Introduction Document
... which is situated upstream (before the START codon AUG). Termination is not well-known (polyadenization). - the template strand is the one that is transcribed (mRNA is composed by binding together ribonucleotides complementary to this strand). ...
... which is situated upstream (before the START codon AUG). Termination is not well-known (polyadenization). - the template strand is the one that is transcribed (mRNA is composed by binding together ribonucleotides complementary to this strand). ...
Section 1.5 Name:
... Remember, proteins are a molecule of life that are made from different kinds of monomers known as ___________________________. Proteins can have many different shapes and functions. ...
... Remember, proteins are a molecule of life that are made from different kinds of monomers known as ___________________________. Proteins can have many different shapes and functions. ...
Protein Synthesis
... Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) which always bonds with Guanine (G). Each stand of DNA is complementary to the other. ...
... Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) which always bonds with Guanine (G). Each stand of DNA is complementary to the other. ...
study guide - Dorman High School
... 16. Describe how polysaccharides, polypeptides, and triglycerides are formed and broken ...
... 16. Describe how polysaccharides, polypeptides, and triglycerides are formed and broken ...
Cartoon modeling of proteins
... proteins modeled as simplified 3D structures including a number of subunits / binding sites / conformational states water not modeled explicitly proteins moved by brownian motion bonding / state transition probabilities set as parameters ...
... proteins modeled as simplified 3D structures including a number of subunits / binding sites / conformational states water not modeled explicitly proteins moved by brownian motion bonding / state transition probabilities set as parameters ...
Cartoon modeling of proteins
... proteins modeled as simplified 3D structures including a number of subunits / binding sites / conformational states water not modeled explicitly proteins moved by brownian motion bonding / state transition probabilities set as parameters ...
... proteins modeled as simplified 3D structures including a number of subunits / binding sites / conformational states water not modeled explicitly proteins moved by brownian motion bonding / state transition probabilities set as parameters ...
Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Proteins
... Proteins • A huge variety of proteins exist • Proteins have very specific functions throughout the body • 20 amino acids (monomers) that bond together to form proteins (polymers) – Interestingly, our bodies can only make 12 of the amino acids, we need the other 8 from eating ...
... Proteins • A huge variety of proteins exist • Proteins have very specific functions throughout the body • 20 amino acids (monomers) that bond together to form proteins (polymers) – Interestingly, our bodies can only make 12 of the amino acids, we need the other 8 from eating ...
DNA/RNA/Protein Questions
... What is a codon? What is a start codon? Stop codon? What does Translation mean? What organelle makes proteins? What role does tRNA play in making proteins? What is an "anticodon"? What structure is it on? How is mRNA used to make proteins. Why are proteins so important to life? Given a strand of mRN ...
... What is a codon? What is a start codon? Stop codon? What does Translation mean? What organelle makes proteins? What role does tRNA play in making proteins? What is an "anticodon"? What structure is it on? How is mRNA used to make proteins. Why are proteins so important to life? Given a strand of mRN ...
Proteins: Primary Structure
... the term quaternary structure Describe the properties and functions of fibrous proteins ...
... the term quaternary structure Describe the properties and functions of fibrous proteins ...
PP-Protein Synthesis
... Proteins have MANY different functions Enzymes to help control/speed up chemical reactions Help to build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
... Proteins have MANY different functions Enzymes to help control/speed up chemical reactions Help to build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
Pedigree Analysis & Developmental Genetics
... It is thought to bind more than 20 different proteins It is very sensitive to the position of the gene (nucleus) within the developing giant cell The different concentrations of the different proteins impact on the expression of ‘Eve’ ...
... It is thought to bind more than 20 different proteins It is very sensitive to the position of the gene (nucleus) within the developing giant cell The different concentrations of the different proteins impact on the expression of ‘Eve’ ...
Fates of Proteins in Cells
... Step 6 – when the ribosome reaches the end of the mRNA, the complete protein is released into the ER lumen – It needs to undergo folding – usually with the help of a chaperone protein that is not shown in this cartoon. ...
... Step 6 – when the ribosome reaches the end of the mRNA, the complete protein is released into the ER lumen – It needs to undergo folding – usually with the help of a chaperone protein that is not shown in this cartoon. ...
Bio200 Au13 Lec19 10-29 Slides
... • A 5’ protein cap and a 3’ poly-A tail are added to give stability • Non-coding introns are spliced out of the mRNA by the spliceosome ...
... • A 5’ protein cap and a 3’ poly-A tail are added to give stability • Non-coding introns are spliced out of the mRNA by the spliceosome ...
Glossary
... (pre-miRNAs), transported to the cytoplasm where they are further cleaved by the Dicer-TRBP complex, and then released as miRNA duplexes. miRNA duplexes are incorporated into Argonaute (Ago) family proteins, from which one of the two strands of the duplex is discarded, and finally the effector compl ...
... (pre-miRNAs), transported to the cytoplasm where they are further cleaved by the Dicer-TRBP complex, and then released as miRNA duplexes. miRNA duplexes are incorporated into Argonaute (Ago) family proteins, from which one of the two strands of the duplex is discarded, and finally the effector compl ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... • DNA “directs” synthesis of proteins • Proteins made on ribosomes • Transcription: - RNA polymerase unzips DNA - occurs in nucleus • Translation: DNARNAProtein - occurs in cytoplasm - mRNA(codon) and tRNA(anticodon) • Genetic Code is UNIVERSAL!!!!!!! ...
... • DNA “directs” synthesis of proteins • Proteins made on ribosomes • Transcription: - RNA polymerase unzips DNA - occurs in nucleus • Translation: DNARNAProtein - occurs in cytoplasm - mRNA(codon) and tRNA(anticodon) • Genetic Code is UNIVERSAL!!!!!!! ...
Unit 1 PPT 1 (2a Proteomics)
... composed of introns and exons. • Introns are the non-coding sequence of the mRNA and will not be expressed in the protein molecule. They are spliced out (removed) from the mRNA. • Exons are the coding sequence and will be expressed in the protein molecule. • RNA splicing in detail. ...
... composed of introns and exons. • Introns are the non-coding sequence of the mRNA and will not be expressed in the protein molecule. They are spliced out (removed) from the mRNA. • Exons are the coding sequence and will be expressed in the protein molecule. • RNA splicing in detail. ...
File
... added to 3’ end by enzymes in nucleus a) same functions as 5’ cap b) also may assist with exit from nucleus ...
... added to 3’ end by enzymes in nucleus a) same functions as 5’ cap b) also may assist with exit from nucleus ...
Estimating the Recovery Kinetics of tER Sites
... The transitional Endoplasmic Reticulum (tER) site is a small spot on the Endoplasmic Reticulum that proteins must pass through on their way from the ER to the Golgi apparatus. Through fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) imaging techniques the rate proteins attached to specific genes tr ...
... The transitional Endoplasmic Reticulum (tER) site is a small spot on the Endoplasmic Reticulum that proteins must pass through on their way from the ER to the Golgi apparatus. Through fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) imaging techniques the rate proteins attached to specific genes tr ...
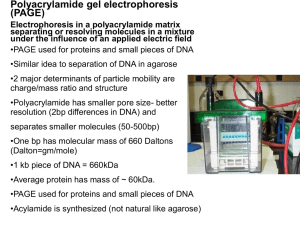
Polyacrylamide gels
... • Proteins separated based on size charge and shape. • Used when want to keep protein active to study conformation, self-association or aggregation, and the binding of other proteins ...
... • Proteins separated based on size charge and shape. • Used when want to keep protein active to study conformation, self-association or aggregation, and the binding of other proteins ...
DNA -> RNA -> Proteins
... • This process is called transcription, because the DNA transcribes “copies” itself • It takes advantage of base pairing ...
... • This process is called transcription, because the DNA transcribes “copies” itself • It takes advantage of base pairing ...
Book Reviews - Cancer Research
... Two papers deal with the cytochemistry of proteins. J. F. Danielli describes the use of chromogenic reagents along with specific blocking reagents, and B. P. Kauf man, H. Gay, and M. R. McDonald ...
... Two papers deal with the cytochemistry of proteins. J. F. Danielli describes the use of chromogenic reagents along with specific blocking reagents, and B. P. Kauf man, H. Gay, and M. R. McDonald ...
Document
... (UUU..UUU….) added it to a test tube with amino acids, ribosomes, RNA polymerase and other needed materials. It resulted in a protein made of only phenylalanine. Further research determined the rest of the code. ...
... (UUU..UUU….) added it to a test tube with amino acids, ribosomes, RNA polymerase and other needed materials. It resulted in a protein made of only phenylalanine. Further research determined the rest of the code. ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.