Transcription and Translation
... Remember: MR CATAP (mRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, tRNA, amino acid, polypeptide) • mRNA binds to a ribosome which initiates translation • The mRNA is read in codons (from start codon = AUG) • Anticodons on tRNA align opposite appropriate codons ...
... Remember: MR CATAP (mRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, tRNA, amino acid, polypeptide) • mRNA binds to a ribosome which initiates translation • The mRNA is read in codons (from start codon = AUG) • Anticodons on tRNA align opposite appropriate codons ...
protein synthesis (simplified)
... It is the Sequence of bases that act like a code The sequence (order) of bases tells the cell what proteins to make. The sequence of bases dictates the sequence of amino acids, which determines the shape of a protein. ...
... It is the Sequence of bases that act like a code The sequence (order) of bases tells the cell what proteins to make. The sequence of bases dictates the sequence of amino acids, which determines the shape of a protein. ...
Operons: The Basic Concept
... Corepressor = A molecule, usually a metabolite, that binds to a repressor protein, causing the repressor to change into its active conformation. ...
... Corepressor = A molecule, usually a metabolite, that binds to a repressor protein, causing the repressor to change into its active conformation. ...
Science 103: Outline 17
... (iv) Ribosome moves one codon to the right. (v) A tRNA (plus amino acid) with the anticodon corresponding to the third codon binds and the first tRNA (empty) leaves. (v) The ribosomes move down the mRNA until they reach a stop codon. The ribosomes detach from the mRNA and the protein is released. 4. ...
... (iv) Ribosome moves one codon to the right. (v) A tRNA (plus amino acid) with the anticodon corresponding to the third codon binds and the first tRNA (empty) leaves. (v) The ribosomes move down the mRNA until they reach a stop codon. The ribosomes detach from the mRNA and the protein is released. 4. ...
Oct 14 Central Dogma II
... “Transcription Factors”$ Accessory proteins associate with the promoter sequence (and other sequences) RNA polymerase and other proteins join in to form the “Transcription Initiation Complex” ...
... “Transcription Factors”$ Accessory proteins associate with the promoter sequence (and other sequences) RNA polymerase and other proteins join in to form the “Transcription Initiation Complex” ...
Gene Expression Gene expression involves coded information on
... exposing the nucleotides on the DNA strand. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the promotor region on the template strand. However, RNA polymerase alone cannot start transcription of the gene. Transcription factors must also bind to the promotor region. Transcription factors are attached to an enhan ...
... exposing the nucleotides on the DNA strand. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the promotor region on the template strand. However, RNA polymerase alone cannot start transcription of the gene. Transcription factors must also bind to the promotor region. Transcription factors are attached to an enhan ...
Operons: The Basic Concept
... Corepressor = A molecule, usually a metabolite, that binds to a repressor protein, causing the repressor to change into its active conformation. ...
... Corepressor = A molecule, usually a metabolite, that binds to a repressor protein, causing the repressor to change into its active conformation. ...
TUTORIAL FIGURES: Basic Molecular Biology
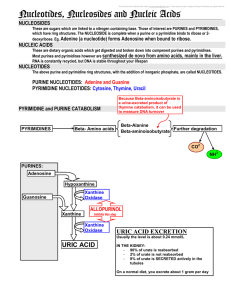
... consisting of nucleotide units. The basic structure of each nucleotide comprises of a phosphate, a deoxyribose sugar, and a base (nucleotide = P-S-Base). There are 4 DNA bases: A (adenine), G (guanine), T (thymine), and C (cytosine). The nucleotides p-s-A and p-s-G are called purine nucleotides and ...
... consisting of nucleotide units. The basic structure of each nucleotide comprises of a phosphate, a deoxyribose sugar, and a base (nucleotide = P-S-Base). There are 4 DNA bases: A (adenine), G (guanine), T (thymine), and C (cytosine). The nucleotides p-s-A and p-s-G are called purine nucleotides and ...
No Slide Title
... At specific regions / From DNA to RNA Transcription / Transcribe / Transcript Changes in composition : properties : function : ...
... At specific regions / From DNA to RNA Transcription / Transcribe / Transcript Changes in composition : properties : function : ...
Exam 1 Q2 Review Sheet
... 5. Explain how nucleotide excision repair works. 6. Describe the role of telomeres in DNA. Why do we need these repeats on the ends of our chromosomes? 7. Describe the process of transcription and translation in a cell using a combination of drawings and text. Make sure every aspect is described fro ...
... 5. Explain how nucleotide excision repair works. 6. Describe the role of telomeres in DNA. Why do we need these repeats on the ends of our chromosomes? 7. Describe the process of transcription and translation in a cell using a combination of drawings and text. Make sure every aspect is described fro ...
overview rna, transcription, translation
... itself to leave the nucleus, enzymes cut out and remove the introns. The remaining exons are spliced back together again by a different enzyme. This modified m RNA is what comes to the ribosome to be translated into polypeptides. ...
... itself to leave the nucleus, enzymes cut out and remove the introns. The remaining exons are spliced back together again by a different enzyme. This modified m RNA is what comes to the ribosome to be translated into polypeptides. ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... tRNA (compliment of mRNA) picks up specific amino acids from the cytoplasm and attaches to the mRNA strand. ...
... tRNA (compliment of mRNA) picks up specific amino acids from the cytoplasm and attaches to the mRNA strand. ...
Transcription, RNA Processing, and
... Nascent RNA strand synthesis (elongation) occurs only in the 5’ 3’ direction, with new nucleotides added to the 3’ end of the nascent strand Transcription is catalyzed by DNA-directed RNA polymerases ...
... Nascent RNA strand synthesis (elongation) occurs only in the 5’ 3’ direction, with new nucleotides added to the 3’ end of the nascent strand Transcription is catalyzed by DNA-directed RNA polymerases ...
REGULATING GENE EXPRESSION
... Prokaryotes have no nucleus so as a gene is being transcribed, it can be translated at the same time Eukaryotes do have a nucleus so transcription and translation occur at different times Eukaryotic gene regulation can occur at transcription or after transcription Prokaryotic gene regulation ...
... Prokaryotes have no nucleus so as a gene is being transcribed, it can be translated at the same time Eukaryotes do have a nucleus so transcription and translation occur at different times Eukaryotic gene regulation can occur at transcription or after transcription Prokaryotic gene regulation ...
RNA
... Occurs in three steps – the same but different than transcription – initiation, elongation, and termination. ...
... Occurs in three steps – the same but different than transcription – initiation, elongation, and termination. ...
Chap 12.3 Notes: DNA to RNA - Transcription and Translation Notes
... RNA is then sent to the ribosome and “translated” into a protein. Translation – Making the Protein Once the RNA has reached the ribosome , building protein begins. This is called translation ...
... RNA is then sent to the ribosome and “translated” into a protein. Translation – Making the Protein Once the RNA has reached the ribosome , building protein begins. This is called translation ...
3 Nucleosides nucleotides and nucleic acids
... - EXONS are portions of genes which encode protens; - INTRONS are portions of the gene which are not encoded into proteins - PROMOTER regions are near the transcription start of the gene, and this is where RNA polymerase binds to start the encryption of RNA; it usually includes a TATA (thymine-adeni ...
... - EXONS are portions of genes which encode protens; - INTRONS are portions of the gene which are not encoded into proteins - PROMOTER regions are near the transcription start of the gene, and this is where RNA polymerase binds to start the encryption of RNA; it usually includes a TATA (thymine-adeni ...
Translation
... specified by the message. - The formation of the peptide bond between the two amino acids occurs on adjacent sites on the ribosome: the P or peptidyl site and the A or aminoacyl site. - The growing protein occupies the P site, while the next amino acid to be added occupies the A site. - As the pepti ...
... specified by the message. - The formation of the peptide bond between the two amino acids occurs on adjacent sites on the ribosome: the P or peptidyl site and the A or aminoacyl site. - The growing protein occupies the P site, while the next amino acid to be added occupies the A site. - As the pepti ...
Exam 3
... Given a sequence of antisense (template; 3’→5’) strand of DNA, what will be the sequence of the sense (complement; 5’→3’) strand of DNA and that of the RNA transcript? What will be the amino ...
... Given a sequence of antisense (template; 3’→5’) strand of DNA, what will be the sequence of the sense (complement; 5’→3’) strand of DNA and that of the RNA transcript? What will be the amino ...
PPT NOTES_AP Biology Chapter 17 Notes
... They seem to facilitate the ______________ of mRNA They __________________ mRNA from hydrolytic enzymes They help ___________________ attach to the 5 end • Most eukaryotic genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions - called int ...
... They seem to facilitate the ______________ of mRNA They __________________ mRNA from hydrolytic enzymes They help ___________________ attach to the 5 end • Most eukaryotic genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions - called int ...
Transcription Protein Synthesis So what does it mean? Transcription
... • Model that describes how DNA serves as a genetic code for protein synthesis • Proteins are the structural building blocks for cells, and they act as enzymes • Geneticists accept that the basic mechanism of reading and expressing genes is DNA RNA protein. • This chain of events occurs in all li ...
... • Model that describes how DNA serves as a genetic code for protein synthesis • Proteins are the structural building blocks for cells, and they act as enzymes • Geneticists accept that the basic mechanism of reading and expressing genes is DNA RNA protein. • This chain of events occurs in all li ...
投影片 1
... needs to take some processes of modification before entering the cytoplasm. Capping at 5’ end with a methyl G. Splicing and remove introns( non-coding sequences). Polyadenylation at 3’end.( poly-A tail) ...
... needs to take some processes of modification before entering the cytoplasm. Capping at 5’ end with a methyl G. Splicing and remove introns( non-coding sequences). Polyadenylation at 3’end.( poly-A tail) ...
DKN_5-8 TYPE
... Converting DNA to RNA is called TRANSCRIPTION RNA polymerase makes messenger RNA (mRNA) -message can encode: protein, tRNA, rRNA, non-coding RNA DRAW CARTOON: 5 subunits and a single regulatory subunit known as sigma (σ). Different sigma factors help RN ...
... Converting DNA to RNA is called TRANSCRIPTION RNA polymerase makes messenger RNA (mRNA) -message can encode: protein, tRNA, rRNA, non-coding RNA DRAW CARTOON: 5 subunits and a single regulatory subunit known as sigma (σ). Different sigma factors help RN ...
AP Biology - Naber Biology
... 35. Write a paragraph to describe the process by which mRNA is formed. Use these terms correctly in your essay, and highlight (or underline) each one: TATA box, gene, terminator, promoter, elongation, 5’ to 3’, termination, ignition RNA, polymerase RNA nucleotides, template, start point, termination ...
... 35. Write a paragraph to describe the process by which mRNA is formed. Use these terms correctly in your essay, and highlight (or underline) each one: TATA box, gene, terminator, promoter, elongation, 5’ to 3’, termination, ignition RNA, polymerase RNA nucleotides, template, start point, termination ...