AHD Darwich Apr 15
... insects, or strands of music. • These perceived auditory events are accompanied by more typical symptoms of pontine lesions, such as cranial nerve deficits and/or long tract signs. • A perception of noise or sounds may also be experienced by patients with temporal lobe seizures or a temporal lobe le ...
... insects, or strands of music. • These perceived auditory events are accompanied by more typical symptoms of pontine lesions, such as cranial nerve deficits and/or long tract signs. • A perception of noise or sounds may also be experienced by patients with temporal lobe seizures or a temporal lobe le ...
Lungs
... Each principal bronchus divides into lobar bronchi (two on the left, three on the right), each of which supplies a lobe of lung. Each lobar bronchus then divided into segmental bronchi, which supply specific segments of the lung. ...
... Each principal bronchus divides into lobar bronchi (two on the left, three on the right), each of which supplies a lobe of lung. Each lobar bronchus then divided into segmental bronchi, which supply specific segments of the lung. ...
the development of the chondrocranium in the seahorse, hippocampus
... The ventral surface of the notochord is flat in this region and the dorsal surface continues to be arched or rounded. As the notochord approaches the occipital region it increases enormously in thickness-particularly the ventral half. The dorsal surface of the notochord and the basal plate are in th ...
... The ventral surface of the notochord is flat in this region and the dorsal surface continues to be arched or rounded. As the notochord approaches the occipital region it increases enormously in thickness-particularly the ventral half. The dorsal surface of the notochord and the basal plate are in th ...
Cochlear - Association of Surgical Technologists
... study, which they reported on at the 1973 meeting of the American Otological Society. House and Urban used multichannel electrodes in their patients and developed a takehome device for one particular patient. During this period, the science of the implant field grew exponentially and many questions ...
... study, which they reported on at the 1973 meeting of the American Otological Society. House and Urban used multichannel electrodes in their patients and developed a takehome device for one particular patient. During this period, the science of the implant field grew exponentially and many questions ...
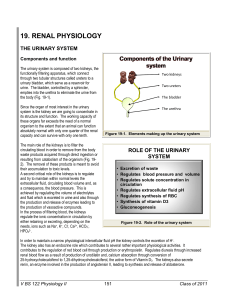
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
... Given that the function of the kidney is to filter the blood, this organ receives a disproportionally high supply of blood in comparison to other parts of the organism. For an organ that accounts for only about 0.4 % of the body weight it receives between 20 and 25 % of the cardiac output. The kidne ...
... Given that the function of the kidney is to filter the blood, this organ receives a disproportionally high supply of blood in comparison to other parts of the organism. For an organ that accounts for only about 0.4 % of the body weight it receives between 20 and 25 % of the cardiac output. The kidne ...
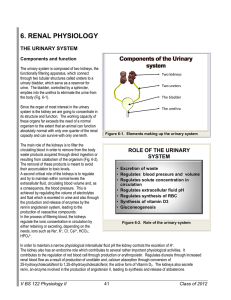
6. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
... Given that the function of the kidney is to filter the blood, this organ receives a disproportionally high supply of blood in comparison to other parts of the organism. For an organ that accounts for only about 0.4 % of the body weight it receives between 20 and 25 % of the cardiac output. The kidne ...
... Given that the function of the kidney is to filter the blood, this organ receives a disproportionally high supply of blood in comparison to other parts of the organism. For an organ that accounts for only about 0.4 % of the body weight it receives between 20 and 25 % of the cardiac output. The kidne ...
Face Development Lecture
... derived from neural crest. Ectomesenchyme forms intramembranous bone and fascia of the face and cranium. (Bones along the floor of the skull develop endochondrally from mesodermal mesenchyme derived from occipital somites.) • Skeletal muscle of the head is derived from either somite or somitomere my ...
... derived from neural crest. Ectomesenchyme forms intramembranous bone and fascia of the face and cranium. (Bones along the floor of the skull develop endochondrally from mesodermal mesenchyme derived from occipital somites.) • Skeletal muscle of the head is derived from either somite or somitomere my ...
Reproductive Organs
... Bipinnaria Primary free-swimming larval stage of asteroids. Biradial symmetry Body plan with two planes of symmetry. Biramous An annelid or arthropod appendage with two branches. Blastaea Hypothetical ancestor that is suggested by the blastula stage which occurs in the development of all animals. Bl ...
... Bipinnaria Primary free-swimming larval stage of asteroids. Biradial symmetry Body plan with two planes of symmetry. Biramous An annelid or arthropod appendage with two branches. Blastaea Hypothetical ancestor that is suggested by the blastula stage which occurs in the development of all animals. Bl ...
Uterine rupture
... Management of Rupture Uterus At this point, a decision must be made to perform hysterectomy or to repair the rupture site. In most cases, hysterectomy should be performed. In selected cases, repair of the rupture can be attempted. When rupture occurs in the body of the uterus, Bladder rupture ...
... Management of Rupture Uterus At this point, a decision must be made to perform hysterectomy or to repair the rupture site. In most cases, hysterectomy should be performed. In selected cases, repair of the rupture can be attempted. When rupture occurs in the body of the uterus, Bladder rupture ...
Anatomy of Fat
... FAT ANATOMY Embryology During 3rd month of gestation perivascular stem cells—adipoblasts give rise to adipocyte precursors which then differentiate into mature fat cells Some adipocytes differentiate into postadipocytes—capable of cellular replication After adolescence, no new adipocytes are f ...
... FAT ANATOMY Embryology During 3rd month of gestation perivascular stem cells—adipoblasts give rise to adipocyte precursors which then differentiate into mature fat cells Some adipocytes differentiate into postadipocytes—capable of cellular replication After adolescence, no new adipocytes are f ...
Export To Word
... explains how blood is classified into types based on the presence of antigens. It describes a process whereby antigens can be removed by an enzyme to make all blood types the same as the universal donor. This informational text resource is intended to support reading in the content area. This articl ...
... explains how blood is classified into types based on the presence of antigens. It describes a process whereby antigens can be removed by an enzyme to make all blood types the same as the universal donor. This informational text resource is intended to support reading in the content area. This articl ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 2 of 12
... Endothelium-lined spaces between the dural periosteal and meningeal layers Large veins from the surface of the brain empty into these sinuses; most blood from the brain ultimately drains via these to the internal jugular veins (IJVs) The main sinuses are superior sagittal, inferior sagittal, occipit ...
... Endothelium-lined spaces between the dural periosteal and meningeal layers Large veins from the surface of the brain empty into these sinuses; most blood from the brain ultimately drains via these to the internal jugular veins (IJVs) The main sinuses are superior sagittal, inferior sagittal, occipit ...
The Development of the Cape Species of Peripatus. PART IV.
... at about the same time in Stage G ; but how and when they are developed I am unable to say. As may be seen from an inspection of the sections (Part III, figs. 37—39) there is in Stage F a certain amount of this fibrous tissue, especially at the ventro-lateral corners of the body, close to the outer ...
... at about the same time in Stage G ; but how and when they are developed I am unable to say. As may be seen from an inspection of the sections (Part III, figs. 37—39) there is in Stage F a certain amount of this fibrous tissue, especially at the ventro-lateral corners of the body, close to the outer ...
Illustrated Review of the Embryology and Development of the Facial
... develops; palatal shelves elevate and fuse, forming secondary palate; future nostril now complete; eyes move more to midline; fusion of maxillary and mandibular processes narrows the width of the mouth and completes lower cheeks 8th Lateral nasal wall well-developed; facial muscle primordia appear ( ...
... develops; palatal shelves elevate and fuse, forming secondary palate; future nostril now complete; eyes move more to midline; fusion of maxillary and mandibular processes narrows the width of the mouth and completes lower cheeks 8th Lateral nasal wall well-developed; facial muscle primordia appear ( ...
Folio Bound VIEWS - Gray`s Anatomy
... tissues (membranes) develop. The extraembryonic tissues are derived from both the epiblast and hypoblast, (see p. 98 ), whereas the embryonic tissues are derived from the epiblast alone. This critical division of cell lineages into embryonic and extraembryonic distinguishes the amniota from the ana ...
... tissues (membranes) develop. The extraembryonic tissues are derived from both the epiblast and hypoblast, (see p. 98 ), whereas the embryonic tissues are derived from the epiblast alone. This critical division of cell lineages into embryonic and extraembryonic distinguishes the amniota from the ana ...
The Mode of Growth of the Tail in Urodele Larvae
... principal 'motor' for the outgrowth of the tail, though they ascribe an important function in this process to the neural tube and the myotomes as well. Devillers (1948), however, has concluded from extirpation experiments in the trout that at least in early stages elongation of the body can take pla ...
... principal 'motor' for the outgrowth of the tail, though they ascribe an important function in this process to the neural tube and the myotomes as well. Devillers (1948), however, has concluded from extirpation experiments in the trout that at least in early stages elongation of the body can take pla ...
Keys to 2402 Models
... The major parts of the circulatory system A. Heart B. Circulatory system C. Vein D. Artery Principal structures of the heart ...
... The major parts of the circulatory system A. Heart B. Circulatory system C. Vein D. Artery Principal structures of the heart ...
Keys to 2402 Models
... The major parts of the circulatory system A. Heart B. Circulatory system C. Vein D. Artery Principal structures of the heart ...
... The major parts of the circulatory system A. Heart B. Circulatory system C. Vein D. Artery Principal structures of the heart ...
The Lymphatic System
... • Lymphatic vessels then lead to larger vessels that unite with the veins in the thorax. • Lymphatic capillaries – microscopic, closed-ended tubes that extend from interstitial (“between tissues”) spaces forming complex networks. – They resemble the blood vessels, except they don’t carry blood. ...
... • Lymphatic vessels then lead to larger vessels that unite with the veins in the thorax. • Lymphatic capillaries – microscopic, closed-ended tubes that extend from interstitial (“between tissues”) spaces forming complex networks. – They resemble the blood vessels, except they don’t carry blood. ...
detailed lecture outline
... o Ingestion occurs when materials enter the digestive tract via the mouth. Ingestion is an active process involving conscious choice and decision making. o Mechanical processing is crushing and shearing that makes materials easier to propel along the digestive tract. It also increases their surface ...
... o Ingestion occurs when materials enter the digestive tract via the mouth. Ingestion is an active process involving conscious choice and decision making. o Mechanical processing is crushing and shearing that makes materials easier to propel along the digestive tract. It also increases their surface ...
Chapter 24: The Digestive System The Digestive System: An
... o Ingestion occurs when materials enter the digestive tract via the mouth. Ingestion is an active process involving conscious choice and decision making. o Mechanical processing is crushing and shearing that makes materials easier to propel along the digestive tract. It also increases their surface ...
... o Ingestion occurs when materials enter the digestive tract via the mouth. Ingestion is an active process involving conscious choice and decision making. o Mechanical processing is crushing and shearing that makes materials easier to propel along the digestive tract. It also increases their surface ...
Nancy Caroline`s Emergency Care in the Streets, Seventh Edition
... a. Refers to the patient’s right and left sides, not to yours. 5. Superior and inferior a. Superior is nearer to the head, and inferior is nearer to the feet. 6. Lateral and medial a. Lateral is farther from the midline, and medial is nearer to the midline. 7. Proximal and distal a. Proximal is near ...
... a. Refers to the patient’s right and left sides, not to yours. 5. Superior and inferior a. Superior is nearer to the head, and inferior is nearer to the feet. 6. Lateral and medial a. Lateral is farther from the midline, and medial is nearer to the midline. 7. Proximal and distal a. Proximal is near ...
anatomy of nose brig muhammad ashfaq mbbs
... Blood Supply of Nasal Cavity (1) branches from the internal carotid, namely the branches of the anterior and posterior ethmoid arteries from the ophthalmic artery, and (2) branches from the external carotid, namely the sphenopalatine, greater palatine, superior labial, and angular ...
... Blood Supply of Nasal Cavity (1) branches from the internal carotid, namely the branches of the anterior and posterior ethmoid arteries from the ophthalmic artery, and (2) branches from the external carotid, namely the sphenopalatine, greater palatine, superior labial, and angular ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.