1) Semiconservative DNA replication means that A) each daughter
... ______ This molecule carries a message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm _____ These are the monomers that make up proteins ...
... ______ This molecule carries a message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm _____ These are the monomers that make up proteins ...
Molecular Biology Databases - Computational Bioscience Program
... – Genomic, expressed, protein (amino acid vs. nucleic acid) – Complete or fragmentary sequences ...
... – Genomic, expressed, protein (amino acid vs. nucleic acid) – Complete or fragmentary sequences ...
Lecture 21 Student Powerpoint
... a. Usually 20–25 bases in length b. 10–20 different oligonucleotides for each gene 2. Oligonucleotides for each gene selected by computer program to be the following: a. Unique in genome b. Nonoverlapping 3. Composition based on design rules a. Empirically derived ...
... a. Usually 20–25 bases in length b. 10–20 different oligonucleotides for each gene 2. Oligonucleotides for each gene selected by computer program to be the following: a. Unique in genome b. Nonoverlapping 3. Composition based on design rules a. Empirically derived ...
Document
... • proteins that bind sequences of DNA to control transcription • can act as activators or repressors to transcription – activating TFs - proteins that recruit the RNA polymerase to a promoter region – repressing TFs – proteins that prevent transcription in many ways • must contain a DNA binding doma ...
... • proteins that bind sequences of DNA to control transcription • can act as activators or repressors to transcription – activating TFs - proteins that recruit the RNA polymerase to a promoter region – repressing TFs – proteins that prevent transcription in many ways • must contain a DNA binding doma ...
NucleicAcids
... next with a phosphodiester link. • This creates a repeating backbone of sugarphosphate units with the nitrogen bases as appendages. ...
... next with a phosphodiester link. • This creates a repeating backbone of sugarphosphate units with the nitrogen bases as appendages. ...
Exam 4
... A) Prokaryotic translation starts at AUG, which codes for methionine B) Prokaryotic mRNA receives a 5’ cap before translation C) In prokaryotes, transcription and translation of an RNA molecule can occur at the same time D) Prokaryotic DNA includes a promoter for each gene E) Prokaryotic ribosomes s ...
... A) Prokaryotic translation starts at AUG, which codes for methionine B) Prokaryotic mRNA receives a 5’ cap before translation C) In prokaryotes, transcription and translation of an RNA molecule can occur at the same time D) Prokaryotic DNA includes a promoter for each gene E) Prokaryotic ribosomes s ...
video slide
... Positive Gene Regulation • Some operons are also subject to positive control through a stimulatory activator protein, such as catabolite activator protein (CAP) • When glucose (a preferred food source of E. coli ) is scarce, the lac operon is activated by the binding of CAP ...
... Positive Gene Regulation • Some operons are also subject to positive control through a stimulatory activator protein, such as catabolite activator protein (CAP) • When glucose (a preferred food source of E. coli ) is scarce, the lac operon is activated by the binding of CAP ...
The DNA Song
... Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA), is composed of monomers, called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of 4 bases: cytosine, guanine, thymine, and adenine. These nucleotides link together by covalent (strong) bonds between the sugars and phosphate grou ...
... Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA), is composed of monomers, called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of 4 bases: cytosine, guanine, thymine, and adenine. These nucleotides link together by covalent (strong) bonds between the sugars and phosphate grou ...
Ch. 10: Presentation Slides
... RNA Synthesis • The nucleotide sequence in the transcribed mRNA is complementary to the base sequence in DNA • RNA is copied from the template strand which is 3’-to-5’ in the 5’-to-3’ direction = antiparallela • RNA synthesis does not require a primer and proceeds by the addition of nucleotides to ...
... RNA Synthesis • The nucleotide sequence in the transcribed mRNA is complementary to the base sequence in DNA • RNA is copied from the template strand which is 3’-to-5’ in the 5’-to-3’ direction = antiparallela • RNA synthesis does not require a primer and proceeds by the addition of nucleotides to ...
Protein Synthesis - BLI-Research-SynBio-2016-session-2
... mRNA- type of RNA that encodes information for the synthesis of proteins and carries it to a ribosome from the nucleus ...
... mRNA- type of RNA that encodes information for the synthesis of proteins and carries it to a ribosome from the nucleus ...
Biotechnology ppt
... 4. Stem cells can be used to generate virtually any type of specialized cell in the human ...
... 4. Stem cells can be used to generate virtually any type of specialized cell in the human ...
Overview: The Flow of Genetic Information • The information content
... • The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the belief that all biological catalysts were proteins • Three properties of RNA enable it to function as an enzyme – It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base-pair with itself – Some bases in RNA contain functional groups ...
... • The discovery of ribozymes rendered obsolete the belief that all biological catalysts were proteins • Three properties of RNA enable it to function as an enzyme – It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base-pair with itself – Some bases in RNA contain functional groups ...
Document
... 1. RNA polymerases differ – only one in prokaryotes; 3 in eukaryotes 2. transcription factors used by eukaryotes 3. transcription is terminated differently in prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes 4. ribosomes – bacterial ones are smaller 5. lack of compartmentalization in bacteria – transcribe and translate a ...
... 1. RNA polymerases differ – only one in prokaryotes; 3 in eukaryotes 2. transcription factors used by eukaryotes 3. transcription is terminated differently in prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes 4. ribosomes – bacterial ones are smaller 5. lack of compartmentalization in bacteria – transcribe and translate a ...
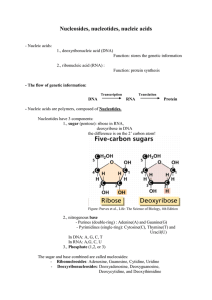
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... protein synthesis. Single stranded. - ribosomal RNA = rRNA : components of the ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis (translation). rRNA forms self-complementary double-stranded regions (in RNA there is Uracil instead of Thymine as a base, it forms double hydrogen bonds with Adenine). - t ...
... protein synthesis. Single stranded. - ribosomal RNA = rRNA : components of the ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis (translation). rRNA forms self-complementary double-stranded regions (in RNA there is Uracil instead of Thymine as a base, it forms double hydrogen bonds with Adenine). - t ...
Ti (ID) - Educational Assistance
... A. List of Physarum known sequences found in the pilot assay. B. “Top Ten Dictyo Hits”. Highest scores obtained by comparing translated Physarum traces to the Dictyo genome. A. Here is a list of “traces” that correspond to previously known sequences of Physarum. There are of two types: either a defi ...
... A. List of Physarum known sequences found in the pilot assay. B. “Top Ten Dictyo Hits”. Highest scores obtained by comparing translated Physarum traces to the Dictyo genome. A. Here is a list of “traces” that correspond to previously known sequences of Physarum. There are of two types: either a defi ...
Chapter 21
... 3’ to 5’ direction lagging strand. 5’ to 3’ direction is the leading strand. Okazaki fragments are made on the lagging strand. DNA returns to a coiled structure. Two identical DNA strands are made. • Takes about 8 hours to complete 3 billion base pairs. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dKubyIRiN84 ...
... 3’ to 5’ direction lagging strand. 5’ to 3’ direction is the leading strand. Okazaki fragments are made on the lagging strand. DNA returns to a coiled structure. Two identical DNA strands are made. • Takes about 8 hours to complete 3 billion base pairs. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dKubyIRiN84 ...
Regulation of Transcription in Eukaryotes
... sites at first suggested that they work by mechanisms different from those of promoters. However, this has turned out not to be the case: Enhancers, like promoters, function by binding transcription factors that then regulate RNA polymerase. This is possible because of DNA looping, which allows a tr ...
... sites at first suggested that they work by mechanisms different from those of promoters. However, this has turned out not to be the case: Enhancers, like promoters, function by binding transcription factors that then regulate RNA polymerase. This is possible because of DNA looping, which allows a tr ...
DNA Technology
... vector - bacterial plasmid Has ampR – ampicillin resistance gene Has lacZ gene – catalyzes hydrolysis of ...
... vector - bacterial plasmid Has ampR – ampicillin resistance gene Has lacZ gene – catalyzes hydrolysis of ...
CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... 2. Describe how sex is genetically determined in humans and explain the significance of the SRY gene. 3. Explain why sex-linked diseases are more common in human males. 4. Perform a Punett square of calculation of probabilities for a sex-linked disorder or trait. 5. Describe the process of X inactiv ...
... 2. Describe how sex is genetically determined in humans and explain the significance of the SRY gene. 3. Explain why sex-linked diseases are more common in human males. 4. Perform a Punett square of calculation of probabilities for a sex-linked disorder or trait. 5. Describe the process of X inactiv ...
What is a protein? - Hicksville Public Schools
... DNA-PROTEIN CONNECTION • Genes contain coded information • This information is used to make proteins that are required for it’s shape and function. ...
... DNA-PROTEIN CONNECTION • Genes contain coded information • This information is used to make proteins that are required for it’s shape and function. ...
Glossary
... (pre-miRNAs), transported to the cytoplasm where they are further cleaved by the Dicer-TRBP complex, and then released as miRNA duplexes. miRNA duplexes are incorporated into Argonaute (Ago) family proteins, from which one of the two strands of the duplex is discarded, and finally the effector compl ...
... (pre-miRNAs), transported to the cytoplasm where they are further cleaved by the Dicer-TRBP complex, and then released as miRNA duplexes. miRNA duplexes are incorporated into Argonaute (Ago) family proteins, from which one of the two strands of the duplex is discarded, and finally the effector compl ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.