Answers to Biology Unit Handout
... telophase and extends to the sides eventually forming a new cell wall. This splits the original parent cell into 2 daughter cells. 9. a) What are stem cells? How are they controversial? An unspecialized cell that can become any type of cell in the body. b) What is a meristem? Why is a meristem impor ...
... telophase and extends to the sides eventually forming a new cell wall. This splits the original parent cell into 2 daughter cells. 9. a) What are stem cells? How are they controversial? An unspecialized cell that can become any type of cell in the body. b) What is a meristem? Why is a meristem impor ...
Patterns_In_Nature
... Respiratory surfaces have a large surface area to maximise diffusion Respiratory surfaces have a good blood supply to carry oxygen to body cells Respiratory surfaces are thin so that gases can quickly move into the blood ...
... Respiratory surfaces have a large surface area to maximise diffusion Respiratory surfaces have a good blood supply to carry oxygen to body cells Respiratory surfaces are thin so that gases can quickly move into the blood ...
The Six Kingdoms - What are the general characteristics that
... of plants? ( page 175 - 181 ) 1. the assistance of animals (eg. bees) and wind in pollination 2. the presence of structures in plants specific to attracting certain animal pollinators whom the plants supply with food (ie. flowers - different color and shape flowers attract different types of pollina ...
... of plants? ( page 175 - 181 ) 1. the assistance of animals (eg. bees) and wind in pollination 2. the presence of structures in plants specific to attracting certain animal pollinators whom the plants supply with food (ie. flowers - different color and shape flowers attract different types of pollina ...
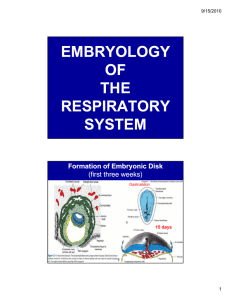
Embryology of the Respiratory System
... At 25 weeks the alveolar sacs give rise to primitive alveoli with cuboidal epithelium. By 26 weeks the alveoli have become vascularized. vascularized By this stage the production of surfactant has begun and the fetus might survive if born prematurely. ...
... At 25 weeks the alveolar sacs give rise to primitive alveoli with cuboidal epithelium. By 26 weeks the alveoli have become vascularized. vascularized By this stage the production of surfactant has begun and the fetus might survive if born prematurely. ...
1 Cellular Organization Objectives • Describe
... water and nutrients, tissue that uses the Sun’s energy to make sugar, and tissue that moves sugar to other parts of the plant. ...
... water and nutrients, tissue that uses the Sun’s energy to make sugar, and tissue that moves sugar to other parts of the plant. ...
The Human Immune System
... • Closely parallel veins • Located in almost all tissues and organs that have blood vessels • Lymph flow goes only in one direction-from body organs to the heart ...
... • Closely parallel veins • Located in almost all tissues and organs that have blood vessels • Lymph flow goes only in one direction-from body organs to the heart ...
OriginalArticle
... journey, which ends with the laying of the egg, a start has been made toward the formation of a visible embryo. Thus, before external incubation begins, the processes of cleavage and ectodermal formation are completed. When it is laid the embryonic area is represental by the familiar whitish disc to ...
... journey, which ends with the laying of the egg, a start has been made toward the formation of a visible embryo. Thus, before external incubation begins, the processes of cleavage and ectodermal formation are completed. When it is laid the embryonic area is represental by the familiar whitish disc to ...
Ch 4 study guide page 1
... ____________ The most abundant protein in dead epidermal structures such as hair and nails is melanin ____________ Sebum is an oily mixture of lipids, cholesterol, and cell fragments. ____________ The oldest epidermal cells in the epidermis are found in the stratum basale. ____________ The externall ...
... ____________ The most abundant protein in dead epidermal structures such as hair and nails is melanin ____________ Sebum is an oily mixture of lipids, cholesterol, and cell fragments. ____________ The oldest epidermal cells in the epidermis are found in the stratum basale. ____________ The externall ...
File
... Ciliary body – a thickened ring of tissue made up of smooth muscles bundles called ciliary muscles that surrounds the lens and controls its shape Suspensary ligaments – attach the lens to the ciliary ...
... Ciliary body – a thickened ring of tissue made up of smooth muscles bundles called ciliary muscles that surrounds the lens and controls its shape Suspensary ligaments – attach the lens to the ciliary ...
Special Senses
... using format at start of lab text. Weber/Rhine tuning fork test. 1. Question: Does sound remain centralized (normal) or lateralize to one side indicating _____? 2. Comparision of bone conduction and air conduction of sound waves pg. 283 ...
... using format at start of lab text. Weber/Rhine tuning fork test. 1. Question: Does sound remain centralized (normal) or lateralize to one side indicating _____? 2. Comparision of bone conduction and air conduction of sound waves pg. 283 ...
Chapter 32 - Workforce Solutions
... • Eumetazoa – have well-defined symmetry and well defined tissues and differentiation is irreversible ...
... • Eumetazoa – have well-defined symmetry and well defined tissues and differentiation is irreversible ...
Document
... What is our first line of defense? • SKIN!!!!!!! – Cuts and wounds are entry points What are the other entry points? ...
... What is our first line of defense? • SKIN!!!!!!! – Cuts and wounds are entry points What are the other entry points? ...
Animal Systems
... A _____________________ is sent from the brain to the target organ along a ____________________ neuron Neuron structure __________________: contains the nucleus; main part of the neuron __________________: many extension that receive stimulus and send it to the cell body __________: single exten ...
... A _____________________ is sent from the brain to the target organ along a ____________________ neuron Neuron structure __________________: contains the nucleus; main part of the neuron __________________: many extension that receive stimulus and send it to the cell body __________: single exten ...
ii. sycon body form - sponge wall appears folded
... • 3. sperm cells exit one sponge by osculum and enter another with incurrent water. they are trapped by choanocytes and put in vacuoles. • 4.sperm lose collar and flagella, become ameboid and transfer sperm to eggs ...
... • 3. sperm cells exit one sponge by osculum and enter another with incurrent water. they are trapped by choanocytes and put in vacuoles. • 4.sperm lose collar and flagella, become ameboid and transfer sperm to eggs ...
Animals
... Embryology • Embryology – early development • Zygote undergoes series of divisions to become a blastula • Blastula - Hollow ball of cells • Gastrula - Blastula folds on itself, forming a single opening (blastopore) and the gastrula. – Blastopore leads into a central tube that runs the length of the ...
... Embryology • Embryology – early development • Zygote undergoes series of divisions to become a blastula • Blastula - Hollow ball of cells • Gastrula - Blastula folds on itself, forming a single opening (blastopore) and the gastrula. – Blastopore leads into a central tube that runs the length of the ...
animal cells and tissues
... Thermoregulation in mammals: o The major control center is the hypothalamus o When too hot – thermoreceptors in the skin, blood vessels detect the heat – stimulate the heat-losing center of the hypothalamus – cause dilation in the peripheral (skin) blood vessels, production of sweat stimulated (swea ...
... Thermoregulation in mammals: o The major control center is the hypothalamus o When too hot – thermoreceptors in the skin, blood vessels detect the heat – stimulate the heat-losing center of the hypothalamus – cause dilation in the peripheral (skin) blood vessels, production of sweat stimulated (swea ...
Cells - TeacherWeb
... Living things have different levels of organization. The simplest level of organization is that of the cell. A group of cells with a similar function is called a tissue. Groups of tissues working together to perform a common function are called organs. An example of this would include the nervous, m ...
... Living things have different levels of organization. The simplest level of organization is that of the cell. A group of cells with a similar function is called a tissue. Groups of tissues working together to perform a common function are called organs. An example of this would include the nervous, m ...
Human Body Systems Power Point
... • System: Give the name • Main Job: one sentence description of the job of the system • Organs: list main organs ...
... • System: Give the name • Main Job: one sentence description of the job of the system • Organs: list main organs ...
Human Embryology and Natural Stem Cells iPS…..induced
... E. Blastocyst - embryo turns into a hollow sphere by days 5 - 6 Where does this all take place? Uterus (womb), Fallopian Tubes, Ovaries Fertilization occurs in the tube = day 1; first four days…..‘going down the tube’ Implantation on days 6-10; embryo implants in uterine wall . produces sprouts Pre ...
... E. Blastocyst - embryo turns into a hollow sphere by days 5 - 6 Where does this all take place? Uterus (womb), Fallopian Tubes, Ovaries Fertilization occurs in the tube = day 1; first four days…..‘going down the tube’ Implantation on days 6-10; embryo implants in uterine wall . produces sprouts Pre ...
What is an Animal? Chapter 25
... • Most have Sexual Reproduction • Egg + Sperm = Fertilization – Can be internal or external fertilization – Forms a single celled zygote – Undergoes cell division during cleavage to form two cells – Hermaphrodites – have both male and female reproductive parts ...
... • Most have Sexual Reproduction • Egg + Sperm = Fertilization – Can be internal or external fertilization – Forms a single celled zygote – Undergoes cell division during cleavage to form two cells – Hermaphrodites – have both male and female reproductive parts ...
Gastrulation COO
... 4) Delamination: splitting of a tissue into 2 or more parallel cellular layers ...
... 4) Delamination: splitting of a tissue into 2 or more parallel cellular layers ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.