2016 Course Outline
... Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not result in phenotypic change in an organism. Explain how mutations in gametes may result in phenotypic changes in offspring. Evolution and Biodiversity Central Concepts: Evolution is the result of genetic changes that occur in const ...
... Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not result in phenotypic change in an organism. Explain how mutations in gametes may result in phenotypic changes in offspring. Evolution and Biodiversity Central Concepts: Evolution is the result of genetic changes that occur in const ...
CELLS
... • Picture in your mind an animal. Think about all the internal body parts that work together to help that animal survive. ...
... • Picture in your mind an animal. Think about all the internal body parts that work together to help that animal survive. ...
UNIT 1 LESSON 4 Specialised cells
... 2. controls the cell and contains instructions to make more cells – nucleus 3. the jelly-like part of the cell where chemical reactions take place – cytoplasm 4. found only in plant cells, these capture light energy and use it in photosynthesis – chloroplasts 5. found around the outside of a plant c ...
... 2. controls the cell and contains instructions to make more cells – nucleus 3. the jelly-like part of the cell where chemical reactions take place – cytoplasm 4. found only in plant cells, these capture light energy and use it in photosynthesis – chloroplasts 5. found around the outside of a plant c ...
Slayt 1
... to investigate how evolution worked i.e., how characteristics were passed down the generations. • He figured out the basic principles of genetics. He showed that offspring received characteristics from both parents, but only the dominant characteristic trait was expressed. Mendel’s work only came to ...
... to investigate how evolution worked i.e., how characteristics were passed down the generations. • He figured out the basic principles of genetics. He showed that offspring received characteristics from both parents, but only the dominant characteristic trait was expressed. Mendel’s work only came to ...
EvolutionClass ReviewFall2008
... 31. Why is it important to have a universal scientific name for an organism? 32. How is evolutionary classification different from traditional classification? TraditionalModern Evidence used _______________________ ____________________ Categories ____________________________ ________________________ ...
... 31. Why is it important to have a universal scientific name for an organism? 32. How is evolutionary classification different from traditional classification? TraditionalModern Evidence used _______________________ ____________________ Categories ____________________________ ________________________ ...
Human Structure and Function (HUMB1000) – UNIT NOTES
... - groups of cells that are grouped together having the same goal 5) Organ level : tissues of cells that are grouped together having the same goal 6) system level: one or more organs make up a system 7) Organism level: all the systems make up a organism ...
... - groups of cells that are grouped together having the same goal 5) Organ level : tissues of cells that are grouped together having the same goal 6) system level: one or more organs make up a system 7) Organism level: all the systems make up a organism ...
Characteristics of Life Notes Packet
... b. cells may group into tissues, organs, organ systems in more complex organisms examples: plants, animals, most fungi, some protists. ...
... b. cells may group into tissues, organs, organ systems in more complex organisms examples: plants, animals, most fungi, some protists. ...
Ch 1 PPT - Ludlow Independent Schools
... Order • Analyzing a biological structure gives us clues about what it does and how it works ...
... Order • Analyzing a biological structure gives us clues about what it does and how it works ...
Cellular organisation
... Unlike animals, many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate and specialise throughout their life. These cells are found in tissues called meristems. ...
... Unlike animals, many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate and specialise throughout their life. These cells are found in tissues called meristems. ...
In order for evolution by natural selection to explain the adaptation
... product of past selection. However, the construction of a theoretical framework to formalise such ‘evolution of evolvability’ has been continually frustrated by the indisputable fact that natural selection cannot favour structures for benefits they have not yet produced. Here we resolve this problem ...
... product of past selection. However, the construction of a theoretical framework to formalise such ‘evolution of evolvability’ has been continually frustrated by the indisputable fact that natural selection cannot favour structures for benefits they have not yet produced. Here we resolve this problem ...
4-4 Cell Differentiation I. Differentiation 1. Differentiation
... 1. Once a cell’s future has been determined, when and how much it changes depends on is DNA, its function, and the type of organisms. A. Cell Differentiation Among Animals 1. Many adult animals, such as insects and some crustaceans and reptiles can grow a limb or tail to replace a lost one. Cells a ...
... 1. Once a cell’s future has been determined, when and how much it changes depends on is DNA, its function, and the type of organisms. A. Cell Differentiation Among Animals 1. Many adult animals, such as insects and some crustaceans and reptiles can grow a limb or tail to replace a lost one. Cells a ...
Document
... _________________. The inside of the cell is _____________ and jelly-like. You can’t see them just using you eyes. You need a ____________________. A cell can be considered the smallest part of an _____________ that can ______________ on its own. Some organisms have only ___________ cell, while more ...
... _________________. The inside of the cell is _____________ and jelly-like. You can’t see them just using you eyes. You need a ____________________. A cell can be considered the smallest part of an _____________ that can ______________ on its own. Some organisms have only ___________ cell, while more ...
Honors Standards Unit 5 Evolution
... comparative embryology, biogeography, molecular biology, and observed evolutionary change 5.2 Describe the conditions required for natural selection, including: overpopulation of offspring, inherited variation, and the struggle to survive, which results in differential reproductive success 5.3 Descr ...
... comparative embryology, biogeography, molecular biology, and observed evolutionary change 5.2 Describe the conditions required for natural selection, including: overpopulation of offspring, inherited variation, and the struggle to survive, which results in differential reproductive success 5.3 Descr ...
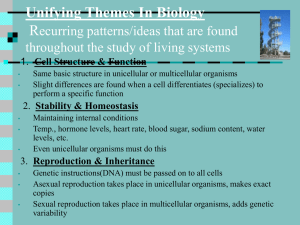
Unifying Themes in Biology Represent recurring patterns
... Same basic structure in unicellular or multicellular organisms Slight differences are found when a cell differentiates (specializes) to perform a specific function ...
... Same basic structure in unicellular or multicellular organisms Slight differences are found when a cell differentiates (specializes) to perform a specific function ...
Biology EOC Voc Review
... Any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence, numbers, reproduction, or Limiting factors distribution of organisms Mechanism for change in populations; occurs when organisms with certain variations Natural selection survive, reproduce, and pass their variations to the next generation Me ...
... Any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence, numbers, reproduction, or Limiting factors distribution of organisms Mechanism for change in populations; occurs when organisms with certain variations Natural selection survive, reproduce, and pass their variations to the next generation Me ...
Chapter 1: What is Biology
... Linnaeus: modern system binomial nomenclature o Scientific names are in Latin o 1st name: _________ 2nd name: ________ o Humans: __________ __________ 6 Kingdoms: _______________ _______________ _______________ ...
... Linnaeus: modern system binomial nomenclature o Scientific names are in Latin o 1st name: _________ 2nd name: ________ o Humans: __________ __________ 6 Kingdoms: _______________ _______________ _______________ ...
Themes of Life
... Part A: Identify a structural difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells that is directly related to their difference in size. Part B: Based on the structural difference, explain why prokaryotic cells can be much smaller than eukaryotic cells. Part C: Describe one similarity between p ...
... Part A: Identify a structural difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells that is directly related to their difference in size. Part B: Based on the structural difference, explain why prokaryotic cells can be much smaller than eukaryotic cells. Part C: Describe one similarity between p ...
Big Ideas in Biology - juan-roldan
... Descent from a common ancestor with modification Natural Selection as the main mechanism that drives the evolution of adaptive evolutionary novelties ...
... Descent from a common ancestor with modification Natural Selection as the main mechanism that drives the evolution of adaptive evolutionary novelties ...
Science Grade 7
... Mutualism – relationship between 2 species in which both species ______________ Parasitism - relationship in which 1 organism ___________ on or in side another and ______________ it. Commensalism – relationship in which 1 species ___________________ and the other is neither __________________ ...
... Mutualism – relationship between 2 species in which both species ______________ Parasitism - relationship in which 1 organism ___________ on or in side another and ______________ it. Commensalism – relationship in which 1 species ___________________ and the other is neither __________________ ...
Hit List vocabulary cards
... Body structure that has no function in a present day organism but was probably useful to an ancestor; provides evidence for evolution ...
... Body structure that has no function in a present day organism but was probably useful to an ancestor; provides evidence for evolution ...
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
... All organisms, including humans, have the ability to regenerate something in the body. But the process is much more developed in lower organisms such as plants – mammals do regenerate skin, muscle, and blood. – other types of cells, such as those in the brain also regenerate. – researchers are activ ...
... All organisms, including humans, have the ability to regenerate something in the body. But the process is much more developed in lower organisms such as plants – mammals do regenerate skin, muscle, and blood. – other types of cells, such as those in the brain also regenerate. – researchers are activ ...
kakamega south cemtral districts mock examination
... a) A-Thick iner wall; Rej ; inner wall B-Thin outer wall; Re ; outer wall b) Regulate the openings and closing of the stoma;; a) Light - Activates germination hormones; - Raises internal temperatures of the seed; Award for one b) Soaking in water - softens seedcoat; Autotrophs are organisms who util ...
... a) A-Thick iner wall; Rej ; inner wall B-Thin outer wall; Re ; outer wall b) Regulate the openings and closing of the stoma;; a) Light - Activates germination hormones; - Raises internal temperatures of the seed; Award for one b) Soaking in water - softens seedcoat; Autotrophs are organisms who util ...
evolution notes
... Natural Selection – the individuals that are best adapted to their environment (nature) will survive and pass their traits onto their offspring. Nature, in essence, is selecting the best to survive. Overproduction – necessary for evolution to happen. A species produces more offspring than their envi ...
... Natural Selection – the individuals that are best adapted to their environment (nature) will survive and pass their traits onto their offspring. Nature, in essence, is selecting the best to survive. Overproduction – necessary for evolution to happen. A species produces more offspring than their envi ...
Chapter 3
... 29) Found in the epidermis, esophagus, and mouth, these stacked layers of cells prevent exchange, while they resist chemicals, bacteria, and other destructive forces. ...
... 29) Found in the epidermis, esophagus, and mouth, these stacked layers of cells prevent exchange, while they resist chemicals, bacteria, and other destructive forces. ...
Biology 1406 - HCC Learning Web
... environment to create orderly processes for themselves and return disorder to their environment in order to get rid of it. (heat, waste products, etc.) 6. (P. 9 – 15) There is unity in diversity. All of biology is about this topic – the most important concept in biology, because it explains how livi ...
... environment to create orderly processes for themselves and return disorder to their environment in order to get rid of it. (heat, waste products, etc.) 6. (P. 9 – 15) There is unity in diversity. All of biology is about this topic – the most important concept in biology, because it explains how livi ...