![[Fe(NH 3 ) 6 ] 2+ Finding optimal parameters for spin](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008100713_1-7d638d4cd4cd73a8d1a509d7fe17060e-300x300.png)
[Fe(NH 3 ) 6 ] 2+ Finding optimal parameters for spin
... binding functions. Computer modelling can help probe their properties but few methods exist that model transition metalcontaining proteins effectively, either using quantum or classical mechanical methods. Here is outlined a very promising new molecular modelling approach to deal with transition met ...
... binding functions. Computer modelling can help probe their properties but few methods exist that model transition metalcontaining proteins effectively, either using quantum or classical mechanical methods. Here is outlined a very promising new molecular modelling approach to deal with transition met ...
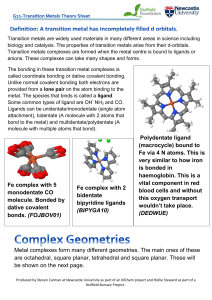
Polydentate ligand (macrocycle) bound to Fe via 4 N atoms. This is
... wouldn’t take place. (DEDWUE) ...
... wouldn’t take place. (DEDWUE) ...
Electronic Spectra
... ground state of the free ion (2D) is again split into 2T2g and 2Eg but this ion consists of 2Eg term with lower energy than 2T2g. The d9 and d1 configurations are related by a positive hole concept. For d9 ion in an octahedral field, the splitting diagram is an inversion of that for the octahedral d ...
... ground state of the free ion (2D) is again split into 2T2g and 2Eg but this ion consists of 2Eg term with lower energy than 2T2g. The d9 and d1 configurations are related by a positive hole concept. For d9 ion in an octahedral field, the splitting diagram is an inversion of that for the octahedral d ...
InorgCh11.1
... 1. Electron-Electron Interactions complicate the spectra of multi-electron species 2. Example: [V(H2O)6]3+ is an octahedral d2 metal ion [V(H2O)6]3+ ...
... 1. Electron-Electron Interactions complicate the spectra of multi-electron species 2. Example: [V(H2O)6]3+ is an octahedral d2 metal ion [V(H2O)6]3+ ...
13.2: First Row D
... – In free ions, the five D orbitals are degenerate (have the same energy) – In complex ions, the orbitals are split into 2 distinct energy levels ...
... – In free ions, the five D orbitals are degenerate (have the same energy) – In complex ions, the orbitals are split into 2 distinct energy levels ...
all work must be shown to receive full credit
... or at a shorter wavelength (assume low spin configuration is maintained)? According to the spectrochemical series H2O is a weaker field ligand that NH3. Therefore, the crystal field splitting Δ will be smaller and the absorption maximum will be shifted to longer wavelengths. 2. [6 points] The follow ...
... or at a shorter wavelength (assume low spin configuration is maintained)? According to the spectrochemical series H2O is a weaker field ligand that NH3. Therefore, the crystal field splitting Δ will be smaller and the absorption maximum will be shifted to longer wavelengths. 2. [6 points] The follow ...
TRANSITION METALS - Pennsylvania State University
... temp applications, e.g. in the reentry shield on the Apollo capsules. TiO2 is a white pigment in all white paints. V Vanadium steel (Fe/V alloy) is the toughest steel known. It is used in car springs. V2O5 is a catalyst used in sulfuric acid production. ...
... temp applications, e.g. in the reentry shield on the Apollo capsules. TiO2 is a white pigment in all white paints. V Vanadium steel (Fe/V alloy) is the toughest steel known. It is used in car springs. V2O5 is a catalyst used in sulfuric acid production. ...
CH 23 HW
... 11. How crystal field theory explains that approaching ligands cause d-orbital energies to split (§23.4) 12. How the relative crystal field strength of ligands (spectrochemical series) affects the d-orbital splitting energy (∆) (§23.4) 13. How the magnitude of ∆ accounts for the energy of light abso ...
... 11. How crystal field theory explains that approaching ligands cause d-orbital energies to split (§23.4) 12. How the relative crystal field strength of ligands (spectrochemical series) affects the d-orbital splitting energy (∆) (§23.4) 13. How the magnitude of ∆ accounts for the energy of light abso ...
A1988Q406700001
... plexes of atom-ions. V02+ have appeared since my review, there I believed then—and still believe—that per- have been valuable summaries of selected haps the best, simplest, and most stable and areas of research, such as the 2~inorganic and persistent such molecule-cation is VO~,oxo- biochemical aspe ...
... plexes of atom-ions. V02+ have appeared since my review, there I believed then—and still believe—that per- have been valuable summaries of selected haps the best, simplest, and most stable and areas of research, such as the 2~inorganic and persistent such molecule-cation is VO~,oxo- biochemical aspe ...
Crystal field theory (II) Octahedral complexes and Jahn
... The splitting of d orbitals contradicts with those found in the octahedral complex. The donor atoms in tetrahedral coordination do not overlap well with the metal d‐orbitals, so that Δtet is much smaller than Δoct in octahedral complexes with the same ligands ...
... The splitting of d orbitals contradicts with those found in the octahedral complex. The donor atoms in tetrahedral coordination do not overlap well with the metal d‐orbitals, so that Δtet is much smaller than Δoct in octahedral complexes with the same ligands ...
Spin crossover

Spin Crossover (SCO), sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior, is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to external stimuli such as a variation of temperature, pressure, light irradiation or an influence of a magnetic field.With regard to a ligand field and ligand field theory, the change in spin state is a transition from a low spin (LS) ground state electron configuration to a high spin (HS) ground state electron configuration of the metal’s d atomic orbitals (AOs), or vice versa. The magnitude of the ligand field splitting along with the pairing energy of the complex determines whether it will have a LS or HS electron configuration. A LS state occurs because the ligand field splitting (Δ) is greater than the pairing energy of the complex (which is an unfavorable process).Figure 1 is a simplified illustration of the metal’s d orbital splitting in the presence of an octahedral ligand field. A large splitting between the t2g and eg AOs requires a substantial amount of energy for the electrons to overcome the energy gap (Δ) to comply with Hund’s Rule. Therefore, electrons will fill the lower energy t2g orbitals completely before populating the higher energy eg orbitals. Conversely, a HS state occurs with weaker ligand fields and smaller orbital splitting. In this case the energy required to populate the higher levels is substantially less than the pairing energy and the electrons fill the orbitals according to Hund’s Rule by populating the higher energy orbitals before pairing with electrons in the lower lying orbitals. An example of a metal ion that can exist in either a LS or HS state is Fe3+ in an octahedral ligand field. Depending on the ligands that are coordinated to this complex the Fe3+ can attain a LS or a HS state, as in Figure 1.Spin crossover refers to the transitions between high to low, or low to high, spin states. This phenomenon is commonly observed with some first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves are a common representation of SCO phenomenon with the most commonly observed types depicted in Figure 2 in which γHS (the high-spin molar fraction) is plotted vs. T. The figure shows a gradual spin transition (left), an abrupt transition with hysteresis (middle) and a two-step transition (right). For a transition to be considered gradual, it typically takes place over a large temperature range, even up to several hundred K, whereas for a transition to be considered abrupt, it should take place within 10 K or less.These curves indicate that a spin transition has occurred in a metal complex as temperature changed. The gradual transition curve is an indication that not all metal centers within the complex are undergoing the transition at the same temperature. The abrupt spin change with hysteresis indicates a strong cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of external stimuli (temperature in this case) for the two phenomena, namely LS → HS and HS → LS. The two-step transition is relatively rare but is observed, for example, with dinuclear SCO complexes for which the spin transition in one metal center renders the transition in the second metal center less favorable.There are several types of spin crossover that can occur in a complex; some of them are light induced excited state spin trapping (LIESST), ligand-driven light induced spin change (LD-LISC), and charge transfer induced spin transition (CTIST).