Patterns of neuronal migration in the embryonic cortex
... that translocation might be the major mode of migration for cortical neurons [53]. However, the Golgi method fails to label freely migrating neurons that are known to be present during embryonic ages (e.g. interneurons), and it is often difficult to phenotype cells based on morphology alone. Brittis ...
... that translocation might be the major mode of migration for cortical neurons [53]. However, the Golgi method fails to label freely migrating neurons that are known to be present during embryonic ages (e.g. interneurons), and it is often difficult to phenotype cells based on morphology alone. Brittis ...
Axon
... b. Which glial cell protects the CNS from chemicals and hormones circulating in the blood? c. Which type of neuroglia would occur in increased numbers in the brain tissue of a person with a CNS infection? © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... b. Which glial cell protects the CNS from chemicals and hormones circulating in the blood? c. Which type of neuroglia would occur in increased numbers in the brain tissue of a person with a CNS infection? © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
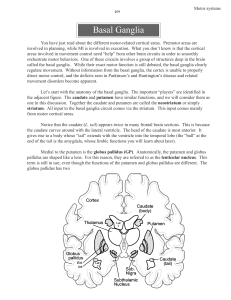
Motor systems Basal ganglia
... nucleus. This is the subthalamic nucleus. This nucleus lies just above the rostral portion of the substantia nigra (levels 13, 14). Cells in GP(external) project to the subthalamic nucleus. Cells in the subthalamic nucleus then project to GP(internal), which in turn projects to VA/VL. So, the indire ...
... nucleus. This is the subthalamic nucleus. This nucleus lies just above the rostral portion of the substantia nigra (levels 13, 14). Cells in GP(external) project to the subthalamic nucleus. Cells in the subthalamic nucleus then project to GP(internal), which in turn projects to VA/VL. So, the indire ...
Reprint () - Centre de recherche CERVO
... consistently showed up after all injections made into SP5i. Collectively, these axons project to a number of sites in the thalamus and upper brainstem. The most robust projections are to the superior colliculus, the pretectum, the ventral division of the zona incerta (ZIv), and the prerubral field, ...
... consistently showed up after all injections made into SP5i. Collectively, these axons project to a number of sites in the thalamus and upper brainstem. The most robust projections are to the superior colliculus, the pretectum, the ventral division of the zona incerta (ZIv), and the prerubral field, ...
Cortical projections to the nucleus of the optic tract and dorsal
... project to the dorsal cap of the inferior olive (e.g., Hoffmann and Schoppmann, 1975; Hoffmann et al., 1988); jerk neurons that respond to saccade-like stimulus movement (e.g., Ballas and Hoffmann, 1985) and project to the lateralis posterior nucleus of the thalamus (Sudkamp and Schmidt, 1995); and ...
... project to the dorsal cap of the inferior olive (e.g., Hoffmann and Schoppmann, 1975; Hoffmann et al., 1988); jerk neurons that respond to saccade-like stimulus movement (e.g., Ballas and Hoffmann, 1985) and project to the lateralis posterior nucleus of the thalamus (Sudkamp and Schmidt, 1995); and ...
neural circuitry approaches to understanding the pathophysiology
... However, in recent years, these two general approaches have given way to neural circuitry-based models that reflect a fuller appreciation of the fact that neurotransmitters act in an anatomically constrained fashion to produce specific biochemical effects at the cellular level, and that the localiza ...
... However, in recent years, these two general approaches have given way to neural circuitry-based models that reflect a fuller appreciation of the fact that neurotransmitters act in an anatomically constrained fashion to produce specific biochemical effects at the cellular level, and that the localiza ...
Document
... Influence muscular activity – particularly starting and stopping movements and regulating the intensity of these movements particularly those that are slow and stereotyped like arm swinging while ...
... Influence muscular activity – particularly starting and stopping movements and regulating the intensity of these movements particularly those that are slow and stereotyped like arm swinging while ...
Engagement of brain areas implicated in processing inner speech in
... intention to speak (rather than articulation per se) se) and mediated by the direct anatomical connections linking areas that generate and perceive speech, within the left inferior frontal and bilateral temporal cortices respectively. Contemporary cognitive models propose that auditory verbal halluc ...
... intention to speak (rather than articulation per se) se) and mediated by the direct anatomical connections linking areas that generate and perceive speech, within the left inferior frontal and bilateral temporal cortices respectively. Contemporary cognitive models propose that auditory verbal halluc ...
[3h]cyclohexyladenosine
... autoradiographic grains will be associated with specific adenosine receptor binding sites. Scatchard analysis of the binding indicates a dissociation constant (Ko) of 0.77 nM and a maximal number of binding sites (B,,,) of 423 fmol/mg of protein (Fig. 1A). These KO and B,,, values are about the same ...
... autoradiographic grains will be associated with specific adenosine receptor binding sites. Scatchard analysis of the binding indicates a dissociation constant (Ko) of 0.77 nM and a maximal number of binding sites (B,,,) of 423 fmol/mg of protein (Fig. 1A). These KO and B,,, values are about the same ...
A Self-Organizing Neural Network for Contour Integration through Synchronized Firing
... the correlation coefficient r as calculated by equation 3. When the contour elements are smooth, the MUAs are highly correlated, but the correlation is very low when the contour elements are randomly oriented relative to each other. This indicates that the network binds smooth contours together thro ...
... the correlation coefficient r as calculated by equation 3. When the contour elements are smooth, the MUAs are highly correlated, but the correlation is very low when the contour elements are randomly oriented relative to each other. This indicates that the network binds smooth contours together thro ...
Kenedy,Dehay Cell-cycle control and cortical development
... between modes are not completely understood46. Mechanisms determining neuron number. The computations carried out by the cerebral cortex require specific patterns of connections between precise numbers of diverse types of neurons51. One possibility is that there is a tight spatio-temporal control of ...
... between modes are not completely understood46. Mechanisms determining neuron number. The computations carried out by the cerebral cortex require specific patterns of connections between precise numbers of diverse types of neurons51. One possibility is that there is a tight spatio-temporal control of ...
Cell-cycle control and cortical development - Stem
... between modes are not completely understood46. Mechanisms determining neuron number. The computations carried out by the cerebral cortex require specific patterns of connections between precise numbers of diverse types of neurons51. One possibility is that there is a tight spatio-temporal control of ...
... between modes are not completely understood46. Mechanisms determining neuron number. The computations carried out by the cerebral cortex require specific patterns of connections between precise numbers of diverse types of neurons51. One possibility is that there is a tight spatio-temporal control of ...
The W cell pathway to cat primary visual cortex
... JOHN C. ANDERSON, NUNO MAÇARICO DA COSTA,* AND KEVAN A.C. MARTIN Institute for Neuroinformatics, University of Zürich, and ETH Zürich, 8057 Zürich, Switzerland ...
... JOHN C. ANDERSON, NUNO MAÇARICO DA COSTA,* AND KEVAN A.C. MARTIN Institute for Neuroinformatics, University of Zürich, and ETH Zürich, 8057 Zürich, Switzerland ...
Aging reduces total neuron number in the dorsal component of the
... For cresyl violet staining, a 1:5 series of sections was mounted onto coated slides, dried, and stained in 2.5% cresyl violet acetate (Sigma, St. Louis, MO). Stained slides were then dehydrated through increasing concentrations of ethanol, cleared with Citrisolv, and coverslipped under Permount. For ...
... For cresyl violet staining, a 1:5 series of sections was mounted onto coated slides, dried, and stained in 2.5% cresyl violet acetate (Sigma, St. Louis, MO). Stained slides were then dehydrated through increasing concentrations of ethanol, cleared with Citrisolv, and coverslipped under Permount. For ...
The Fraction of Cortical GABAergic Neurons Is Constant from Near
... neurons generated in the ganglionic eminences by counting on sections the fraction of all GAD67 ⫹ cells that are present in each of three zones: (1) the cortical plate (including cells in the upper intermediate zone) where nearly all GABAergic neurons ultimately reside, (2) the superficial migratory ...
... neurons generated in the ganglionic eminences by counting on sections the fraction of all GAD67 ⫹ cells that are present in each of three zones: (1) the cortical plate (including cells in the upper intermediate zone) where nearly all GABAergic neurons ultimately reside, (2) the superficial migratory ...
String Art: Axon Tracts in the Spinal Cord Spinal reflex arcs
... Upper (open) medulla Cerebellum ...
... Upper (open) medulla Cerebellum ...
Expression of Cux-1 and Cux-2 in the Subventricular Zone and
... Little is known about how neurons in the different layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex are specified at the molecular level. Expression of two homologues of the Drosophila homeobox Cut gene, Cux-1 and Cux-2, is strikingly specific to the pyramidal neurons of the upper layers (II–IV) of the murine ...
... Little is known about how neurons in the different layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex are specified at the molecular level. Expression of two homologues of the Drosophila homeobox Cut gene, Cux-1 and Cux-2, is strikingly specific to the pyramidal neurons of the upper layers (II–IV) of the murine ...
Primary Motor Cortex
... hemispheres • Third ventricle in the diencephalon • Fourth ventricle in the hindbrain, dorsal to the pons, develops from the lumen of the neural ...
... hemispheres • Third ventricle in the diencephalon • Fourth ventricle in the hindbrain, dorsal to the pons, develops from the lumen of the neural ...
Primary Motor Cortex
... hemispheres • Third ventricle in the diencephalon • Fourth ventricle in the hindbrain, dorsal to the pons, develops from the lumen of the neural ...
... hemispheres • Third ventricle in the diencephalon • Fourth ventricle in the hindbrain, dorsal to the pons, develops from the lumen of the neural ...
A Critical Review of the Role of the Proposed VMpo Nucleus in Pain
... Recordings were made by Dostrovsky and Craig48 from a sample of 27 monkey lamina I STT cells that were antidromically activated from the region of what Craig and colleagues regard as the VMpo nucleus (Fig 3A). Of these, 20 were classified as cold cells (activated specifically by cooling stimuli; Fig ...
... Recordings were made by Dostrovsky and Craig48 from a sample of 27 monkey lamina I STT cells that were antidromically activated from the region of what Craig and colleagues regard as the VMpo nucleus (Fig 3A). Of these, 20 were classified as cold cells (activated specifically by cooling stimuli; Fig ...
Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Placement and Functional
... (Hersch and White 1981; LeVay 1973; Parnavelas et al. 1977). These asymmetric synapses, classified as type 1 synapses, are innervated by axons of glutamatergic neurons (Baude et al. 1993). While there are a few reports of specific cell regions on particular types of neurons where type 1 synapses are ...
... (Hersch and White 1981; LeVay 1973; Parnavelas et al. 1977). These asymmetric synapses, classified as type 1 synapses, are innervated by axons of glutamatergic neurons (Baude et al. 1993). While there are a few reports of specific cell regions on particular types of neurons where type 1 synapses are ...
PDF file
... models of the 6-layer architecture of the laminar cortex have been shown to have computational advantage over single-layer models of the cortex. In this study, we present a temporal model of the laminar cortex that applies expectation feedback signals as top-down temporal context in a binocular netw ...
... models of the 6-layer architecture of the laminar cortex have been shown to have computational advantage over single-layer models of the cortex. In this study, we present a temporal model of the laminar cortex that applies expectation feedback signals as top-down temporal context in a binocular netw ...
Motor areas of the frontal lobe by Jarrod Blinch
... supplementary somatosensory area, and the posterior parietal cortex and terminate mostly in the dorsal horn of the spinal grey matter. The termination in the dorsal horn makes it unlikely that these fibers directly influence motor behaviour. It has been suggested that corticospinal fibers that origi ...
... supplementary somatosensory area, and the posterior parietal cortex and terminate mostly in the dorsal horn of the spinal grey matter. The termination in the dorsal horn makes it unlikely that these fibers directly influence motor behaviour. It has been suggested that corticospinal fibers that origi ...
Kandel and Schwartz, 4th Edition Principles of Neural Science Chap
... several connected areas of the cortex—where they cause certain populations of cells to discharge. Initially, sensory information is processed in a series of relays, each of which involves more complex information processing than the preceding relay. Sensory fibers project in an orderly pattern from ...
... several connected areas of the cortex—where they cause certain populations of cells to discharge. Initially, sensory information is processed in a series of relays, each of which involves more complex information processing than the preceding relay. Sensory fibers project in an orderly pattern from ...
3. Connections of the Hypothalamus
... Hormonal and transynaptic regulation. The magno- and parvocellular cell groups producing the hypothalamic hormones receive a variety of stimuli from different parts of the brain, primarily within the hypothalamus, but also from extrahypothalamic areas including the amygdaloid body, hippocampus and v ...
... Hormonal and transynaptic regulation. The magno- and parvocellular cell groups producing the hypothalamic hormones receive a variety of stimuli from different parts of the brain, primarily within the hypothalamus, but also from extrahypothalamic areas including the amygdaloid body, hippocampus and v ...
Anatomy of the cerebellum

The anatomy of the cerebellum can be viewed at three levels. At the level of large-scale anatomy, the cerebellum consists of a tightly folded and crumpled layer of cortex, with white matter underneath, several deep nuclei embedded in the white matter, and a fluid-filled ventricle in the middle. At the intermediate level, the cerebellum and its auxiliary structures can be decomposed into several hundred or thousand independently functioning modules or ""microzones"". At the microscopic level, each module consists of the same small set of neuronal elements, laid out with a highly stereotyped geometry.






![[3h]cyclohexyladenosine](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/012903919_1-6cab9cfb915b9ec701998fe503594a7e-300x300.png)