Scanning the Human Body
... images of the organs and tissues within your body. • The magnetic field temporarily realigns hydrogen atoms in your body. Radio waves cause these aligned atoms to produce very faint signals, which are used to create crosssectional MRI images — like slices in a loaf of bread • An fMRI (functional MRI ...
... images of the organs and tissues within your body. • The magnetic field temporarily realigns hydrogen atoms in your body. Radio waves cause these aligned atoms to produce very faint signals, which are used to create crosssectional MRI images — like slices in a loaf of bread • An fMRI (functional MRI ...
Central Nervous System
... • Composed of two structures – Thalamus • Encloses third ventricle • Relay station for sensory impulses ...
... • Composed of two structures – Thalamus • Encloses third ventricle • Relay station for sensory impulses ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... The chemical component of neural communication is accomplished through neurotransmitters released at the synapse ...
... The chemical component of neural communication is accomplished through neurotransmitters released at the synapse ...
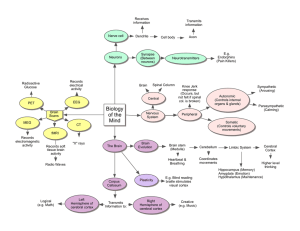
How Does the Brain Work?
... The outermost layer, the cerebral cortex, is a fraction of an inch thick but contains 70 percent of all neurons. This most evolved part of the brain is divided into lobes specialized to regulate sensory experience, language and memory, and our sense of space. The frontal lobe is the most distinctive ...
... The outermost layer, the cerebral cortex, is a fraction of an inch thick but contains 70 percent of all neurons. This most evolved part of the brain is divided into lobes specialized to regulate sensory experience, language and memory, and our sense of space. The frontal lobe is the most distinctive ...
Ch. 3 Discovering Psy Behaving Brain Video
... 1. In the beginning of the video, Philip Zimbardo compared our brain to a _____________. 2. The human brain houses approximately _____________ number of brain cells. 3. Neurons and glia are designed to do 3 things: a. ___________________________________________________________ b. ___________________ ...
... 1. In the beginning of the video, Philip Zimbardo compared our brain to a _____________. 2. The human brain houses approximately _____________ number of brain cells. 3. Neurons and glia are designed to do 3 things: a. ___________________________________________________________ b. ___________________ ...
specimen jar craft - National Wildlife Federation
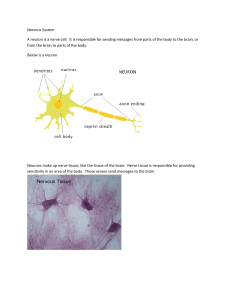
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually ...
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually ...
46 Chapter Review: Fill-in-the
... is the ability of the brain to reorganize and compensate for brain damage. 19. The branchlike extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons are called the 20. The is a set of inheritance rules in which the presence of a single dominant gene causes a trait to be expressed but two gen ...
... is the ability of the brain to reorganize and compensate for brain damage. 19. The branchlike extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons are called the 20. The is a set of inheritance rules in which the presence of a single dominant gene causes a trait to be expressed but two gen ...
Abstract n Bio - Prof Arto Nurmikko
... electrical microcircuits in the brain has been a central research topic of modern neuroscience for at least a century. More recently, engineers, physicists, and mathematicians have been bringing their tools of trade to both experimental and theoretical research in brain science. Pursu ...
... electrical microcircuits in the brain has been a central research topic of modern neuroscience for at least a century. More recently, engineers, physicists, and mathematicians have been bringing their tools of trade to both experimental and theoretical research in brain science. Pursu ...
The Promise and Peril of Tomorrow`s Neuroscience
... specifically define what the mind is. On the other hand, the book goes into great detail in explaining how human beings evolved over time with particular attention to the human brain. One of the great strengths of the human brain is its “plasticity” – its ability to assemble and disassemble neurons ...
... specifically define what the mind is. On the other hand, the book goes into great detail in explaining how human beings evolved over time with particular attention to the human brain. One of the great strengths of the human brain is its “plasticity” – its ability to assemble and disassemble neurons ...
connectome - LjcdsNeuro2011
... Timeline of brain research • 450BC The Greek physician Alcmaeon concludes that the brain is the central organ for sensation and not the heart as previously believed by Pythagorian thinkers. • 300BC The first detailed account of the structure of the brain is completed by the Alexandrian biologists H ...
... Timeline of brain research • 450BC The Greek physician Alcmaeon concludes that the brain is the central organ for sensation and not the heart as previously believed by Pythagorian thinkers. • 300BC The first detailed account of the structure of the brain is completed by the Alexandrian biologists H ...
MAPPINGS BETWEEN BRAINS - Wichita State University
... triggered only by specific stimuli falling on specific areas of the retina. • Once the lateral geniculate neurons are triggered, in returning to the visual cortex; if they are hypercomplex cells what happens next? ...
... triggered only by specific stimuli falling on specific areas of the retina. • Once the lateral geniculate neurons are triggered, in returning to the visual cortex; if they are hypercomplex cells what happens next? ...
The Anatomy of the Sheep Brain
... Anatomically, the human brain shares many basic structures and brain areas with the brains of other animals. For example, in the sheep brain (see Image below), one observes a cerebrum, a brain stem, cerebellum, medulla oblongata and glands, such as the pineal gland and the pituitary gland. Like the ...
... Anatomically, the human brain shares many basic structures and brain areas with the brains of other animals. For example, in the sheep brain (see Image below), one observes a cerebrum, a brain stem, cerebellum, medulla oblongata and glands, such as the pineal gland and the pituitary gland. Like the ...
CNS
... CNS: Spinal Cord Anatomy • Central canal with gray matter surrounded by white matter. • The central canal contains cerebrospinal fluid. • Portions of sensory and motor neurons reside in the gray matter as do interneurons. The posterior root of a spinal nerve enters here and the anterior root (conta ...
... CNS: Spinal Cord Anatomy • Central canal with gray matter surrounded by white matter. • The central canal contains cerebrospinal fluid. • Portions of sensory and motor neurons reside in the gray matter as do interneurons. The posterior root of a spinal nerve enters here and the anterior root (conta ...
PPT Guide Brain Development
... In the months after birth the brain grows rapidly, producing billions of neurons, dendrites and axons, as well as synapses reaching its peak around the infant’s first birthday. In the first 2 years, the brain increases in size from ______ to _____ of its adult weight. Soon after, synapses soon to gr ...
... In the months after birth the brain grows rapidly, producing billions of neurons, dendrites and axons, as well as synapses reaching its peak around the infant’s first birthday. In the first 2 years, the brain increases in size from ______ to _____ of its adult weight. Soon after, synapses soon to gr ...
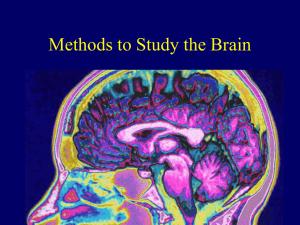
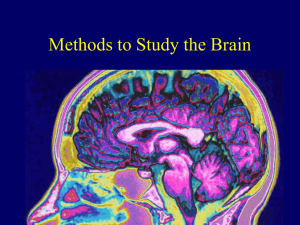
Module 11: Methods to Study the Brain
... • Much-improved version of x-ray imaging. • Takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a three-dimensional image. ...
... • Much-improved version of x-ray imaging. • Takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a three-dimensional image. ...
Module 11: Methods to Study the Brain
... • Much-improved version of x-ray imaging. • Takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a three-dimensional image. ...
... • Much-improved version of x-ray imaging. • Takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a three-dimensional image. ...
Diencephalon sists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla.
... The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull and is made up of billions of nerve cells (neurons) and supporting cells (glia). Neuronal cell bodies group together as gray matter, and their processes group together as white matter. The brain can be divided into four main parts: the cerebrum, ...
... The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull and is made up of billions of nerve cells (neurons) and supporting cells (glia). Neuronal cell bodies group together as gray matter, and their processes group together as white matter. The brain can be divided into four main parts: the cerebrum, ...
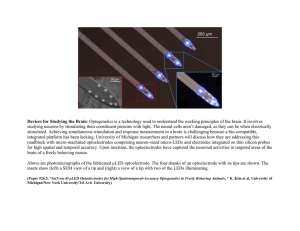
26-5 Devices for Studying the Brain
... Devices for Studying the Brain: Optogenetics is a technology used to understand the working principles of the brain. It involves studying neurons by stimulating their constituent proteins with light. The neural cells aren’t damaged, as they can be when electrically stimulated. Achieving simultaneous ...
... Devices for Studying the Brain: Optogenetics is a technology used to understand the working principles of the brain. It involves studying neurons by stimulating their constituent proteins with light. The neural cells aren’t damaged, as they can be when electrically stimulated. Achieving simultaneous ...
Brain anatomy Guide 9/22
... Anatomy of the Brain video guide THE BRAIN: 1. Structure:______________________________________________ 2. Function:_______________________________________________ 3. Structure is sometimes referred to as_________________________ 4. Function is sometimes referred to as _________________________ 5. T ...
... Anatomy of the Brain video guide THE BRAIN: 1. Structure:______________________________________________ 2. Function:_______________________________________________ 3. Structure is sometimes referred to as_________________________ 4. Function is sometimes referred to as _________________________ 5. T ...