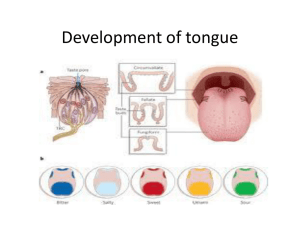
Development of tongue
... mouth one elevation (swelling)appear in the Medline which is called median tongue or tuberculum median tongue it arise from endodermal floor of the ...
... mouth one elevation (swelling)appear in the Medline which is called median tongue or tuberculum median tongue it arise from endodermal floor of the ...
Nose & Para nasal sinuses
... The skin of the external nose and its surrounds contains many sebaceous glands and hair follicles which may become blocked and infected Facial veins, which may become secondarily infected, communicate directly with the ophthalmic veins and hence with the cavernous sinus. For this reason, this zone i ...
... The skin of the external nose and its surrounds contains many sebaceous glands and hair follicles which may become blocked and infected Facial veins, which may become secondarily infected, communicate directly with the ophthalmic veins and hence with the cavernous sinus. For this reason, this zone i ...
1 Organisation of resp syst
... 2. Exchange O2 & CO2 between lungs (alveoli) and blood (pulmonary capillaries) by diffusion 3. Transportation of O2 & CO2 between lungs and tissues 4. Exchange O2 & CO2 between blood and body tissues by ...
... 2. Exchange O2 & CO2 between lungs (alveoli) and blood (pulmonary capillaries) by diffusion 3. Transportation of O2 & CO2 between lungs and tissues 4. Exchange O2 & CO2 between blood and body tissues by ...
Sponges and Cnidarians Notes PowerPoint
... • Sessile: they live their entire life attached to a single spot • They are animals. Why…? ...
... • Sessile: they live their entire life attached to a single spot • They are animals. Why…? ...
molecular physiology
... constitute less than 0.5% of the total body mass but they receive 20-25% of the resting cardiac output via the renal artery. Renal artery enter the kidney at the pelvis and then branch into several segmental arteries, which enter the parenchyma and pass through the renal columns between the renal py ...
... constitute less than 0.5% of the total body mass but they receive 20-25% of the resting cardiac output via the renal artery. Renal artery enter the kidney at the pelvis and then branch into several segmental arteries, which enter the parenchyma and pass through the renal columns between the renal py ...
1-The dorsal nasal meatus
... the junction of the skin and mucosa. In pig there is second opening of the nasolacrimal duct located on the lateral surface of the ventral nasal concha near its caudal end. 4-the vomeronasal organ: consist of a pair of ducts which lie in the flour of the nasal cavity on either side of the nasal sept ...
... the junction of the skin and mucosa. In pig there is second opening of the nasolacrimal duct located on the lateral surface of the ventral nasal concha near its caudal end. 4-the vomeronasal organ: consist of a pair of ducts which lie in the flour of the nasal cavity on either side of the nasal sept ...
Reproductive Organs
... Bipinnaria Primary free-swimming larval stage of asteroids. Biradial symmetry Body plan with two planes of symmetry. Biramous An annelid or arthropod appendage with two branches. Blastaea Hypothetical ancestor that is suggested by the blastula stage which occurs in the development of all animals. Bl ...
... Bipinnaria Primary free-swimming larval stage of asteroids. Biradial symmetry Body plan with two planes of symmetry. Biramous An annelid or arthropod appendage with two branches. Blastaea Hypothetical ancestor that is suggested by the blastula stage which occurs in the development of all animals. Bl ...
ppt
... Is formed by the lateral wall of the inner ear. The greater part of the wall shows a rounded projection, called the promontory, which results from the underlying first turn of the ...
... Is formed by the lateral wall of the inner ear. The greater part of the wall shows a rounded projection, called the promontory, which results from the underlying first turn of the ...
Pharynx - mcstmf
... When the apertures of the sinuses are blocked or they become filled with fluid, the quality of the voice is markedly changed. ...
... When the apertures of the sinuses are blocked or they become filled with fluid, the quality of the voice is markedly changed. ...
Class Calcarea (Calciospongiae)
... a nematocyst is released, its cnidoblast cell dies. New cnidoblast cells and nematocysts are therefore continually being produced. Despite the difference in shape between polyps and medusae, the internal structure of these two body forms is very similar. Each has a central coelenteron or gastrovascu ...
... a nematocyst is released, its cnidoblast cell dies. New cnidoblast cells and nematocysts are therefore continually being produced. Despite the difference in shape between polyps and medusae, the internal structure of these two body forms is very similar. Each has a central coelenteron or gastrovascu ...
Support material annexes
... From http://www.usoe.k12.ut.us/curr/science/sciber00/7th/cells/sciber/cellhist.htm ...
... From http://www.usoe.k12.ut.us/curr/science/sciber00/7th/cells/sciber/cellhist.htm ...
Sensory Part 2
... The Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Two tubes are associated with the inner ear The opening from the auditory canal is covered by the tympanic ...
... The Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Two tubes are associated with the inner ear The opening from the auditory canal is covered by the tympanic ...
Middle ear cavity and its contents
... Middle ear or tympanic cavity is an irregular, laterally compressed space within the temporal bone. It is filled with air, which is conveyed to it from the nasal part of the pharynx through the auditory tube. ...
... Middle ear or tympanic cavity is an irregular, laterally compressed space within the temporal bone. It is filled with air, which is conveyed to it from the nasal part of the pharynx through the auditory tube. ...
Sensory
... 1. Locate and identify the accessory structures associated with vision. _____ palpebrae (also called eyelid) (pal-PĒ-bre) _____ palpebral fissures (also called eye slits) (PAL-pē-bral) (The upper and lower lids are separated by the eye slits.) _____ medial palpebral commissures (also called medial c ...
... 1. Locate and identify the accessory structures associated with vision. _____ palpebrae (also called eyelid) (pal-PĒ-bre) _____ palpebral fissures (also called eye slits) (PAL-pē-bral) (The upper and lower lids are separated by the eye slits.) _____ medial palpebral commissures (also called medial c ...
Hearing
... • Bending of hairs in direction of kinocilia – Depolarizes hair cells – Increases amount of neurotransmitter release – More impulses travel up vestibular nerve to ...
... • Bending of hairs in direction of kinocilia – Depolarizes hair cells – Increases amount of neurotransmitter release – More impulses travel up vestibular nerve to ...
Ophiacodontidae - Dr. Stuart Sumida
... amphibious adaptations Fed on food items which required little mastication; this is due to features such as their long snout, lightly built skulls and jaws, and undifferentiated dentitions ...
... amphibious adaptations Fed on food items which required little mastication; this is due to features such as their long snout, lightly built skulls and jaws, and undifferentiated dentitions ...
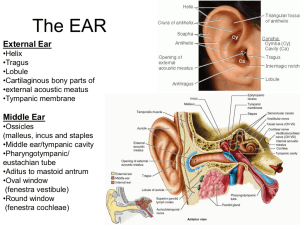
The EAR - Ipswich-Year2-Med-PBL-Gp-2
... bronchial arteries branches supply the upper oesophagus, the main bronchi respiratory bronchioles anastomose with branches of the pulmonary arteries The two bronchial veins drain only part of the blood supplied to the lungs by the bronchial arteries, primarily that near the more proximal part of t ...
... bronchial arteries branches supply the upper oesophagus, the main bronchi respiratory bronchioles anastomose with branches of the pulmonary arteries The two bronchial veins drain only part of the blood supplied to the lungs by the bronchial arteries, primarily that near the more proximal part of t ...
7-4 Hearing and Equlibirium
... lobule - bottom, earlobe attached to head by ligaments and muscles ...
... lobule - bottom, earlobe attached to head by ligaments and muscles ...
Third ventricular tumours
... • Diagnosis: CT scan- hyperdense lesion (protein and calcium) but can be iso or hypodense, MRI-oval or round lesion in the region of foramen Munro with or without hydrocephalus (variable intensity usually high on T2) • Histology: outer fibrous layer and inner layer pseudo stratified columnar or cub ...
... • Diagnosis: CT scan- hyperdense lesion (protein and calcium) but can be iso or hypodense, MRI-oval or round lesion in the region of foramen Munro with or without hydrocephalus (variable intensity usually high on T2) • Histology: outer fibrous layer and inner layer pseudo stratified columnar or cub ...
uberon-and-cl-in-go-2013
... Import chain hell • Which ontology to use? – For ontology work, use composite-metazoan – This avoids lattice hell • E.g. only one somite, one brain, one heart, … ...
... Import chain hell • Which ontology to use? – For ontology work, use composite-metazoan – This avoids lattice hell • E.g. only one somite, one brain, one heart, … ...
terminal bronchioles
... diverge throughout the lungs before terminating in terminal bronchioles. Incomplete rings of hyaline cartilage support the walls of the primary bronchi to ensure that they remain open. Right primary bronchus is shorter, wider, and more vertically oriented than the left primary bronchus. Foreign part ...
... diverge throughout the lungs before terminating in terminal bronchioles. Incomplete rings of hyaline cartilage support the walls of the primary bronchi to ensure that they remain open. Right primary bronchus is shorter, wider, and more vertically oriented than the left primary bronchus. Foreign part ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.