Nervous System: General Principles
... Neurotransmission • Electrical signal (action potential (AP)) descends axon to synaptic knob (nerve end) • Depolarization opens Ca++ channels to open in presynaptic membrane • Triggers a number of synaptic vesicles to fuse with outer membrane • Dumps neurotransmitter (NT) into synaptic cleft • NT d ...
... Neurotransmission • Electrical signal (action potential (AP)) descends axon to synaptic knob (nerve end) • Depolarization opens Ca++ channels to open in presynaptic membrane • Triggers a number of synaptic vesicles to fuse with outer membrane • Dumps neurotransmitter (NT) into synaptic cleft • NT d ...
What is mental life
... myocarditis and seizures at very high doses o Sedation, weight gain, orthostatic hypotension. o This is a GREAT drug but you must first fail two other drugs before you can be started on this because of serious side effect risks. ...
... myocarditis and seizures at very high doses o Sedation, weight gain, orthostatic hypotension. o This is a GREAT drug but you must first fail two other drugs before you can be started on this because of serious side effect risks. ...
introduction – what is parkinson`s disease?
... • Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a chronic and progressive movement disorder characterised by: – Coordination problems – Slowed movements – Generalised tremor • It is the second most common neurodegenerative disease and affects 1-2% of people over 60. There are currently more than 4 million people suff ...
... • Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a chronic and progressive movement disorder characterised by: – Coordination problems – Slowed movements – Generalised tremor • It is the second most common neurodegenerative disease and affects 1-2% of people over 60. There are currently more than 4 million people suff ...
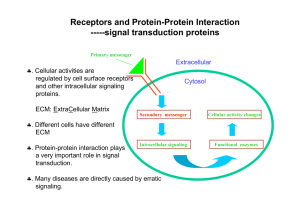
Receptors and Protein-Protein Interaction ----
... A. Abnormal level of hormones, Such as GABA ↓ ⇔ Epilepsy seizures, convulsions Adjust hormone level by metabolic intervention Adjust hormone level by agonists and antagonists. ...
... A. Abnormal level of hormones, Such as GABA ↓ ⇔ Epilepsy seizures, convulsions Adjust hormone level by metabolic intervention Adjust hormone level by agonists and antagonists. ...
Write down on your post it note
... drugs can have on the body To consider the reasons why people start using drugs ...
... drugs can have on the body To consider the reasons why people start using drugs ...
Lexapro Information
... 10mg. = placebo in # pt.’s discontinuing treatment secondary to adverse reactions. 3. Study 3 – comparing escitalopram with Celexa. Separation from placebo at week one seen with escitalopram 4. Study 4 – completers from 8 week trial randomized to 36 weeks double blind (placebo vs. continued escita ...
... 10mg. = placebo in # pt.’s discontinuing treatment secondary to adverse reactions. 3. Study 3 – comparing escitalopram with Celexa. Separation from placebo at week one seen with escitalopram 4. Study 4 – completers from 8 week trial randomized to 36 weeks double blind (placebo vs. continued escita ...
9-12-04 Intro Terminol
... – Location within the body where the drug exerts its therapeutic effect • E.g. aspirin acts at the hypothalamus to reduce fever ...
... – Location within the body where the drug exerts its therapeutic effect • E.g. aspirin acts at the hypothalamus to reduce fever ...
Chapter 1 - Drugs and Agents - Factors Affecting their Action
... Study of how drugs may best be used in the treatment of illnesses Study of which drug would be most appropriate or least appropriate to use for a specific disease; what dose would be required; etc. ...
... Study of how drugs may best be used in the treatment of illnesses Study of which drug would be most appropriate or least appropriate to use for a specific disease; what dose would be required; etc. ...
Chapter 16 Cholinesterase Inhibitors
... Serotonin, glucocorticoids, substance P, neurokinin1, dopamine, acetylcholine, and histamine Many antiemetics interact with one or more of the receptors ...
... Serotonin, glucocorticoids, substance P, neurokinin1, dopamine, acetylcholine, and histamine Many antiemetics interact with one or more of the receptors ...
H. Sodium Channel Blockers
... A. Absorption 1. Time the drug enters the body until it gets into the bloodstream 2. Affected by dosage form, route, GI motility B. Distribution 1. Drug distributed to site of action 2. Protein binding 3. Blood brain barrier C. Metabolism 1. Liver 2. Hepatic First Pass Effect 3. Infants and Elderly ...
... A. Absorption 1. Time the drug enters the body until it gets into the bloodstream 2. Affected by dosage form, route, GI motility B. Distribution 1. Drug distributed to site of action 2. Protein binding 3. Blood brain barrier C. Metabolism 1. Liver 2. Hepatic First Pass Effect 3. Infants and Elderly ...
I. The direct-acting drugs
... chemical structures and mechanism of action To understand major pharmacological effects and therapeutic applications To understand major adverse reactions ...
... chemical structures and mechanism of action To understand major pharmacological effects and therapeutic applications To understand major adverse reactions ...
ISHIK UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY
... Enteric coated tablets: The drugs which are destroyed by the gastric juices in the stomach, arecoated with keratin, shellac and cellulose acid phosphate. These substances are not dissolved by the acid juice of the stomach, but are dissolved in the intestinal juice (alkaline) only. ◦ Preventing gas ...
... Enteric coated tablets: The drugs which are destroyed by the gastric juices in the stomach, arecoated with keratin, shellac and cellulose acid phosphate. These substances are not dissolved by the acid juice of the stomach, but are dissolved in the intestinal juice (alkaline) only. ◦ Preventing gas ...
Bromo-DragonFly DragonFly
... LSD. The chemical name of the drug is bromobenzodifuranyl-isopropylamine; the common name, bromo-dragonfly, is based upon the shape of the chemical structure which can be viewed as resembling a dragonfly. The drug is typically sold either as a powder or spotted on blotter paper. ...
... LSD. The chemical name of the drug is bromobenzodifuranyl-isopropylamine; the common name, bromo-dragonfly, is based upon the shape of the chemical structure which can be viewed as resembling a dragonfly. The drug is typically sold either as a powder or spotted on blotter paper. ...
Losartar is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist drug used mainly to
... account for its nephroprotective effects.[4] Effects on TGF-β expression may also ...
... account for its nephroprotective effects.[4] Effects on TGF-β expression may also ...
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior
... •Studies have shown that alcohol impairs memory by suppressing the processing of events into long term memory. •Alcohol impairs REM sleep, further disrupting memory storage. C. Stimulants Stimulants ...
... •Studies have shown that alcohol impairs memory by suppressing the processing of events into long term memory. •Alcohol impairs REM sleep, further disrupting memory storage. C. Stimulants Stimulants ...
5-HT2a – receptor agonist
... hallucinations and irrational behavior, myosis) • MDMA-like chemical structure + weak inhibitor MAO • extremely long time before peak (4-7 hours), effects last for 24-72 hours ...
... hallucinations and irrational behavior, myosis) • MDMA-like chemical structure + weak inhibitor MAO • extremely long time before peak (4-7 hours), effects last for 24-72 hours ...
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY
... BZ Diazepam (valium) Lorazepam (lorivan) Clonazepam (clonex) Alprazolam (xanax) Brotizolam (bondormin) ...
... BZ Diazepam (valium) Lorazepam (lorivan) Clonazepam (clonex) Alprazolam (xanax) Brotizolam (bondormin) ...
4F_O`Dwyer_understanding recovery NO GRAPHICS
... • Finding integrated treatment programs for clients in the justice system • Jails are becoming surrogate mental hospitals • Youth and juvenile justice system experience substantially higher rates of mental disorders than the general population • At least 1 in 5 have a serious mental disorder • Adult ...
... • Finding integrated treatment programs for clients in the justice system • Jails are becoming surrogate mental hospitals • Youth and juvenile justice system experience substantially higher rates of mental disorders than the general population • At least 1 in 5 have a serious mental disorder • Adult ...
5-HT receptor - Pharmatutor
... The serotonin receptors also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors or 5-HT receptors are a group of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) found in the central and peripheral nervous systems.[1][2] They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The ...
... The serotonin receptors also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors or 5-HT receptors are a group of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) found in the central and peripheral nervous systems.[1][2] They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The ...
Collecting Data --- Experiments Example: testing of new
... doctor know which is given to the subject. (to minimize psychological effects, also called placebo effects) • Only a high level committee know. ...
... doctor know which is given to the subject. (to minimize psychological effects, also called placebo effects) • Only a high level committee know. ...
Caffeine
... • Caffeine antagonizes the adenosine A1 receptor & inhibits phosphodiesterase resulting in an increase in both adenylyl cyclase activity and cAMP formation. • Further, voltage-gated calcium channels are open which allows calcium entry and potassium channels are blocked. • This allows the cell to be ...
... • Caffeine antagonizes the adenosine A1 receptor & inhibits phosphodiesterase resulting in an increase in both adenylyl cyclase activity and cAMP formation. • Further, voltage-gated calcium channels are open which allows calcium entry and potassium channels are blocked. • This allows the cell to be ...
Slide 1
... When you are assessing him, his breathing becomes more labored and eventually he has to be intubated. He progressively becomes hypotensive and requires pressors. An TTE is done at the bedside and reveals severe dilated cardiomyopathy with an EF of 15%. What is the offending drug? ...
... When you are assessing him, his breathing becomes more labored and eventually he has to be intubated. He progressively becomes hypotensive and requires pressors. An TTE is done at the bedside and reveals severe dilated cardiomyopathy with an EF of 15%. What is the offending drug? ...