Cell Theory - Teacher Pages
... biology • Credit for the formulation of this theory is given to: – Theodor Schwann – Matthias Schleiden – Rudolph Virchow ...
... biology • Credit for the formulation of this theory is given to: – Theodor Schwann – Matthias Schleiden – Rudolph Virchow ...
File
... and other materials would not be able to reach all parts of the cell quickly enough to keep it alive. 4) List five parts of all cells and their jobs (Mr. Gross’s Note: more than 5 are listed below). The cell’s nucleus contains chromosomes made of DNA, which contain instructions necessary for each ce ...
... and other materials would not be able to reach all parts of the cell quickly enough to keep it alive. 4) List five parts of all cells and their jobs (Mr. Gross’s Note: more than 5 are listed below). The cell’s nucleus contains chromosomes made of DNA, which contain instructions necessary for each ce ...
Unit 1 From Single Cells
... The smallest of these tubes are blood vessels so tiny that blood cells have to move through them in single file. In the respiratory system, air travels into and out of the lungs through tubes. The smallest tubes in tiny sacs called alveoli, which are surrounded by capillaries. 12. villi Nutrient ...
... The smallest of these tubes are blood vessels so tiny that blood cells have to move through them in single file. In the respiratory system, air travels into and out of the lungs through tubes. The smallest tubes in tiny sacs called alveoli, which are surrounded by capillaries. 12. villi Nutrient ...
Studying Life
... – Organs make up the organism (multi-cellular) – A group of similar organisms make up a population (of the same species… can reproduce) – Groups of populations make up a community (interacting or affecting each other) – The community and its non-living surrounding make up the ecosystem – All living ...
... – Organs make up the organism (multi-cellular) – A group of similar organisms make up a population (of the same species… can reproduce) – Groups of populations make up a community (interacting or affecting each other) – The community and its non-living surrounding make up the ecosystem – All living ...
Unit A - apel slice
... 1. Cells that work together to carry out a function make up a _____. 2. The group of organs and tissues that exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs is the _____. 3. A group of organs that work together to carry out life processes is an _____. 4. Tissues that work with your skeleton to help ...
... 1. Cells that work together to carry out a function make up a _____. 2. The group of organs and tissues that exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs is the _____. 3. A group of organs that work together to carry out life processes is an _____. 4. Tissues that work with your skeleton to help ...
Fun with Cells with the Amoeba Sisters
... What does a cell contain within itself, apart from the jelly like cytoplasm? And what do they do? But, wait. There are basically 2 kinds of cells, right? One that is found in simple life forms like amoeba. And such cells are called as prokaryotes. And the other that is found in complex life forms l ...
... What does a cell contain within itself, apart from the jelly like cytoplasm? And what do they do? But, wait. There are basically 2 kinds of cells, right? One that is found in simple life forms like amoeba. And such cells are called as prokaryotes. And the other that is found in complex life forms l ...
Studying cells_online activity
... 4. What type of microscope would allow you to study the orderly sequence of events that lead to the separation of chromosomes during mitosis? (Chromosomes are found inside of the cell's nucleus.) ...
... 4. What type of microscope would allow you to study the orderly sequence of events that lead to the separation of chromosomes during mitosis? (Chromosomes are found inside of the cell's nucleus.) ...
Activity: Cell Levels of Organization
... a. Main organ of Excretory system _____________ b. Cells which fight off foreign substances ____________ c. Helps blood to clot when there is a cut _____________ d. Blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart ___________ e. Has four chambers part of the Circulatory system___________ f. Where ...
... a. Main organ of Excretory system _____________ b. Cells which fight off foreign substances ____________ c. Helps blood to clot when there is a cut _____________ d. Blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart ___________ e. Has four chambers part of the Circulatory system___________ f. Where ...
7A Cells
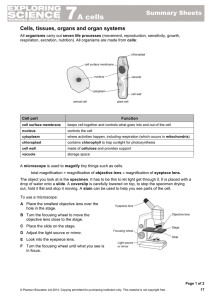
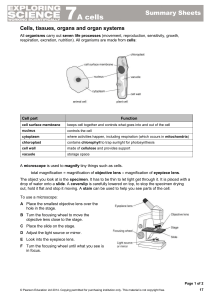
... drop of water onto a slide. A coverslip is carefully lowered on top, to stop the specimen drying out, hold it flat and stop it moving. A stain can be used to help you see parts of the cell. To use a microscope: A Place the smallest objective lens over the hole in the stage. B Turn the focusing wheel ...
... drop of water onto a slide. A coverslip is carefully lowered on top, to stop the specimen drying out, hold it flat and stop it moving. A stain can be used to help you see parts of the cell. To use a microscope: A Place the smallest objective lens over the hole in the stage. B Turn the focusing wheel ...
KS3 Science - Benjamin Britten School
... drop of water onto a slide. A coverslip is carefully lowered on top, to stop the specimen drying out, hold it flat and stop it moving. A stain can be used to help you see parts of the cell. To use a microscope: A Place the smallest objective lens over the hole in the stage. B Turn the focusing wheel ...
... drop of water onto a slide. A coverslip is carefully lowered on top, to stop the specimen drying out, hold it flat and stop it moving. A stain can be used to help you see parts of the cell. To use a microscope: A Place the smallest objective lens over the hole in the stage. B Turn the focusing wheel ...
7A cells
... drop of water onto a slide. A coverslip is carefully lowered on top, to stop the specimen drying out, hold it flat and stop it moving. A stain can be used to help you see parts of the cell. To use a microscope: A Place the smallest objective lens over the hole in the stage. B Turn the focusing wheel ...
... drop of water onto a slide. A coverslip is carefully lowered on top, to stop the specimen drying out, hold it flat and stop it moving. A stain can be used to help you see parts of the cell. To use a microscope: A Place the smallest objective lens over the hole in the stage. B Turn the focusing wheel ...
KS3 Science
... drop of water onto a slide. A coverslip is carefully lowered on top, to stop the specimen drying out, hold it flat and stop it moving. A stain can be used to help you see parts of the cell. To use a microscope: A Place the smallest objective lens over the hole in the stage. B Turn the focusing wheel ...
... drop of water onto a slide. A coverslip is carefully lowered on top, to stop the specimen drying out, hold it flat and stop it moving. A stain can be used to help you see parts of the cell. To use a microscope: A Place the smallest objective lens over the hole in the stage. B Turn the focusing wheel ...
NAME: : ______ DUE/DOQ
... 10. This organelle gives plant cells their shape and protects it from bursting: ______________________________________. ...
... 10. This organelle gives plant cells their shape and protects it from bursting: ______________________________________. ...
kakamega south cemtral districts mock examination
... daughter cells; while mitosis is a type of cell division where a single parent cell divides to form two diploid daughter cells; b) Lead to formation of haploid gamete cells who through fussion maintains the diploid state of ...
... daughter cells; while mitosis is a type of cell division where a single parent cell divides to form two diploid daughter cells; b) Lead to formation of haploid gamete cells who through fussion maintains the diploid state of ...
3. What two organelles are unique to plant cells? • cell wall: ______
... Which system is responsible for filtering chemical waste from the blood (other than CO2)? Use the organs in this system to explain. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ...
... Which system is responsible for filtering chemical waste from the blood (other than CO2)? Use the organs in this system to explain. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ...
General Biology Bozeman Cell Membrane video 1. Describe what
... General Biology Bozeman Cell Membrane video 1. Describe what selective permeability is. ...
... General Biology Bozeman Cell Membrane video 1. Describe what selective permeability is. ...
SNC2D – Biology Review
... - how to screen for cancer - diagnosing cancer - treatments for cancer 6. Stem Cells - embryonic vs. adult stem cells - pluripotent 7. The Animal Body – levels of organization and tissue types - relationship between cells ,tissues, organs, organ system - 4 types of tissues and examples - be able to ...
... - how to screen for cancer - diagnosing cancer - treatments for cancer 6. Stem Cells - embryonic vs. adult stem cells - pluripotent 7. The Animal Body – levels of organization and tissue types - relationship between cells ,tissues, organs, organ system - 4 types of tissues and examples - be able to ...
National 4/5 Biology - Multicelluar Organisms
... * Cells will vary in size, shape, and structure * - this allows these cells to perform different functions ...
... * Cells will vary in size, shape, and structure * - this allows these cells to perform different functions ...
Chapter 1 (C) Review
... _____ 7. Which of the following best describes an organ? a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. T ...
... _____ 7. Which of the following best describes an organ? a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. T ...
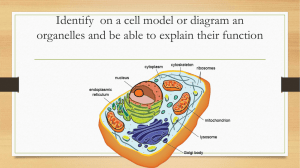
Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to
... Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to explain their function ...
... Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to explain their function ...
Cell Processes Overview
... 3. Diffusion in the digestive system - When we eat food, it gets broken down into smaller particles like amino acids (protein building blocks) and sugars. These particles move from the _______________ where the concentration is high to the _______________ where the concentration is low because of th ...
... 3. Diffusion in the digestive system - When we eat food, it gets broken down into smaller particles like amino acids (protein building blocks) and sugars. These particles move from the _______________ where the concentration is high to the _______________ where the concentration is low because of th ...
Ch. 4 Cells
... -Diffusion is: movement of molecules from greater concentration to lower conc. example: oxygen in alveoli to the blood Carbon dioxide in blood to the alveoli ...
... -Diffusion is: movement of molecules from greater concentration to lower conc. example: oxygen in alveoli to the blood Carbon dioxide in blood to the alveoli ...
Flyer Ces.pages
... ETH Hönggerberg, 04/05/2016 HCI J 7, 15.00 h The Seminar will be followed by an Apéro ...
... ETH Hönggerberg, 04/05/2016 HCI J 7, 15.00 h The Seminar will be followed by an Apéro ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Living Things
... 9. A. Animal Cell—B. Plant Cell I know this because the plant cell had a cell wall and a chloroplast; Which only plants have and not animals. And diagram B. had large vacuole in its cells, which again a plant has and the animal cells would only have small vacuole. 10. Reproduction, because an indiv ...
... 9. A. Animal Cell—B. Plant Cell I know this because the plant cell had a cell wall and a chloroplast; Which only plants have and not animals. And diagram B. had large vacuole in its cells, which again a plant has and the animal cells would only have small vacuole. 10. Reproduction, because an indiv ...
Artificial cell

An artificial cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. The term does not refer to a specific physical entity, but rather to the idea that certain functions or structures of biological cells can be replaced or supplemented with a synthetic entity. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, nanoparticles, liposomes, polymersomes, microcapsules and a number of other particles have qualified as artificial cells. Micro-encapsulation allows for metabolism within the membrane, exchange of small molecules and prevention of passage of large substances across it. The main advantages of encapsulation include improved mimicry in the body, increased solubility of the cargo and decreased immune responses. Notably, artificial cells have been clinically successful in hemoperfusion.In the area of synthetic biology, a ""living"" artificial cell has been defined as a completely synthetically made cell that can capture energy, maintain ion gradients, contain macromolecules as well as store information and have the ability to mutate. Such a cell is not technically feasible yet, but a variation of an artificial cell has been created in which a completely synthetic genome was introduced to genomically emptied host cells. Although not completely artificial because the cytoplasmic components as well as the membrane from the host cell are kept, the engineered cell is under control of a synthetic genome and is able to replicate.