Introduction to Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology II Losiana
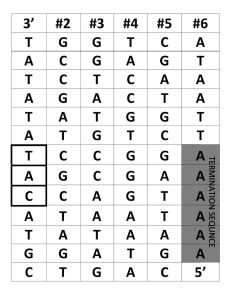
... Rho, that binds to and slides along the RNA transcript. The terminator sequence slows down the elongation complex, Rho catches up and knocks it off the DNA Rho independent termination depends on both slowing down the elongation complex, and an AT rich region that destabilizes the elongation complex ...
... Rho, that binds to and slides along the RNA transcript. The terminator sequence slows down the elongation complex, Rho catches up and knocks it off the DNA Rho independent termination depends on both slowing down the elongation complex, and an AT rich region that destabilizes the elongation complex ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... other strand, the information strand, will not be used in this transcription (this does not mean, however, that it may not be used in future transcription processes). ...
... other strand, the information strand, will not be used in this transcription (this does not mean, however, that it may not be used in future transcription processes). ...
Light-stimulated neurons
... just that; small RNA oligonucleoties bind to complementary sequences on the mRNA and trigger its degradation. Unfortunately, despite its great potential and wide use, RNA interference does not always work effectively. This prompted David Corey and his team at the University of Texas to look for site ...
... just that; small RNA oligonucleoties bind to complementary sequences on the mRNA and trigger its degradation. Unfortunately, despite its great potential and wide use, RNA interference does not always work effectively. This prompted David Corey and his team at the University of Texas to look for site ...
Lac Operon - FCE LTER
... 5. RNA polymerase moves on to the next gene, lac Y that makes the enzyme permease a. Permease is a transport protein that carries lactose into the cell 6. RNA polymerase finally moves to the lac A gene which is responsible for making transacetylase a. Scientists are not sure of transacetylase’s func ...
... 5. RNA polymerase moves on to the next gene, lac Y that makes the enzyme permease a. Permease is a transport protein that carries lactose into the cell 6. RNA polymerase finally moves to the lac A gene which is responsible for making transacetylase a. Scientists are not sure of transacetylase’s func ...
Slide 1
... • RNA is the same as DNA except that the sugars in RNA have an extra oxygen and T is replaced by another pyrimidine called ...
... • RNA is the same as DNA except that the sugars in RNA have an extra oxygen and T is replaced by another pyrimidine called ...
Transcription
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
Chapter 15 / Lecture Outline 36
... 1. Many DNA-binding proteins contain a helix-turn-helix motif 2. Most regulatory proteins are oligomeric and contain more than one binding domain 3. The looping of DNA is a common feature of regulatory systems 4. How regulatory proteins interact with RNA polymerase 5. In studying gene regulation, re ...
... 1. Many DNA-binding proteins contain a helix-turn-helix motif 2. Most regulatory proteins are oligomeric and contain more than one binding domain 3. The looping of DNA is a common feature of regulatory systems 4. How regulatory proteins interact with RNA polymerase 5. In studying gene regulation, re ...
DNA Transcription and Translation
... DNA does not leave the nucleus so a carrier molecule called messanger RNA (mRNA) is used o mRNA carries the genetic message to the ribosomes RNA is different than DNA in a few ways o RNA contains ribose sugar, not deoxyribose RNA has no thymine base (T), instead has uracil (U) RNA is sin ...
... DNA does not leave the nucleus so a carrier molecule called messanger RNA (mRNA) is used o mRNA carries the genetic message to the ribosomes RNA is different than DNA in a few ways o RNA contains ribose sugar, not deoxyribose RNA has no thymine base (T), instead has uracil (U) RNA is sin ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... (active) where phosphodiester bonds form – E and A sites partially overlap – Rotation of nucleotide between the E and A sites may play a role in base and sugar specificity ...
... (active) where phosphodiester bonds form – E and A sites partially overlap – Rotation of nucleotide between the E and A sites may play a role in base and sugar specificity ...
Eukaryotic transcriptional control
... monomers form a coiled-coil dimer. Basic amino acid residues N-terminal to the leucine zipper form the DNA-binding domain. ...
... monomers form a coiled-coil dimer. Basic amino acid residues N-terminal to the leucine zipper form the DNA-binding domain. ...
Chapter 11 Lecture PowerPoint - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • This transcription factor is an assembly factor that helps the core binding factor to bind to the core promoter element • It works by bending the DNA dramatically • Degree of reliance on UBF varies considerably from one organism to another • Human UBF is a transcription factor that stimulates tran ...
... • This transcription factor is an assembly factor that helps the core binding factor to bind to the core promoter element • It works by bending the DNA dramatically • Degree of reliance on UBF varies considerably from one organism to another • Human UBF is a transcription factor that stimulates tran ...
- Aim4Aiims
... Ref- Cell and Molecular Biology be De Robertis. The CBSE has given (1) as the answer 6. Dr. F. Went noted that if coleoptiles tips were removed and placed on agar for one hour, the agar would produce a bending when placed on one side of freshly-cut coleoptiles stumps. Of what significance is this ex ...
... Ref- Cell and Molecular Biology be De Robertis. The CBSE has given (1) as the answer 6. Dr. F. Went noted that if coleoptiles tips were removed and placed on agar for one hour, the agar would produce a bending when placed on one side of freshly-cut coleoptiles stumps. Of what significance is this ex ...
Feb 24
... Pol I: only makes 45S-rRNA precursor • 50 % of total RNA synthesis • insensitive to a-aminitin •Mg2+ cofactor •Regulated @ initiation frequency ...
... Pol I: only makes 45S-rRNA precursor • 50 % of total RNA synthesis • insensitive to a-aminitin •Mg2+ cofactor •Regulated @ initiation frequency ...
Chapter 17: Gene Expression Gene Expression DNA houses all
... Once mRNA codon produced, must be turned into amino acids (polypeptide) Ribosomal complex (rRNA, mRNA, tRNA) build polypetides o Free Ribosomes in cytosol o Bound Ribosomes on rough ER o Why different locations? tRNA (Transfer RNA) o 80 nucleotide RNA strand Complimentary regions allow it to ...
... Once mRNA codon produced, must be turned into amino acids (polypeptide) Ribosomal complex (rRNA, mRNA, tRNA) build polypetides o Free Ribosomes in cytosol o Bound Ribosomes on rough ER o Why different locations? tRNA (Transfer RNA) o 80 nucleotide RNA strand Complimentary regions allow it to ...
Chapter 1 Study Questions
... 8. Briefly explain how the following terms pertain to the structure of DNA: antiparallel, 5’ end, 3’ end, complementary, major groove, minor groove. 9. How do the following terms pertain to DNA replication: semi-conservative model, Okazaki fragments, leading strand, lagging strand? 10. What are the ...
... 8. Briefly explain how the following terms pertain to the structure of DNA: antiparallel, 5’ end, 3’ end, complementary, major groove, minor groove. 9. How do the following terms pertain to DNA replication: semi-conservative model, Okazaki fragments, leading strand, lagging strand? 10. What are the ...
2054, Chap. 12, page 1 I. Genes: Expression and Regulation A
... I. Genes: Expression and Regulation A. DNA transcription or RNA synthesis 1. transcription = synthesis of RNA under direction of DNA a. RNA has sequence complementary to DNA template b. uracil replaces thymine c. mRNA = contains message for protein synthesis d. tRNA = carries amino acids during prot ...
... I. Genes: Expression and Regulation A. DNA transcription or RNA synthesis 1. transcription = synthesis of RNA under direction of DNA a. RNA has sequence complementary to DNA template b. uracil replaces thymine c. mRNA = contains message for protein synthesis d. tRNA = carries amino acids during prot ...
Transcription - smithlhhsb121
... nucleotides is added – called a poly(A) tail ◦ Again, to assist in holding the pre-mRNA together ...
... nucleotides is added – called a poly(A) tail ◦ Again, to assist in holding the pre-mRNA together ...
DNA Transcription
... DNA replication, the complementary RNA is created from the 5' → 3' direction. Although DNA is arranged as two antiparallel strands in a double helix, only one of the two DNA strands, called the template strand, is used for transcription. ...
... DNA replication, the complementary RNA is created from the 5' → 3' direction. Although DNA is arranged as two antiparallel strands in a double helix, only one of the two DNA strands, called the template strand, is used for transcription. ...
L15 Gene Regulation Part2 Fa08
... • Variations in phenotype depending on whether an allele is inherited from the male or female parent ...
... • Variations in phenotype depending on whether an allele is inherited from the male or female parent ...
Slide 1
... Long sequence of A nucleotides added to 3’ end – facilitate the export of the mRNA from the nucleus, – protect the mRNA from destruction, and ...
... Long sequence of A nucleotides added to 3’ end – facilitate the export of the mRNA from the nucleus, – protect the mRNA from destruction, and ...
Gene Regulation
... These enzymes use the siRNA to recognize mRNA with complementary base sequences, bind to them, and then cut them up before they can be translated. The siRNA concept is now being used to try to turn off expression of genes in plant and animal cells. This is done by artificially producing dsRNA for a ...
... These enzymes use the siRNA to recognize mRNA with complementary base sequences, bind to them, and then cut them up before they can be translated. The siRNA concept is now being used to try to turn off expression of genes in plant and animal cells. This is done by artificially producing dsRNA for a ...
Transcription and Translation
... transcription is numbered “+1” and is called the transcription start site. • Transcription factors that are required at every promoter site for RNA polymerase interaction are called basal transcription factors. ...
... transcription is numbered “+1” and is called the transcription start site. • Transcription factors that are required at every promoter site for RNA polymerase interaction are called basal transcription factors. ...
lacI
... In bacterial RNA polymerse, the core enzyme consists of four subunits: two copies of alpha (α), a single copy of beta (β), and a single copy of ...
... In bacterial RNA polymerse, the core enzyme consists of four subunits: two copies of alpha (α), a single copy of beta (β), and a single copy of ...