Prokaryotic proteins of antioxidant defense in Trichomonas vaginalis
... Reactive molecules derived from molecular oxygen (including the singlet oxygen, the non-reduced molecule in excited state), called reactive oxygen species (ROS), along with reactive nitrogen species (RNS) derived from nitric oxide, are molecules of „two faces“, since they can be either beneficial or ...
... Reactive molecules derived from molecular oxygen (including the singlet oxygen, the non-reduced molecule in excited state), called reactive oxygen species (ROS), along with reactive nitrogen species (RNS) derived from nitric oxide, are molecules of „two faces“, since they can be either beneficial or ...
Cyclic-‐di-‐AMP: another second messenger enters the fray
... Actinobacteria. In addition, the DAC domain is also found in Gram-‐negative bacteria, including the genera Bacteroidetes, Deltaproteobacteria, Cyanobacteria Chlamydiae and Fusobacteria (Table S1). Interestingly, m ...
... Actinobacteria. In addition, the DAC domain is also found in Gram-‐negative bacteria, including the genera Bacteroidetes, Deltaproteobacteria, Cyanobacteria Chlamydiae and Fusobacteria (Table S1). Interestingly, m ...
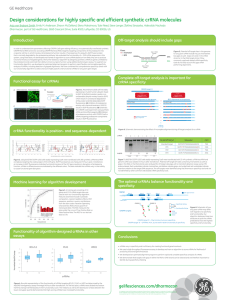
Design considerations for highly specific and efficient
... Off-target analysis should include gaps ...
... Off-target analysis should include gaps ...
BMP binding domains in the extracellular space
... The full-length Xenopus procollagen IIA cDNA was excised with EcoRI from a pUC18 vector (a kind gift of Dr Francesco Ramirez) and ligated to pCS2. For the type IIA procollagen CR construct a PCR fragment (440 bp) containing the CR domain in a SacI-XbaI fragment was cloned into the same pCS2 expressi ...
... The full-length Xenopus procollagen IIA cDNA was excised with EcoRI from a pUC18 vector (a kind gift of Dr Francesco Ramirez) and ligated to pCS2. For the type IIA procollagen CR construct a PCR fragment (440 bp) containing the CR domain in a SacI-XbaI fragment was cloned into the same pCS2 expressi ...
Лекция 2. Структура и функция белка
... chemical entities, with specific sequences of monomeric subunits giving rise to discrete structures and functions. This fundamental theme can be broken down into three interrelated principles: (1) the unique structure of each macromolecule determines its function; (2) noncovalent interactions play a ...
... chemical entities, with specific sequences of monomeric subunits giving rise to discrete structures and functions. This fundamental theme can be broken down into three interrelated principles: (1) the unique structure of each macromolecule determines its function; (2) noncovalent interactions play a ...
Stunned myocardium—an unfinished puzzle
... What about some of the previously discarded causes of myocardial stunning [17]? Impaired energy production by mitochondria or impaired energy use by myofibrils as causes of myocardial stunning have been discarded, since decreased adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels and the extent of contractile dysf ...
... What about some of the previously discarded causes of myocardial stunning [17]? Impaired energy production by mitochondria or impaired energy use by myofibrils as causes of myocardial stunning have been discarded, since decreased adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels and the extent of contractile dysf ...
The use of deuteration for the structural study of larger proteins
... • deuteration level of 50–60% → one sample for backbone and sidechain assignment • 50–60% D is also a reasonable compromise to get NOE information • various isotopomers contribute similarly to diffferent experiments → less problems with isotope shifts • clearly not good enough for proteins > 35 kDa ...
... • deuteration level of 50–60% → one sample for backbone and sidechain assignment • 50–60% D is also a reasonable compromise to get NOE information • various isotopomers contribute similarly to diffferent experiments → less problems with isotope shifts • clearly not good enough for proteins > 35 kDa ...
Functional Characterisation of Plant
... only dually located protein transporter. Furthermore this protein is predicted to contain a conserved PRAT domain and sterile alpha motif (SAM) domain. The latter of which is known to be involved in protein-protein interaction and RNA binding. Utilising T-DNA insertional knockout lines, the function ...
... only dually located protein transporter. Furthermore this protein is predicted to contain a conserved PRAT domain and sterile alpha motif (SAM) domain. The latter of which is known to be involved in protein-protein interaction and RNA binding. Utilising T-DNA insertional knockout lines, the function ...
Direct interaction of iron-regulated surface
... surface determinant (Isd) proteins to capture haem from haemoglobin and transport it into the cell (Skaar et al., 2004; Skaar & Schneewind, 2004). Two of the Isd proteins, IsdA and IsdH, are known to have other biological functions. IsdA interacts with an array of host proteins, and expression of Is ...
... surface determinant (Isd) proteins to capture haem from haemoglobin and transport it into the cell (Skaar et al., 2004; Skaar & Schneewind, 2004). Two of the Isd proteins, IsdA and IsdH, are known to have other biological functions. IsdA interacts with an array of host proteins, and expression of Is ...
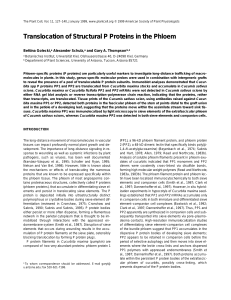
Translocation of Structural P Proteins in the Phloem
... tein was detected among total phloem exudate proteins collected from Cucumis sativus control plants (Figures 2B and 2C, lanes 4). In grafted plants, the respective polyclonal antibodies detected both proteins in the Cucurbita maxima stock (Figures 2B and 2C, lanes 2) and the Cucumis sativus scion (F ...
... tein was detected among total phloem exudate proteins collected from Cucumis sativus control plants (Figures 2B and 2C, lanes 4). In grafted plants, the respective polyclonal antibodies detected both proteins in the Cucurbita maxima stock (Figures 2B and 2C, lanes 2) and the Cucumis sativus scion (F ...
Mitochondrial translation factors of Trypanosoma brucei: elongation
... Most of what we know about mitochondrial translation stems from work in yeast and mammals, which are quite closely related. To understand the conserved features of mitochondrial translation and the evolutionary forces that shaped it, it is important to study the process in a more diverse group of eu ...
... Most of what we know about mitochondrial translation stems from work in yeast and mammals, which are quite closely related. To understand the conserved features of mitochondrial translation and the evolutionary forces that shaped it, it is important to study the process in a more diverse group of eu ...
Depletion of the co-chaperone CDC-37 reveals two
... acts by maintaining the cyclin-dependent kinase Cdc28p in a state that is competent to associate with G1 and mitotic cyclins (Gerber et al., 1995). Vertebrate Cdc37 homologs have been identified in a number of studies as ~50 kDa proteins that associate with Hsp90 and a variety of other proteins, par ...
... acts by maintaining the cyclin-dependent kinase Cdc28p in a state that is competent to associate with G1 and mitotic cyclins (Gerber et al., 1995). Vertebrate Cdc37 homologs have been identified in a number of studies as ~50 kDa proteins that associate with Hsp90 and a variety of other proteins, par ...
The LIR motif – crucial for selective autophagy
... Fig. 3. LIR motif consensus and structural determinants of LIR–ATG8 interactions. (A) Surface representation of LC3B bound to the p62-LIR peptide (top left), yeast Atg8 bound to the Atg19-LIR peptide (top right), GABARAP-L1 bound to the NBR1-LIR peptide (bottom left) and LC3C bound to the NDP52-LIR ...
... Fig. 3. LIR motif consensus and structural determinants of LIR–ATG8 interactions. (A) Surface representation of LC3B bound to the p62-LIR peptide (top left), yeast Atg8 bound to the Atg19-LIR peptide (top right), GABARAP-L1 bound to the NBR1-LIR peptide (bottom left) and LC3C bound to the NDP52-LIR ...
Accumulation of xylem transported protein at pit membranes and
... instead of transpirational uptake gave similar results (not shown). No pit-specific fluorescence was observable in protein-free controls or when xylem was perfused with solutions of a smaller Alexafluor 488–cadaverin conjugate (MW 0.64 kDa) at equivalent concentrations. It therefore seemed that some ...
... instead of transpirational uptake gave similar results (not shown). No pit-specific fluorescence was observable in protein-free controls or when xylem was perfused with solutions of a smaller Alexafluor 488–cadaverin conjugate (MW 0.64 kDa) at equivalent concentrations. It therefore seemed that some ...
Effects of Macromolecular Crowding on Protein Folding
... Protein folding is the process whereby an extended and unstructured polypeptide is converted into a compact folded structure that typically constitutes its functional form. The process has been characterized extensively in-vitro in dilute buffer solutions over the last few decades. However, invivo, ...
... Protein folding is the process whereby an extended and unstructured polypeptide is converted into a compact folded structure that typically constitutes its functional form. The process has been characterized extensively in-vitro in dilute buffer solutions over the last few decades. However, invivo, ...
Identification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins that bind to
... The following individuals and institutions are hereby acknowledged and thanked for their contribution to this project. Dr Gabre Kemp, thank you for your support and sacrifice in the completion of this project. Your willingness to help and guide me along the way is greatly appreciated. Thank you for ...
... The following individuals and institutions are hereby acknowledged and thanked for their contribution to this project. Dr Gabre Kemp, thank you for your support and sacrifice in the completion of this project. Your willingness to help and guide me along the way is greatly appreciated. Thank you for ...
HIBERNATING BEARS, ANTIBIOTICS AND THE EVOLVING RIBOSOME
... are made of amino acids arranged in a linear chain that folds into globular or fibrillar forms, depending on the sequence of their amino acids, which is defined by the sequence of a gene that encoded in the genetic code. Proteins are constantly being degraded. Therefore simultaneous production of p ...
... are made of amino acids arranged in a linear chain that folds into globular or fibrillar forms, depending on the sequence of their amino acids, which is defined by the sequence of a gene that encoded in the genetic code. Proteins are constantly being degraded. Therefore simultaneous production of p ...
Lactobacillus plantarum - UEF Electronic Publications
... Liquid feeding is a common system in Finland for feeding pigs of all ages. Although feeding pigs with a liquid diet is not a new technique, much recent research has focused on explaining the benefits because it can replace the use of antibiotics in animal production. However, pig liquid feed is rapi ...
... Liquid feeding is a common system in Finland for feeding pigs of all ages. Although feeding pigs with a liquid diet is not a new technique, much recent research has focused on explaining the benefits because it can replace the use of antibiotics in animal production. However, pig liquid feed is rapi ...
Multiple Lines of Evidence Localize Signaling
... mitochondrial membrane may also contain proteins involved in signal transduction and mediating retrograde signals from the mitochondrion to the nucleus or even from the mitochondrion to the plastid. Proteins such as Nuclear Control of ATPase (Camougrand et al., 1995) in yeast and the mammalian Mitoc ...
... mitochondrial membrane may also contain proteins involved in signal transduction and mediating retrograde signals from the mitochondrion to the nucleus or even from the mitochondrion to the plastid. Proteins such as Nuclear Control of ATPase (Camougrand et al., 1995) in yeast and the mammalian Mitoc ...
Functional unit of RNA polymerase II
... transcription cycle; it has been likened to a symphony conductor, orchestrating a dizzying array of protein-protein interactions required for proper transcript initiation, elongation, and cotranscriptional mRNA processing (14). Specific binding of additional proteins in vitro also has implicated the ...
... transcription cycle; it has been likened to a symphony conductor, orchestrating a dizzying array of protein-protein interactions required for proper transcript initiation, elongation, and cotranscriptional mRNA processing (14). Specific binding of additional proteins in vitro also has implicated the ...
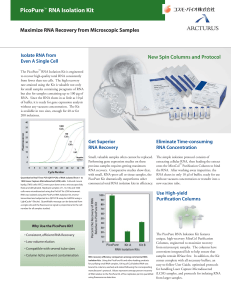
PicoPure RNA Isolation Kit
... two rounds using the RiboAmp Kit, labeled with Cy5-dUTP, and hybridized onto 9000- element mouse cDNA arrays. One region of two arrays illustrates high correlation between gene expression patterns (R = 0.979). ...
... two rounds using the RiboAmp Kit, labeled with Cy5-dUTP, and hybridized onto 9000- element mouse cDNA arrays. One region of two arrays illustrates high correlation between gene expression patterns (R = 0.979). ...
REVIEWS
... C1 domains are considered ‘honorary’ phospholipidbinding domains here, as their physiological binding target (diacylglycerol (DAG)) is one phosphate group short of qualifying as a phospholipid. Fused to green fluorescent protein (GFP), the target-specific domains described in this section provide a ...
... C1 domains are considered ‘honorary’ phospholipidbinding domains here, as their physiological binding target (diacylglycerol (DAG)) is one phosphate group short of qualifying as a phospholipid. Fused to green fluorescent protein (GFP), the target-specific domains described in this section provide a ...
Identification of a C-terminal Poly(A)-binding Protein (PABP)
... sufficient to confer viability to cells depleted of the normal PABP gene (11). In Xenopus oocytes, RRMs can stimulate translation when tethered to reporter mRNA (18). As to the C terminus, although it does not bind RNA, it enables PABP to multimerize on poly(A) (12). Recently it was shown to include ...
... sufficient to confer viability to cells depleted of the normal PABP gene (11). In Xenopus oocytes, RRMs can stimulate translation when tethered to reporter mRNA (18). As to the C terminus, although it does not bind RNA, it enables PABP to multimerize on poly(A) (12). Recently it was shown to include ...
Viroids - general characteristics and examples of diseases caused
... Infection with viroids does not result in obvious macroscopic symptoms. Common symptoms of viroid diseases include retardation of plant gowth and stunting. Potato plants infected with the potato spindle tuber viroid are smaller than healthy plants. However, tuber symptoms are prominent. The diseases ...
... Infection with viroids does not result in obvious macroscopic symptoms. Common symptoms of viroid diseases include retardation of plant gowth and stunting. Potato plants infected with the potato spindle tuber viroid are smaller than healthy plants. However, tuber symptoms are prominent. The diseases ...
488KB - The Doudna Lab - University of California, Berkeley
... RNA products into multiprotein RNA-induced silencing complexes4–7, where they direct cognate gene silencing by targeted mRNA degradation8, translational repression9 and heterochromatin formation10. Dicer contains two copies of the universally conserved catalytic domain of RNase III proteins. Dicer e ...
... RNA products into multiprotein RNA-induced silencing complexes4–7, where they direct cognate gene silencing by targeted mRNA degradation8, translational repression9 and heterochromatin formation10. Dicer contains two copies of the universally conserved catalytic domain of RNase III proteins. Dicer e ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.