GENE EXPRESSION CH 17
... • Only one strand of the DNA is transcribed into RNA, the template strand • RNA strand is complementary to DNA strand copied • Enzyme is RNA polymerase ...
... • Only one strand of the DNA is transcribed into RNA, the template strand • RNA strand is complementary to DNA strand copied • Enzyme is RNA polymerase ...
Lecture#5 - Introduction to gene regulation and operons in
... It is called a Constitutive mutant - always "on" - expressed - unregulated by inducers. Genetically mapped close to, but distinct from, the ZYA genes ...
... It is called a Constitutive mutant - always "on" - expressed - unregulated by inducers. Genetically mapped close to, but distinct from, the ZYA genes ...
key
... 1. Which of the following is not involved with initiation of transcription in human genes ...
... 1. Which of the following is not involved with initiation of transcription in human genes ...
Unit 5 practice FRQ #3 for final - KEY 3. 2009 AP Bio FRQ # 4 The
... Transports amino acids (b) Cells regulate both protein synthesis and protein activity. Discuss TWO specific mechanisms of protein regulation in eukaryotic cells. (4 points maximum) Idea of the mechanism Discussion (1 point) (1 point) Promotor ................................. increases RNA polymeras ...
... Transports amino acids (b) Cells regulate both protein synthesis and protein activity. Discuss TWO specific mechanisms of protein regulation in eukaryotic cells. (4 points maximum) Idea of the mechanism Discussion (1 point) (1 point) Promotor ................................. increases RNA polymeras ...
Photo Album
... current model of CREB-mediated transcription. Under basal conditions, unphosphorylated CREB is bound to the CRE element in the promoter of its target genes. Upon neural activity, CREB is phosphorylated at Ser-133 by various kinases within the KID domain. The KIX domain of CBP can then bind to CREB a ...
... current model of CREB-mediated transcription. Under basal conditions, unphosphorylated CREB is bound to the CRE element in the promoter of its target genes. Upon neural activity, CREB is phosphorylated at Ser-133 by various kinases within the KID domain. The KIX domain of CBP can then bind to CREB a ...
Protein Synthesis Notes File
... I. Protein Synthesis A. ____________________- the process by which DNA is copied to RNA 1. The enzyme responsible for transcription is ____________________________ 2. RNA polymerase must bind with DNA at a _______________________ a) ___________________- series of repeating nucleotides up stream of t ...
... I. Protein Synthesis A. ____________________- the process by which DNA is copied to RNA 1. The enzyme responsible for transcription is ____________________________ 2. RNA polymerase must bind with DNA at a _______________________ a) ___________________- series of repeating nucleotides up stream of t ...
Matching review Connect with lines
... multicellular/ no cell wall mold alternation of generations ...
... multicellular/ no cell wall mold alternation of generations ...
last year`s final exam
... 23) What is the function of snRNPs? 24) Mature, unfertilized eggs of many species have mRNAs for several genes but the proteins haven’t been made yet. What is preventing their synthesis? 25) What is the first amino acid to be added during synthesis of almost all eukaryotic proteins? 26) Describe one ...
... 23) What is the function of snRNPs? 24) Mature, unfertilized eggs of many species have mRNAs for several genes but the proteins haven’t been made yet. What is preventing their synthesis? 25) What is the first amino acid to be added during synthesis of almost all eukaryotic proteins? 26) Describe one ...
Regulation of Transcription
... • Essentially the molecule “RNA polymerase” must bind to an “exposed“ part of DNA strand called a promoter; it must then move, in the 5’ to 3’ direction, “transcribing” the DNA sequence of “the gene” to RNA. – The transcribed sequence begins at the Transcription start site (TSS) and finishes at the ...
... • Essentially the molecule “RNA polymerase” must bind to an “exposed“ part of DNA strand called a promoter; it must then move, in the 5’ to 3’ direction, “transcribing” the DNA sequence of “the gene” to RNA. – The transcribed sequence begins at the Transcription start site (TSS) and finishes at the ...
Document
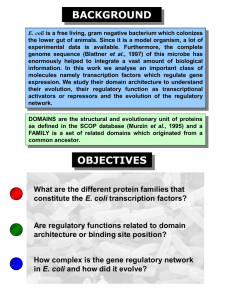
... enormously helped to integrate a vast amount of biological information. In this work we analyse an important class of molecules namely transcription factors which regulate gene expression. We study their domain architecture to understand their evolution, their regulatory function as transcriptional ...
... enormously helped to integrate a vast amount of biological information. In this work we analyse an important class of molecules namely transcription factors which regulate gene expression. We study their domain architecture to understand their evolution, their regulatory function as transcriptional ...
Gene ExpressionâTranscription
... that remain are called exons. The methyl cap (sometimes called the GTP cap or 5ʹ cap) helps the mRNA molecule move through the nuclear pore and attach to a ribosome, its final destination. mRNA is a shortlived molecule. Once in the cytoplasm the mRNA will be subject to exonucleases that immediately ...
... that remain are called exons. The methyl cap (sometimes called the GTP cap or 5ʹ cap) helps the mRNA molecule move through the nuclear pore and attach to a ribosome, its final destination. mRNA is a shortlived molecule. Once in the cytoplasm the mRNA will be subject to exonucleases that immediately ...
Transcription in Bacteria
... E. coli RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA with remarkable fidelity in vivo. Its low error rate may be achieved by two proofreading mechanisms. Pyrophosphorolytic editing The RNA polymerase use its active site in a simple back-reaction, to catalyze the removal of an incorrectly inserted ribonucleotide b ...
... E. coli RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA with remarkable fidelity in vivo. Its low error rate may be achieved by two proofreading mechanisms. Pyrophosphorolytic editing The RNA polymerase use its active site in a simple back-reaction, to catalyze the removal of an incorrectly inserted ribonucleotide b ...
No Slide Title
... 1) In Bacteria transcription and translation are initially coupled • RNA polymerase quits if ribosomes lag too much • Recent studies show that ribosomes continue translating once mRNA is complete; i.e after transcription is done ...
... 1) In Bacteria transcription and translation are initially coupled • RNA polymerase quits if ribosomes lag too much • Recent studies show that ribosomes continue translating once mRNA is complete; i.e after transcription is done ...
Wed 12-2 Computers Lab (40 points if all correct or 0 if not) Open up
... RNA is transcribed from DNA by enzymes called RNA polymerases and is generally further processed by other enzymes. RNA is central to protein synthesis. Here, a type of RNA called messenger RNA carries information from DNA to structures called ribosomes. These ribosomes are made from proteins and rib ...
... RNA is transcribed from DNA by enzymes called RNA polymerases and is generally further processed by other enzymes. RNA is central to protein synthesis. Here, a type of RNA called messenger RNA carries information from DNA to structures called ribosomes. These ribosomes are made from proteins and rib ...
PROTIEN SYNTHESIS
... The form of RNA that mediates the transfer of genetic information from the cell nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. It is synthesized from a DNA template during the process of transcription. transfer RNA One of a class of RNA molecules that tra ...
... The form of RNA that mediates the transfer of genetic information from the cell nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. It is synthesized from a DNA template during the process of transcription. transfer RNA One of a class of RNA molecules that tra ...
Transcription - Effingham County Schools
... reference material back on the shelf so that others can use it too. Can you imagine if DNA was physically lost? That’s why chromosomes never leave the nucleus. ...
... reference material back on the shelf so that others can use it too. Can you imagine if DNA was physically lost? That’s why chromosomes never leave the nucleus. ...
Cellular Control miniQUIZ
... Using the diagram above answer the following questions: a) Which segment of the fruit fly develops wings? b) Are plant homeobox genes homologous to the homeobox genes in the fruit fly? 17. Apoptosis is important during development. Define the meaning of apoptosis and give an example. ...
... Using the diagram above answer the following questions: a) Which segment of the fruit fly develops wings? b) Are plant homeobox genes homologous to the homeobox genes in the fruit fly? 17. Apoptosis is important during development. Define the meaning of apoptosis and give an example. ...
CH. 13 - Weebly
... How does the cell make RNA? • In transcription, segments of DNA serve as templates to produce complementary RNA molecules. • Complementary: ...
... How does the cell make RNA? • In transcription, segments of DNA serve as templates to produce complementary RNA molecules. • Complementary: ...
Name:
... 10. What are the names of the gene and the enzyme responsible for the glowing in a firefly’s tail? 11. After finding the correct gene, what does RNA Polymerase actually do? 12. After transcription, what happens to the mRNA strand? (Where in the cell ...
... 10. What are the names of the gene and the enzyme responsible for the glowing in a firefly’s tail? 11. After finding the correct gene, what does RNA Polymerase actually do? 12. After transcription, what happens to the mRNA strand? (Where in the cell ...
sample
... 1. Which of the following is not involved with initiation of transcription in human genes ...
... 1. Which of the following is not involved with initiation of transcription in human genes ...
Slide 1
... It is not transcribed into mRNA, but plays a role in controlling the transcription of the gene. Transcription factors bind to specific nucleotide sequences in the promoter region and assist in the binding of RNA polymerases. Enhancers. Some transcription factors (called activators) bind to regions c ...
... It is not transcribed into mRNA, but plays a role in controlling the transcription of the gene. Transcription factors bind to specific nucleotide sequences in the promoter region and assist in the binding of RNA polymerases. Enhancers. Some transcription factors (called activators) bind to regions c ...
Chapter 16 and 17 Review
... 22 Following eukaryotic transcription, how are the ends of the RNA molecule altered? Where does this alteration occur and state 3 reasons it is done? 23. How is the middle of the RNA molecules altered following eukaryotic transcription 24. What is the name given to the non-coding segments of RNA? 25 ...
... 22 Following eukaryotic transcription, how are the ends of the RNA molecule altered? Where does this alteration occur and state 3 reasons it is done? 23. How is the middle of the RNA molecules altered following eukaryotic transcription 24. What is the name given to the non-coding segments of RNA? 25 ...