ECOLOGY SPRING 2009 - Florida International University
... Parazoans lack tissues, organs and a definite symmetry -However, they have complex multicellularity Sponges, phylum Porifera, are parazoans -Include marine and freshwater species -Larval sponges are free-swimming, but adults are ...
... Parazoans lack tissues, organs and a definite symmetry -However, they have complex multicellularity Sponges, phylum Porifera, are parazoans -Include marine and freshwater species -Larval sponges are free-swimming, but adults are ...
Chapter 28: The Animal Kingdom
... divide it into dorsal and ventral parts, and transverse sections cross the body and divide it into anterior and posterior parts E. Animals can be grouped according to type of body cavity 1. During embryological development, three germ layers develop in triploblastic organisms (cnidarians and ctenoph ...
... divide it into dorsal and ventral parts, and transverse sections cross the body and divide it into anterior and posterior parts E. Animals can be grouped according to type of body cavity 1. During embryological development, three germ layers develop in triploblastic organisms (cnidarians and ctenoph ...
body systems - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... Connective tissue (cartilage, bone, ligaments, tendons) Spongy bone tissue (Bone marrow) ...
... Connective tissue (cartilage, bone, ligaments, tendons) Spongy bone tissue (Bone marrow) ...
Outline 6: Cnidaria 1
... Coral c) Sea pansies d) Gorgonians D. Evolutionary relationships (briefly) ...
... Coral c) Sea pansies d) Gorgonians D. Evolutionary relationships (briefly) ...
Word Bank: diaphragm capillaries oxygen ATP alveoli blood CO 2
... A) All humans (and most other organisms) begin life as a ___________cell. 1. This single cell is called a_____________. 2. The nucleus of this cell has _______the genes needed to become a complete organism. B) Humans grow as a result of ___________cell division). 1. This quickly increases the number ...
... A) All humans (and most other organisms) begin life as a ___________cell. 1. This single cell is called a_____________. 2. The nucleus of this cell has _______the genes needed to become a complete organism. B) Humans grow as a result of ___________cell division). 1. This quickly increases the number ...
Human Reproduction
... responsible for the physical characteristics in males such as facial hair, a deep voice, and developed muscles. ...
... responsible for the physical characteristics in males such as facial hair, a deep voice, and developed muscles. ...
Chapter 2.1 Invertebrates Study Guide
... A sponge uses ________ to pull water in and releases water out through _____________. (an osculum or pores) Cnidarians have __________ symmetry and flatworms have ___________ symmetry. ...
... A sponge uses ________ to pull water in and releases water out through _____________. (an osculum or pores) Cnidarians have __________ symmetry and flatworms have ___________ symmetry. ...
Section 29–1 Invertebrate Evolution (pages 745–750)
... 11. As larger and more complex animals evolved, in what ways did specialized cells join together? Specialized cells joined together to form tissues, organs, and organ systems that work together to carry out complex functions. ...
... 11. As larger and more complex animals evolved, in what ways did specialized cells join together? Specialized cells joined together to form tissues, organs, and organ systems that work together to carry out complex functions. ...
Document
... iii. lines internal organs, ducts, and tubes iv. glands are made up from this type of tissue v. ex. lines heart chamber to prevent fluid leakage, skin C. connective tissue: i. holds organs in place ii. binds different parts of the body together iii. keeps organs flexible, but strong by secreting str ...
... iii. lines internal organs, ducts, and tubes iv. glands are made up from this type of tissue v. ex. lines heart chamber to prevent fluid leakage, skin C. connective tissue: i. holds organs in place ii. binds different parts of the body together iii. keeps organs flexible, but strong by secreting str ...
Nicole`s teacher asked her to make a diagram of a good chain for a
... the arms and legs. Cardiac Muscle cells move blood into and out of the heart. Smoother muscle cells move food through the digestive system. While each of the muscle cells performs a different job, they function in a similar way. What makes muscle cells different from other cells in the body. ...
... the arms and legs. Cardiac Muscle cells move blood into and out of the heart. Smoother muscle cells move food through the digestive system. While each of the muscle cells performs a different job, they function in a similar way. What makes muscle cells different from other cells in the body. ...
Stem Cell Line Glossary Adult stem cells: Also known as somatic
... A flat, transparent dish capable of holding some sort of liquid (medium) on which cells are grown. Differentiation: The ability of a cell to change from one type to another. A stem cell can differentiate into other types of cells, such as a mesenchymal stem cell changing into an osteocyte, or bone c ...
... A flat, transparent dish capable of holding some sort of liquid (medium) on which cells are grown. Differentiation: The ability of a cell to change from one type to another. A stem cell can differentiate into other types of cells, such as a mesenchymal stem cell changing into an osteocyte, or bone c ...
Unit 9 - Phylum Cnidaria – Guided Notes Introduction Body forms
... o Largest organism to move this way o No cnidocytes instead ___________________ which secrete a sticky substance that binds their prey o Colloblasts normally located on __________ tentacles o Have a sensory structure called an apical organ at one end of their body, allows it to sense its orientation ...
... o Largest organism to move this way o No cnidocytes instead ___________________ which secrete a sticky substance that binds their prey o Colloblasts normally located on __________ tentacles o Have a sensory structure called an apical organ at one end of their body, allows it to sense its orientation ...
Primitive gut
... associated glands of the gastrointestinal tract develop from endoderm • The connective tissue, muscle tissue and mesothelium are derived from splanchnic mesoderm • The enteric nervous system develops from neural crest ...
... associated glands of the gastrointestinal tract develop from endoderm • The connective tissue, muscle tissue and mesothelium are derived from splanchnic mesoderm • The enteric nervous system develops from neural crest ...
From a Cell to an Organism Levels of Organization Life’s Organization
... Cell Differentiation Remember that all cells in a multicellular organism come from one cell, a fertilized egg. Cell division starts quickly after fertilization. The first cells made can become any type of cell, such as a muscle cell, a nerve cell, or a blood cell. The process by which cells become d ...
... Cell Differentiation Remember that all cells in a multicellular organism come from one cell, a fertilized egg. Cell division starts quickly after fertilization. The first cells made can become any type of cell, such as a muscle cell, a nerve cell, or a blood cell. The process by which cells become d ...
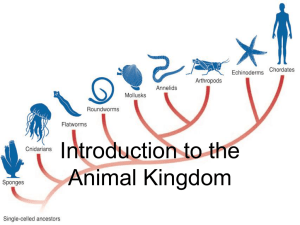
Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
... specialization and internal body organization, bilateral body symmetry, a front end, or head, with sense organs, and a body cavity. ...
... specialization and internal body organization, bilateral body symmetry, a front end, or head, with sense organs, and a body cavity. ...
The Tissue Level of Organization
... Covers body surfaces, lines cavities and tubular structures ...
... Covers body surfaces, lines cavities and tubular structures ...
Chapter 14 The reproductive systems
... Connective tissue: the most prominent type of tissue in the body; this tissue provides support. Corpus luteum: a yellowish body found in the ovary when a follicle has discharged its secondary oocyte. Distal: further away from the attachment of a limb to the trunk of the body. Endometrium: the mucous ...
... Connective tissue: the most prominent type of tissue in the body; this tissue provides support. Corpus luteum: a yellowish body found in the ovary when a follicle has discharged its secondary oocyte. Distal: further away from the attachment of a limb to the trunk of the body. Endometrium: the mucous ...
Embryology Notes
... Development Initial development in fallopian tubes Implantation in the uterus occurs after ~ a week Zygote divides through mitosis in a process called cleavage. Once the zygote divides, it is known as an embryo. The cells continue to divide until a ball of cells forms. This is called a blastula. ...
... Development Initial development in fallopian tubes Implantation in the uterus occurs after ~ a week Zygote divides through mitosis in a process called cleavage. Once the zygote divides, it is known as an embryo. The cells continue to divide until a ball of cells forms. This is called a blastula. ...
Goal 6: Cell Theory Review Guide
... 1. A cell is _the basic unit of structure and function in all organisms___. 2. Cells are too _small__ to be seen with the naked eye. What important “tool” or instrument needed to be discovered/invented before we could learn what we know about cells so far? microscope 3. Summarize the three statement ...
... 1. A cell is _the basic unit of structure and function in all organisms___. 2. Cells are too _small__ to be seen with the naked eye. What important “tool” or instrument needed to be discovered/invented before we could learn what we know about cells so far? microscope 3. Summarize the three statement ...
Chapter 19: The Animal Body and How It Moves
... •Two advantages result from embryonic segmentation –1. Each segment may develop a more or less complete set of adult organ systems –2. Locomotion is far more effective because of increased flexibility of movement ...
... •Two advantages result from embryonic segmentation –1. Each segment may develop a more or less complete set of adult organ systems –2. Locomotion is far more effective because of increased flexibility of movement ...
Moore 1 Timothy Moore Life Science: Semester 1 Assessment 22
... 32. Write a paragraph to compare plant and animal cells. Use the terms chloroplast, nucleus, cell wall, and mitochondria in your writing. Plant and animal cells are different. Plant cells have a rigid cell wall in addition to the cell membrane. Animal cells have only the cell membrane. Also, plants ...
... 32. Write a paragraph to compare plant and animal cells. Use the terms chloroplast, nucleus, cell wall, and mitochondria in your writing. Plant and animal cells are different. Plant cells have a rigid cell wall in addition to the cell membrane. Animal cells have only the cell membrane. Also, plants ...
Kingdom Protista
... body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues ...
... body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues ...
The Animal Kingdom
... symmetry. (Think of an orange.) 3. Organisms whose body parts are arranged along a longitudinal axis where right and left half are mirror images of each other exhibit bilaterial symmetry. (Think of a butterfly.) ...
... symmetry. (Think of an orange.) 3. Organisms whose body parts are arranged along a longitudinal axis where right and left half are mirror images of each other exhibit bilaterial symmetry. (Think of a butterfly.) ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.