Cells - Livingstone High School
... • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function form a system. Example: circulatory system. • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such a ...
... • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function form a system. Example: circulatory system. • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together, forming organs, such a ...
Name
... 27. The diagram below shows the key steps for making proteins. Which step involves ribosomes? ...
... 27. The diagram below shows the key steps for making proteins. Which step involves ribosomes? ...
Respiratory Levels of Organization
... binds to hemoglobin in the red blood cells in the capillaries of the lungs. Some of this oxygen displaces carbon dioxide that was transported from peripheral cells. The exchange of gases occurs in red blood cells (where hemoglobin is concentrated) at the interface of the circulatory system and respi ...
... binds to hemoglobin in the red blood cells in the capillaries of the lungs. Some of this oxygen displaces carbon dioxide that was transported from peripheral cells. The exchange of gases occurs in red blood cells (where hemoglobin is concentrated) at the interface of the circulatory system and respi ...
CELLS
... • Picture in your mind an animal. Think about all the internal body parts that work together to help that animal survive. ...
... • Picture in your mind an animal. Think about all the internal body parts that work together to help that animal survive. ...
what know about protists cells and human body
... Important levels of organization for structure and function include cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, whole organisms and ecosystems. Specialized cells perform specialized functions in multi-cellular organisms. Groups of specialized cells cooperate to form a tissue, such as muscle. Diff ...
... Important levels of organization for structure and function include cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, whole organisms and ecosystems. Specialized cells perform specialized functions in multi-cellular organisms. Groups of specialized cells cooperate to form a tissue, such as muscle. Diff ...
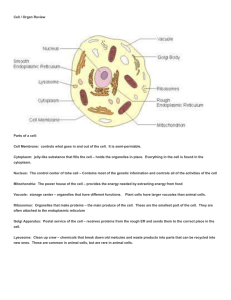
Cell / Organ Review Parts of a cell: Cell Membrane: controls what
... Golgi Apparatus: Postal service of the cell – receives proteins from the rough ER and sends them to the correct place in the cell. Lysosome: Clean up crew – chemicals that break down old melcules and waste products into parts that can be recycled into new ones. These are common in animal cells, but ...
... Golgi Apparatus: Postal service of the cell – receives proteins from the rough ER and sends them to the correct place in the cell. Lysosome: Clean up crew – chemicals that break down old melcules and waste products into parts that can be recycled into new ones. These are common in animal cells, but ...
Cellular organisation
... made up of around 200 different types of cell, all working together. Most cells are specialized, meaning that each type of cell has a specific structure and function. All cells with a nucleus contain the same genes, but different cells activate different genes so they only produce the proteins they ...
... made up of around 200 different types of cell, all working together. Most cells are specialized, meaning that each type of cell has a specific structure and function. All cells with a nucleus contain the same genes, but different cells activate different genes so they only produce the proteins they ...
Regents Review
... • Digestion- one-way passage through the body • Respiration- uses oxygen to break down food molecules to release energy • Circulation- involves involves the movement of materials inside the cell as well as the movement between parts of a multicellular organism. • Excretion- removal of all waste prod ...
... • Digestion- one-way passage through the body • Respiration- uses oxygen to break down food molecules to release energy • Circulation- involves involves the movement of materials inside the cell as well as the movement between parts of a multicellular organism. • Excretion- removal of all waste prod ...
CELL SPECIALIZATION - Biology with Miss Amy
... What size or surfaces is/are best then? large surface area to volume ratio – that is – small cells or cells with folds or projections from the ...
... What size or surfaces is/are best then? large surface area to volume ratio – that is – small cells or cells with folds or projections from the ...
Human Bio 11 – Dalesandro
... 2) What blood cell contains histamine and controls allergic reactions? Describe this cell’s appearance. 3) What blood cell controls clotting and stops you from bleeding? Describe this cell’s appearance. 4) What blood cell produces antibodies to fight off invading organisms like bacteria and viruses? ...
... 2) What blood cell contains histamine and controls allergic reactions? Describe this cell’s appearance. 3) What blood cell controls clotting and stops you from bleeding? Describe this cell’s appearance. 4) What blood cell produces antibodies to fight off invading organisms like bacteria and viruses? ...
Cells - TeacherWeb
... Eukaryotes: Have a nucleus (all other cells) 1. Nuclear envelope: Pourous membrane that surrounds the nucleus 2. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid-instructions for cell activity (located in the Nucleolus) ...
... Eukaryotes: Have a nucleus (all other cells) 1. Nuclear envelope: Pourous membrane that surrounds the nucleus 2. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid-instructions for cell activity (located in the Nucleolus) ...
View Press Release
... for Arctic Biology, summed it up by saying, “Neuronascent has captured tolerance to cerebral ischemia in a neural stem cell line derived from Arctic ground squirrels. This unique extremophile can now be explored by scientists throughout the world.” “Neuronascent is excited to partner with Lifeline C ...
... for Arctic Biology, summed it up by saying, “Neuronascent has captured tolerance to cerebral ischemia in a neural stem cell line derived from Arctic ground squirrels. This unique extremophile can now be explored by scientists throughout the world.” “Neuronascent is excited to partner with Lifeline C ...
Cells
... organs to your brain. • It consists of two parts: The central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. • The central nervous system consists of brain and ...
... organs to your brain. • It consists of two parts: The central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. • The central nervous system consists of brain and ...
The Different Jobs of Cells
... I. Special Cells for Special Jobs • Cells that make up many-celled organisms are specialized • Bacteria cells are single celled, all other cells are “many celled” organisms ...
... I. Special Cells for Special Jobs • Cells that make up many-celled organisms are specialized • Bacteria cells are single celled, all other cells are “many celled” organisms ...
Dentistry college - first class Medical biology
... The shape of the cells are highly variable , the bacterial cell could be rod , cocci or spiral shape ,the different cells in multicellular organisms are flat or sequamous as in endothelium of the artery ,cuboidal as in kidney tubules or bile ducts of the liver , columnar as in mucosa of the alimenta ...
... The shape of the cells are highly variable , the bacterial cell could be rod , cocci or spiral shape ,the different cells in multicellular organisms are flat or sequamous as in endothelium of the artery ,cuboidal as in kidney tubules or bile ducts of the liver , columnar as in mucosa of the alimenta ...
of the cell - MrMsciences
... • In plant cells- they are very large and hold lots of water and nutrients; tonoplast membrane controls exchange; also holds pigments the give flowers color • Creates turgid pressure to keep plant up right • In animal cells- very small; transport things inside the cell ...
... • In plant cells- they are very large and hold lots of water and nutrients; tonoplast membrane controls exchange; also holds pigments the give flowers color • Creates turgid pressure to keep plant up right • In animal cells- very small; transport things inside the cell ...
HYGROMYCIN B PRODUCT DESCRIPTION: MOLECULAR
... temperature (15 - 25°C) for 30 minutes before use. Dissolve antibiotic in 1 mL of desired growth medium. ClonaCell®-TCS Medium Add to ClonaCell®-TCS medium at the concentration recommended in the Technical Manual (Catalog #28372). If you are selecting cell lines not mentioned in the Technical Manual ...
... temperature (15 - 25°C) for 30 minutes before use. Dissolve antibiotic in 1 mL of desired growth medium. ClonaCell®-TCS Medium Add to ClonaCell®-TCS medium at the concentration recommended in the Technical Manual (Catalog #28372). If you are selecting cell lines not mentioned in the Technical Manual ...
Specialized Cells Notes
... What is the purpose of hemoglobin? ______________________________________________________________ What category of biomolecules hemoglobin belongs to? ______________________________________________ What is the function red blood cell? ______________________________________________________________ Wh ...
... What is the purpose of hemoglobin? ______________________________________________________________ What category of biomolecules hemoglobin belongs to? ______________________________________________ What is the function red blood cell? ______________________________________________________________ Wh ...
Cillia and flagella
... Cilium , flagellum are projections of cells that can move both in an undulating fashion like a whip or stiffly like an oar .cilia are short (2-10 µm ) while flagella are longer (usually no more than 200 µm).Ciliated cells are critical to our respiratory health and to the ability to reproduce. The ci ...
... Cilium , flagellum are projections of cells that can move both in an undulating fashion like a whip or stiffly like an oar .cilia are short (2-10 µm ) while flagella are longer (usually no more than 200 µm).Ciliated cells are critical to our respiratory health and to the ability to reproduce. The ci ...
Use for Nov. 20,12 Unit 2 Cells Test Study Guide
... 20. Water is a good solvent. Explain what this means. 21. The diagram shows two solutions that are separated by a partially permeable membrane. In which direction will most water molecules move in relation to their concentration gradient? Draw an arrow showing the direction of movement. ...
... 20. Water is a good solvent. Explain what this means. 21. The diagram shows two solutions that are separated by a partially permeable membrane. In which direction will most water molecules move in relation to their concentration gradient? Draw an arrow showing the direction of movement. ...
Human Structure and Function (HUMB1000) – UNIT NOTES
... 3) Cellular level : Organelles form cells 4) tissue level: cells (eg: smooth muscle cells) combine to form tissue (eg: smooth muscle tissue) - groups of cells that are grouped together having the same goal 5) Organ level : tissues of cells that are grouped together having the same goal 6) system lev ...
... 3) Cellular level : Organelles form cells 4) tissue level: cells (eg: smooth muscle cells) combine to form tissue (eg: smooth muscle tissue) - groups of cells that are grouped together having the same goal 5) Organ level : tissues of cells that are grouped together having the same goal 6) system lev ...
UNIT 1 LESSON 4 Specialised cells
... The ova is the cell with the largest volume in the human body. Its function is to produce new offspring. Introduce the discussion by showing the pupils a hen’s egg , crack it and show the contents. Point out the cell membrane which holds the contents of the egg together, the nucleus which is fertili ...
... The ova is the cell with the largest volume in the human body. Its function is to produce new offspring. Introduce the discussion by showing the pupils a hen’s egg , crack it and show the contents. Point out the cell membrane which holds the contents of the egg together, the nucleus which is fertili ...
Cells - Dr Magrann
... 3. Capable of maintaining homeostasis within itself and within the body. The sum of all of the chemical reactions that occur in a cell maintaining a balanced internal environment, such as temperature, pH, glucose levels 1. Mostly water 2. Things dissolved in water Sugars like glucose and energy mole ...
... 3. Capable of maintaining homeostasis within itself and within the body. The sum of all of the chemical reactions that occur in a cell maintaining a balanced internal environment, such as temperature, pH, glucose levels 1. Mostly water 2. Things dissolved in water Sugars like glucose and energy mole ...
Cells - Doral Academy Preparatory
... organs to your brain. • It consists of two parts: The central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. • The central nervous system consists of brain and ...
... organs to your brain. • It consists of two parts: The central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. • The central nervous system consists of brain and ...
Artificial cell

An artificial cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. The term does not refer to a specific physical entity, but rather to the idea that certain functions or structures of biological cells can be replaced or supplemented with a synthetic entity. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, nanoparticles, liposomes, polymersomes, microcapsules and a number of other particles have qualified as artificial cells. Micro-encapsulation allows for metabolism within the membrane, exchange of small molecules and prevention of passage of large substances across it. The main advantages of encapsulation include improved mimicry in the body, increased solubility of the cargo and decreased immune responses. Notably, artificial cells have been clinically successful in hemoperfusion.In the area of synthetic biology, a ""living"" artificial cell has been defined as a completely synthetically made cell that can capture energy, maintain ion gradients, contain macromolecules as well as store information and have the ability to mutate. Such a cell is not technically feasible yet, but a variation of an artificial cell has been created in which a completely synthetic genome was introduced to genomically emptied host cells. Although not completely artificial because the cytoplasmic components as well as the membrane from the host cell are kept, the engineered cell is under control of a synthetic genome and is able to replicate.