BIOL-6A Lab Manual
... o Due to the laboratory set-up needed for practical exams, lab exams may not be made up if missed for any reason! • Online Problem Sets & Quizzes: ~20 problem sets and/or quizzes. Cumulative average of all scores = 100 points. o Each lecture topic coincides with problem sets presented on the 0DVWHUL ...
... o Due to the laboratory set-up needed for practical exams, lab exams may not be made up if missed for any reason! • Online Problem Sets & Quizzes: ~20 problem sets and/or quizzes. Cumulative average of all scores = 100 points. o Each lecture topic coincides with problem sets presented on the 0DVWHUL ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 25 Martini lecture Outline
... Approximately 1 to 2 inches in diameter Consists of: Duodenum: 10 inches long; receives digestive enzymes from the pancreas, bile from the liver and gallbladder Jejunum: 8 feet long; most of the digestion and absorption occurs in the jejunum Ileum: 12 feet long ...
... Approximately 1 to 2 inches in diameter Consists of: Duodenum: 10 inches long; receives digestive enzymes from the pancreas, bile from the liver and gallbladder Jejunum: 8 feet long; most of the digestion and absorption occurs in the jejunum Ileum: 12 feet long ...
Cnidarians-Student_Version
... Body symmetry refers to the spatial arrangement of body parts. If an organism’s body can be divided at least once into equal but opposite parts, then it possesses symmetry determined by the arrangement of planes of symmetry. Humans have only one plane of symmetry and are bilaterally symmetrical with ...
... Body symmetry refers to the spatial arrangement of body parts. If an organism’s body can be divided at least once into equal but opposite parts, then it possesses symmetry determined by the arrangement of planes of symmetry. Humans have only one plane of symmetry and are bilaterally symmetrical with ...
Anatomy of the Reproductive System (Chapter 42) Lab Objectives
... Be able to identify all of the body regions listed in figure 1.1 a and b in the lab manual. Know the following terms for orientation: superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, medial, lateral, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral, proximal, distal, superficial, deep, parietal, visceral Know the common se ...
... Be able to identify all of the body regions listed in figure 1.1 a and b in the lab manual. Know the following terms for orientation: superior, inferior, anterior, posterior, medial, lateral, cranial, caudal, dorsal, ventral, proximal, distal, superficial, deep, parietal, visceral Know the common se ...
Critical Thinking Application Answer
... 1. To stimulate student interest in use of the microscope, you may want to have students prepare wet mounts of pond water and observe the various forms of life present. A plankton net is a helpful device to concentrate pond organisms. Students can be encouraged to bring samples of pond water to clas ...
... 1. To stimulate student interest in use of the microscope, you may want to have students prepare wet mounts of pond water and observe the various forms of life present. A plankton net is a helpful device to concentrate pond organisms. Students can be encouraged to bring samples of pond water to clas ...
The complete iris (consisting. of a mesodermal stroma backed by
... carrying the irido-hyaloid vessels (H) disappears in order to allow of the forward growth of the ectodermii of the optic cup deep to (1) to form the pars iridica retinae. In passing- one may note that the tunica vasculosa lentis is complete at this stage. It is formed posteriorly by the branclhes of ...
... carrying the irido-hyaloid vessels (H) disappears in order to allow of the forward growth of the ectodermii of the optic cup deep to (1) to form the pars iridica retinae. In passing- one may note that the tunica vasculosa lentis is complete at this stage. It is formed posteriorly by the branclhes of ...
Female Reproductive System
... About 10cm long Located in the upper edge of broad ligament of uterus ...
... About 10cm long Located in the upper edge of broad ligament of uterus ...
4. Tissue Level of Organization
... he human body is composed of trillions of cells, which are organized into more complex units called tissues. Tissues are groups of similar cells and extracellular products that carry out a common function, such as providing protection or facilitating body movement. The study of tissues and their rel ...
... he human body is composed of trillions of cells, which are organized into more complex units called tissues. Tissues are groups of similar cells and extracellular products that carry out a common function, such as providing protection or facilitating body movement. The study of tissues and their rel ...
Gynecology. Lecture ONE. Normal Anatomy of the Female Pelvis
... Side-to-Side deviation The long axis of the uterus may also deviate ...
... Side-to-Side deviation The long axis of the uterus may also deviate ...
Surgical Anatomy of the Paranasal Sinus
... arches form ventral to the eyes and caudal to the oral stoma. The maxillary process, derived from the first branchial arch with part of the medial nasal process, becomes the upper jaw (Table 1–1). From days 45 to 48 formation of the secondary palate begins, due to the separation between the nasal ca ...
... arches form ventral to the eyes and caudal to the oral stoma. The maxillary process, derived from the first branchial arch with part of the medial nasal process, becomes the upper jaw (Table 1–1). From days 45 to 48 formation of the secondary palate begins, due to the separation between the nasal ca ...
The Region of the Nose and Nasal Cavities
... above to th e margin of the nasal bone and adjoining nasal process, in front to th e" septum , and below to th e lower cartilage. The latter is curved upon itself so as to form the outer and inner boundaries of the extern al orifice of th e nostril. It approaches its fellow of the opposite side inte ...
... above to th e margin of the nasal bone and adjoining nasal process, in front to th e" septum , and below to th e lower cartilage. The latter is curved upon itself so as to form the outer and inner boundaries of the extern al orifice of th e nostril. It approaches its fellow of the opposite side inte ...
Embryonic Folding and Coelom Development
... positioned with respect to cell X as it had been previously. We see that the allantois and connecting stalk are getting tucked in under the back end of the ballooned-out roof of the yolk sac. And that little region of the extraembryonic coelom we had marked with an asterisk is getting tucked in as w ...
... positioned with respect to cell X as it had been previously. We see that the allantois and connecting stalk are getting tucked in under the back end of the ballooned-out roof of the yolk sac. And that little region of the extraembryonic coelom we had marked with an asterisk is getting tucked in as w ...
Head
... it communicates superiorly with the ophthalmic vein it is more tortuous than the facial artery it lies anterior to the facial artery as it passes through the face it usually empties into the external jugular vein ...
... it communicates superiorly with the ophthalmic vein it is more tortuous than the facial artery it lies anterior to the facial artery as it passes through the face it usually empties into the external jugular vein ...
Characteristics ~
... The gastrula is made up of three parts: – Ectoderm, a layer of cells on the outer surface of the gastrula, grows and divides developing into skin and nervous tissue. – Endoderm, a layer of cells lining the inner surface of the gastrula, develops into the lining of the animal’s digestive tract. – Mes ...
... The gastrula is made up of three parts: – Ectoderm, a layer of cells on the outer surface of the gastrula, grows and divides developing into skin and nervous tissue. – Endoderm, a layer of cells lining the inner surface of the gastrula, develops into the lining of the animal’s digestive tract. – Mes ...
Cyclostome embryology and early evolutionary history of vertebrates
... 2001). This conserved segmental organization of the embryonic structures must be linked to some specific patern of gene expression. As expected, the expression patterns of some Hox genes [paralogue group (PG) 2 genes expressed in the ectomesenchyme of the second and more-posterior pharyngeal arches, ...
... 2001). This conserved segmental organization of the embryonic structures must be linked to some specific patern of gene expression. As expected, the expression patterns of some Hox genes [paralogue group (PG) 2 genes expressed in the ectomesenchyme of the second and more-posterior pharyngeal arches, ...
Simple Marine Organisms
... •They eat plankton and other particles that are drawn in by their ciliated tentacles •Bodies are contained in a “box” made of Calcium or Chitin ...
... •They eat plankton and other particles that are drawn in by their ciliated tentacles •Bodies are contained in a “box” made of Calcium or Chitin ...
Pelvic Anatomy - Creighton University School of Medicine
... Uterus: thick, muscular organ Derived from the fusion of the paramesonephric (mullerian) ducts. These ducts also form the upper 2/3 of the vagina and the fallopian tubes. ...
... Uterus: thick, muscular organ Derived from the fusion of the paramesonephric (mullerian) ducts. These ducts also form the upper 2/3 of the vagina and the fallopian tubes. ...
6e430d442f8069e
... notch on the lateral side of the inferior dental nerve. In this notch the bone grow medially below the incisive nerve & soon afterward it goes upward between the incisive nerve & meckel’s car. so contained in a trough channel of bone formed by medial & lateral plates which united below the nerve. At ...
... notch on the lateral side of the inferior dental nerve. In this notch the bone grow medially below the incisive nerve & soon afterward it goes upward between the incisive nerve & meckel’s car. so contained in a trough channel of bone formed by medial & lateral plates which united below the nerve. At ...
Why do we yawn?
... Providing an extensive area for gas exchange between air and circulating blood. To move the air from the exchanged surfaces of the lungs. To protect respiratory surfaces from dehydration, temperature changes, or other environmental variations and to defend the respiratory system and other tissues fr ...
... Providing an extensive area for gas exchange between air and circulating blood. To move the air from the exchanged surfaces of the lungs. To protect respiratory surfaces from dehydration, temperature changes, or other environmental variations and to defend the respiratory system and other tissues fr ...
Anatomy and Physiology - Columbus City Schools
... Most histologists place all animal tissues in four or five general categories. The following is a widely accepted classification. 1. Epithelial Tissue covers the outsides of animal bodies and their organs, and lines the insides of organs and body cavities. It protects other tissues. Some epithelial ...
... Most histologists place all animal tissues in four or five general categories. The following is a widely accepted classification. 1. Epithelial Tissue covers the outsides of animal bodies and their organs, and lines the insides of organs and body cavities. It protects other tissues. Some epithelial ...
The Respiratory System
... – The structural divisions of the respiratory system • Identify the components of the respiratory system – The respiratory tract • Define the respiratory tract • Identify the functional divisions of the respiratory tract – The respiratory mucosa • The respiratory mucosa and list its functions • The ...
... – The structural divisions of the respiratory system • Identify the components of the respiratory system – The respiratory tract • Define the respiratory tract • Identify the functional divisions of the respiratory tract – The respiratory mucosa • The respiratory mucosa and list its functions • The ...
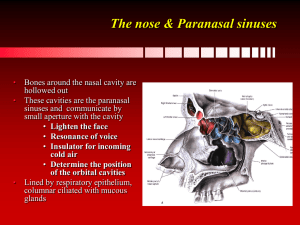
The nose & Paranasal sinuses
... • Begins developing about the 4th month of intra-uterine life and continue to grow till the 3rd decade • It varies in size and is the largest of all the paranasal sinuses ...
... • Begins developing about the 4th month of intra-uterine life and continue to grow till the 3rd decade • It varies in size and is the largest of all the paranasal sinuses ...
Anatomic Considerations on the Middle Ear in Dog
... is the longest of the ossicles and has two ends, an upper end and a lower end. The head of the hammer – the upper end – is rather irregular than round, and it joins the inside of the eardrum. Its caudo-ventral part has a joining area fitting to the anvil (incus). The neck of the hammer is quite long ...
... is the longest of the ossicles and has two ends, an upper end and a lower end. The head of the hammer – the upper end – is rather irregular than round, and it joins the inside of the eardrum. Its caudo-ventral part has a joining area fitting to the anvil (incus). The neck of the hammer is quite long ...
Chapter_009
... Voluntary muscles can be consciously controlled. Involuntary muscles work automatically. • You cannot control them. Cardiac muscle is in the heart. • It is an involuntary muscle. Muscles have three functions. • Movement of body parts • Maintenance of posture or muscle tone • Production of body heat ...
... Voluntary muscles can be consciously controlled. Involuntary muscles work automatically. • You cannot control them. Cardiac muscle is in the heart. • It is an involuntary muscle. Muscles have three functions. • Movement of body parts • Maintenance of posture or muscle tone • Production of body heat ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.