cancer epigenetics - Experimental oncology
... emphasize the important place of histones’ posttranslational modifications as a target of cancer therapy. MicroRNAs (miRNA), an abundant class of small nonprotein-coding RNAs, play a role in posttranscriptional regulation and function as negative gene expression regulators. miRNAs mutations or mis-e ...
... emphasize the important place of histones’ posttranslational modifications as a target of cancer therapy. MicroRNAs (miRNA), an abundant class of small nonprotein-coding RNAs, play a role in posttranscriptional regulation and function as negative gene expression regulators. miRNAs mutations or mis-e ...
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
... - A cell can regulate the production of enzymes by feedback inhibition or by gene regulation. - Bacteria often respond to environmental change by regulating transcription. - Gene expression in bacteria is controlled by the operon model. A. Operons: The Basic Concept - A cluster of functionally relat ...
... - A cell can regulate the production of enzymes by feedback inhibition or by gene regulation. - Bacteria often respond to environmental change by regulating transcription. - Gene expression in bacteria is controlled by the operon model. A. Operons: The Basic Concept - A cluster of functionally relat ...
Ch. 18 Notes
... - A cell can regulate the production of enzymes by feedback inhibition or by gene regulation. - Bacteria often respond to environmental change by regulating transcription. - Gene expression in bacteria is controlled by the operon model. A. Operons: The Basic Concept - A cluster of functionally relat ...
... - A cell can regulate the production of enzymes by feedback inhibition or by gene regulation. - Bacteria often respond to environmental change by regulating transcription. - Gene expression in bacteria is controlled by the operon model. A. Operons: The Basic Concept - A cluster of functionally relat ...
TITLE OF MODULE: From Gene to Function MODULE NUMBER
... Lecture 25. Nuclear export, cytoplasmic localisation and RNA decay. How is mRNA exported from the nucleus. Mechanism and significance of specific mRNA localisation in the cytoplasm. Pathways of mRNA decay with an emphasis on quality control mechanisms. (ALJ) Lecture 26. Non-coding regulatory RNAs. H ...
... Lecture 25. Nuclear export, cytoplasmic localisation and RNA decay. How is mRNA exported from the nucleus. Mechanism and significance of specific mRNA localisation in the cytoplasm. Pathways of mRNA decay with an emphasis on quality control mechanisms. (ALJ) Lecture 26. Non-coding regulatory RNAs. H ...
Molecular Biology - Gene Regulation
... OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0‡ ...
... OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0‡ ...
Gene Expression - Phillips Scientific Methods
... 4. Where does replication occur in eukaryotic cells? 5. Where does transcription occur in eukaryotic cells? 6. Where does post-transcriptional processing occur in eukaryotic cells? 7. Where does translation occur in eukaryotic cells? 8. Circle all that apply a) DNA Polymerase is used in ...
... 4. Where does replication occur in eukaryotic cells? 5. Where does transcription occur in eukaryotic cells? 6. Where does post-transcriptional processing occur in eukaryotic cells? 7. Where does translation occur in eukaryotic cells? 8. Circle all that apply a) DNA Polymerase is used in ...
Gene_expression
... (a “reporter gene”). The jellyfish green fluorscent protein (GFP) gene is often used, as the encoded protein emits green light when exposed to light of the proper wavelength. We can test for CRM activity in transfected cells in culture, or even better, in a transgenic animal: ...
... (a “reporter gene”). The jellyfish green fluorscent protein (GFP) gene is often used, as the encoded protein emits green light when exposed to light of the proper wavelength. We can test for CRM activity in transfected cells in culture, or even better, in a transgenic animal: ...
New Data, Research and Tools at genome.ucsc.edu
... blood cells) share the same DNA, which parts of the DNA are used by cells varies. • As cells divide they differentiate into different cell types based on signals from other cells, the environment, a bit of randomness, and the cell’s internal state. • Most of the differentiation decisions ...
... blood cells) share the same DNA, which parts of the DNA are used by cells varies. • As cells divide they differentiate into different cell types based on signals from other cells, the environment, a bit of randomness, and the cell’s internal state. • Most of the differentiation decisions ...
Walk the Dogma - Nutley Public Schools
... information is copied from DNA to RNA • DNA double-strand “unzips” • RNA polymerase (an enzyme) binds to a specific region on DNA called a promoter • RNA polymerase travels along the gene, creating a chain of mRNA that is complementary to the strand of DNA • RNA polymerase reaches the termination si ...
... information is copied from DNA to RNA • DNA double-strand “unzips” • RNA polymerase (an enzyme) binds to a specific region on DNA called a promoter • RNA polymerase travels along the gene, creating a chain of mRNA that is complementary to the strand of DNA • RNA polymerase reaches the termination si ...
Checklist unit 18: Regulation of Gene Expression
... translated; translation initiation can be blocked by regulatory proteins; and, finally, once a protein has been synthesized, it can be degraded or altered to render it inactive. This may ...
... translated; translation initiation can be blocked by regulatory proteins; and, finally, once a protein has been synthesized, it can be degraded or altered to render it inactive. This may ...
Chapter 12 - North Mac Schools
... therefore passing it down CREATES GENETIC VARIABILITY! This is often how asexually reproducing organisms evolve... a slow process ...
... therefore passing it down CREATES GENETIC VARIABILITY! This is often how asexually reproducing organisms evolve... a slow process ...
Transcription
... – Binds more tightly to DNA as DNA untwists for about 17 bp centered around the –10 box. ...
... – Binds more tightly to DNA as DNA untwists for about 17 bp centered around the –10 box. ...
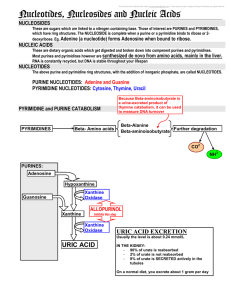
3 Nucleosides nucleotides and nucleic acids
... Extremely long nucleotide chains containing - ADENINE - GUANINE - THYMINE - CYTOSINE The double helix is held together by hudrogen bonds between the bases : - ADENINE BONDS TO THYMINE - GUANINE BONDS TO CYTOSINE A diploid human cell contains 46 chromosomes. Useful factoid to know. - EXONS are portio ...
... Extremely long nucleotide chains containing - ADENINE - GUANINE - THYMINE - CYTOSINE The double helix is held together by hudrogen bonds between the bases : - ADENINE BONDS TO THYMINE - GUANINE BONDS TO CYTOSINE A diploid human cell contains 46 chromosomes. Useful factoid to know. - EXONS are portio ...
Central Dogma WebQuest - Life Science
... 3. In a eukaryotic cell, transcription occurs in the nucleus, and translation occurs in the ______________. 4. Write the functions of the following forms of RNA: mRNA: ___________________________________________________________________________ tRNA: __________________________________________________ ...
... 3. In a eukaryotic cell, transcription occurs in the nucleus, and translation occurs in the ______________. 4. Write the functions of the following forms of RNA: mRNA: ___________________________________________________________________________ tRNA: __________________________________________________ ...
Gene Expression
... sequence of a genome, as the “blueprint” of a cell, organism or species. Sequence the steps of how DNA’s code is transcribed into RNA through the process of transcription. Sequence the steps of how proteins are made from the mRNA transcript through the process of translation. Predict the location wh ...
... sequence of a genome, as the “blueprint” of a cell, organism or species. Sequence the steps of how DNA’s code is transcribed into RNA through the process of transcription. Sequence the steps of how proteins are made from the mRNA transcript through the process of translation. Predict the location wh ...
A quantitative modeling of protein
... We may be able to use heterogeneous experimental data to reveal the underlying mechanisms of differential binding of transcription factor to cis-regulatory region. ...
... We may be able to use heterogeneous experimental data to reveal the underlying mechanisms of differential binding of transcription factor to cis-regulatory region. ...
Transcription PPT
... • Only 1 of the 2 DNA strands is used to make the mRNA; this strand is called the DNA template • DNA code on the mRNA is read three bases at once, and these three letter base combinations on the mRNA are called codons • Codons determine your genetic code and the traits expressed from protein synthes ...
... • Only 1 of the 2 DNA strands is used to make the mRNA; this strand is called the DNA template • DNA code on the mRNA is read three bases at once, and these three letter base combinations on the mRNA are called codons • Codons determine your genetic code and the traits expressed from protein synthes ...
4-5
... Circle the letter of the answer that best completes the statement. A group of genes that work together in a pathway and are controlled by one on/off switch is known as a(n) _______________________ A. codon B. operator C. operon D. gene group When the lac repressor protein binds to the ______________ ...
... Circle the letter of the answer that best completes the statement. A group of genes that work together in a pathway and are controlled by one on/off switch is known as a(n) _______________________ A. codon B. operator C. operon D. gene group When the lac repressor protein binds to the ______________ ...
Power Point Notes
... • Unlike DNA replication – Only small stretch is template – RNA polymerase catalyzes nucleotide addition – Product is a single strand of RNA ...
... • Unlike DNA replication – Only small stretch is template – RNA polymerase catalyzes nucleotide addition – Product is a single strand of RNA ...
Controlling Gene Expression
... Determine when to make more proteins and when to stop making more Cell has mechanisms to control transcription and translation Housekeeping genes are genes that are always needed, and are constantly synthesizing proteins (switched on) ...
... Determine when to make more proteins and when to stop making more Cell has mechanisms to control transcription and translation Housekeeping genes are genes that are always needed, and are constantly synthesizing proteins (switched on) ...