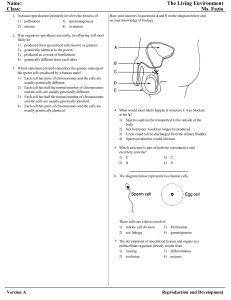
... 3) one cell with a replicated set of homologous chromosomes 4) two cells with only one chromosome from each set of homologous chromosomes 14. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents the human female reproductive system. ...
... 3) one cell with a replicated set of homologous chromosomes 4) two cells with only one chromosome from each set of homologous chromosomes 14. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents the human female reproductive system. ...
Chapter 43
... Tissues are groups of cells of a single type and function • Early in development, the cells of the growing embryo differentiate into the three fundamental embryonic tissues called germ layers -endoderm -mesoderm -ectoderm • Four principal kinds of tissues in adult vertebrates -epithelial, connectiv ...
... Tissues are groups of cells of a single type and function • Early in development, the cells of the growing embryo differentiate into the three fundamental embryonic tissues called germ layers -endoderm -mesoderm -ectoderm • Four principal kinds of tissues in adult vertebrates -epithelial, connectiv ...
Human Systems: Body Organization
... • Cells form tissues (group of same type of cells performing same function) ...
... • Cells form tissues (group of same type of cells performing same function) ...
The Blood Functions: - transport nutrients, gases, wastes (urea
... - function = filter blood of damaged cells and pathogens - also stores and matures lymphocytes. How does lymph flow? 1) lymph vessels contain valves to prevent backflow = lymph flows only in one direction: to the heart 2) contraction of skeletal muscles and osmotic pressure cause lymph to flow from ...
... - function = filter blood of damaged cells and pathogens - also stores and matures lymphocytes. How does lymph flow? 1) lymph vessels contain valves to prevent backflow = lymph flows only in one direction: to the heart 2) contraction of skeletal muscles and osmotic pressure cause lymph to flow from ...
simple animals
... organization of the animal’s tissues • Tissues are collections of specialized cells isolated from other tissues by membranous layers • During development, three germ layers give rise to the tissues and organs of the animal embryo ...
... organization of the animal’s tissues • Tissues are collections of specialized cells isolated from other tissues by membranous layers • During development, three germ layers give rise to the tissues and organs of the animal embryo ...
BY 124 SI Test II, Session I I. Animal Diversity 1. What are some
... so only know the details presented in the book for this chapter ...
... so only know the details presented in the book for this chapter ...
Cardiovascular System
... White cells, or leukocytes, exist in variable numbers and types but make up a very small part of blood's volume--normally only about 1% in healthy people. Leukocytes are not limited to blood. They occur elsewhere in the body as well, most notably in the spleen, liver, and lymph glands. Most are prod ...
... White cells, or leukocytes, exist in variable numbers and types but make up a very small part of blood's volume--normally only about 1% in healthy people. Leukocytes are not limited to blood. They occur elsewhere in the body as well, most notably in the spleen, liver, and lymph glands. Most are prod ...
Section 1: Characteristics of Animals
... In vertebrates, segments are not visible externally, but there is evidence of segmentation in a vertebrate embryo. ...
... In vertebrates, segments are not visible externally, but there is evidence of segmentation in a vertebrate embryo. ...
101 Things to Know About the
... occurs in two distinct stages and is sometimes referred to as reduction division (I know, a math flashback, AAUUGGHHHH!!!!!). In Meiosis 1, each single stranded chromosome replicates and forms sister chromatids. These sister chromatids join together, a process called synapsis, having a total of 4n t ...
... occurs in two distinct stages and is sometimes referred to as reduction division (I know, a math flashback, AAUUGGHHHH!!!!!). In Meiosis 1, each single stranded chromosome replicates and forms sister chromatids. These sister chromatids join together, a process called synapsis, having a total of 4n t ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.