Practice Questions
... transcription. The EF-Tu cycle is critical in gene translation in prokaryotes (not yeast); not gene transcription. Translation also occurs in the cytosol. RNA Pol III is necessary to transcribe RNA for snRNA and scRNA; neither are critical for transcription. The position of the promoter is critical ...
... transcription. The EF-Tu cycle is critical in gene translation in prokaryotes (not yeast); not gene transcription. Translation also occurs in the cytosol. RNA Pol III is necessary to transcribe RNA for snRNA and scRNA; neither are critical for transcription. The position of the promoter is critical ...
Gene Expression
... Elongation. The polymerase moves downstream, unwinding the DNA and elongating the RNA transcript 5¢ Æ 3 ¢. In the wake of transcription, the DNA strands re-form a double helix. ...
... Elongation. The polymerase moves downstream, unwinding the DNA and elongating the RNA transcript 5¢ Æ 3 ¢. In the wake of transcription, the DNA strands re-form a double helix. ...
Glossary Algae: Unicellular or simple multicellular photosynthetic
... structure by which hereditary information is physically transmitted from one generation to the next; in a bacterium, the chromosome consists of a single nacked circle of DNA; in eukaryotes, each chromosome consists of a single linear DNA molecule and associated proteins. Codon bias: Refers to the fa ...
... structure by which hereditary information is physically transmitted from one generation to the next; in a bacterium, the chromosome consists of a single nacked circle of DNA; in eukaryotes, each chromosome consists of a single linear DNA molecule and associated proteins. Codon bias: Refers to the fa ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... FIGURE 27-6: ChIP and microarray analysis of transcription. The chromatin immunoprecipitation assay is depicted on the left-hand portion of this figure. Each of the steps leading to characterization of the DNA sequence associated with selected transcription factors is illustrated for the CREB trans ...
... FIGURE 27-6: ChIP and microarray analysis of transcription. The chromatin immunoprecipitation assay is depicted on the left-hand portion of this figure. Each of the steps leading to characterization of the DNA sequence associated with selected transcription factors is illustrated for the CREB trans ...
Study Guide
... 23. The expression of a gene is said to be ‘turned on’ when certain signals interact with the promoter of a gene and RNA is produced. The strand of RNA that corresponds to a gene is complementary to the sequence of DNA. The process called "Transcription" is: (A) the transfer of gases through the cel ...
... 23. The expression of a gene is said to be ‘turned on’ when certain signals interact with the promoter of a gene and RNA is produced. The strand of RNA that corresponds to a gene is complementary to the sequence of DNA. The process called "Transcription" is: (A) the transfer of gases through the cel ...
DNA Protein Synthesis Review Q`s.doc
... Opposite the attachment site on tRNA are 3 nucleotide bases called the ______________. ...
... Opposite the attachment site on tRNA are 3 nucleotide bases called the ______________. ...
4.13 notes
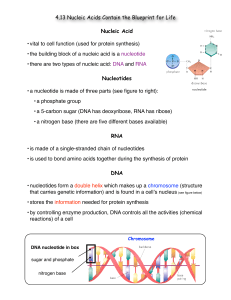
... • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded chain of nucleotides • is used to bond amino acids together during ...
... • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded chain of nucleotides • is used to bond amino acids together during ...
the language of biology - Gonzaga College High School
... blood vessels and cartilage, and holds the inner organs together). there are many other functions for proteins. Together, they tell the complex of "stories" that make up an organism. ...
... blood vessels and cartilage, and holds the inner organs together). there are many other functions for proteins. Together, they tell the complex of "stories" that make up an organism. ...
Zoology 145 course
... • Bacteria have a single type of RNA polymerase that synthesizes all RNA molecules. • In contrast, eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases (I, II, and III) in their nuclei. – RNA polymerase II is used for mRNA synthesis. ...
... • Bacteria have a single type of RNA polymerase that synthesizes all RNA molecules. • In contrast, eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases (I, II, and III) in their nuclei. – RNA polymerase II is used for mRNA synthesis. ...
chapter 3 outline
... The identity of the incorporated bases is dictated by the template sequence. Termination Termination is dependent on specific nucleotide sequence signals. A common motif in prokaryotes is the hairpin loop structure, followed by poly-U sequence. Unlike prokaryotes, where there is one principle RNA po ...
... The identity of the incorporated bases is dictated by the template sequence. Termination Termination is dependent on specific nucleotide sequence signals. A common motif in prokaryotes is the hairpin loop structure, followed by poly-U sequence. Unlike prokaryotes, where there is one principle RNA po ...
lecture notes-molecular biology-web
... • Induction of allolactose might not be sufficient for maximum transcription if a carbon-energy source (e.g. glucose) preferred to lactose is present. • Only when glucose is depleted, the cell will expend energy to create a pathway to utilize the less favorable carbon-energy source lactose. ...
... • Induction of allolactose might not be sufficient for maximum transcription if a carbon-energy source (e.g. glucose) preferred to lactose is present. • Only when glucose is depleted, the cell will expend energy to create a pathway to utilize the less favorable carbon-energy source lactose. ...
File
... – transcription factors bind to promoter region of DNA • proteins • can be activated by hormones (cell signaling) • turn on or off transcription – triggers the binding of RNA polymerase to DNA ...
... – transcription factors bind to promoter region of DNA • proteins • can be activated by hormones (cell signaling) • turn on or off transcription – triggers the binding of RNA polymerase to DNA ...
lac
... • Definition: a cluster of genes in which expression is regulated by operator-repressor protein interactions, operator region, and the promoter. • Its structure: Each Operon is consisted of few structural genes( cistrons) and some cis-acting element such as promoter (P) and operator (O). • Its regul ...
... • Definition: a cluster of genes in which expression is regulated by operator-repressor protein interactions, operator region, and the promoter. • Its structure: Each Operon is consisted of few structural genes( cistrons) and some cis-acting element such as promoter (P) and operator (O). • Its regul ...
university of oslo
... Immunoglobulins consist of heavy and light chains which are both composed of variable and constant amino acid sequences (Figure 14.7). In early B-lymphocyte (or T-cell) development the genes for the immunoglobulin proteins are assembled by recombination from gene segments that code for the variable ...
... Immunoglobulins consist of heavy and light chains which are both composed of variable and constant amino acid sequences (Figure 14.7). In early B-lymphocyte (or T-cell) development the genes for the immunoglobulin proteins are assembled by recombination from gene segments that code for the variable ...
Exam V2002 - English
... Immunoglobulins consist of heavy and light chains which are both composed of variable and constant amino acid sequences (Figure 14.7). In early B-lymphocyte (or T-cell) development the genes for the immunoglobulin proteins are assembled by recombination from gene segments that code for the variable ...
... Immunoglobulins consist of heavy and light chains which are both composed of variable and constant amino acid sequences (Figure 14.7). In early B-lymphocyte (or T-cell) development the genes for the immunoglobulin proteins are assembled by recombination from gene segments that code for the variable ...
CyberPDX Lesson Plan
... 2. Students will break into groups of four to model transcription and translation in the human body. For this activity each person serves a different role. a. Transcriber/mRNA: goes into the “nucleus” and transcribes the DNA sequence into mRNA. Once completed, returns to “cytoplasm” and hands code t ...
... 2. Students will break into groups of four to model transcription and translation in the human body. For this activity each person serves a different role. a. Transcriber/mRNA: goes into the “nucleus” and transcribes the DNA sequence into mRNA. Once completed, returns to “cytoplasm” and hands code t ...
Les 6b RNA Transcription and Translation
... RNA nucleotides “float” into place with the aid of RNA polymerase and complementary base pairing occurs There are nonsense codes at the end of the gene that terminate mRNA synthesis. mRNA breaks off and moves out of the nucleus into the ribosomes of the cytoplasm ...
... RNA nucleotides “float” into place with the aid of RNA polymerase and complementary base pairing occurs There are nonsense codes at the end of the gene that terminate mRNA synthesis. mRNA breaks off and moves out of the nucleus into the ribosomes of the cytoplasm ...
CHAPTER 10 - Protein Synthesis The DNA genotype is expressed
... Review: The flow of genetic information in the cell is DNA→RNA→protein • The sequence of codons in DNA spells out the primary structure of a polypeptide – Polypeptides form proteins that cells and organisms use Describe the process of translation. Include the following: ...
... Review: The flow of genetic information in the cell is DNA→RNA→protein • The sequence of codons in DNA spells out the primary structure of a polypeptide – Polypeptides form proteins that cells and organisms use Describe the process of translation. Include the following: ...
PDF
... by activating Arp2/3 in response to Rac and Cdc42 GTPases. By contrast, the linear actin nucleators Spire and Cappuccino (Capu) function downstream of Rho1 GTPase. But now, Susan Parkhurst and colleagues dzemonstrate that Rho1 and Wash regulate both linear- and branched-filament actin networks (see ...
... by activating Arp2/3 in response to Rac and Cdc42 GTPases. By contrast, the linear actin nucleators Spire and Cappuccino (Capu) function downstream of Rho1 GTPase. But now, Susan Parkhurst and colleagues dzemonstrate that Rho1 and Wash regulate both linear- and branched-filament actin networks (see ...
PDF
... by activating Arp2/3 in response to Rac and Cdc42 GTPases. By contrast, the linear actin nucleators Spire and Cappuccino (Capu) function downstream of Rho1 GTPase. But now, Susan Parkhurst and colleagues dzemonstrate that Rho1 and Wash regulate both linear- and branched-filament actin networks (see ...
... by activating Arp2/3 in response to Rac and Cdc42 GTPases. By contrast, the linear actin nucleators Spire and Cappuccino (Capu) function downstream of Rho1 GTPase. But now, Susan Parkhurst and colleagues dzemonstrate that Rho1 and Wash regulate both linear- and branched-filament actin networks (see ...
Capacity Matrix Name: Date Started: Date Completed: Class/Course
... way. (e.g. Explain or go beyond) ...
... way. (e.g. Explain or go beyond) ...
Name DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis Test Review Study your
... G and C pair with each other. The RNA polymerase adds new nucleotides until it reaches the end of the gene where it stops. ...
... G and C pair with each other. The RNA polymerase adds new nucleotides until it reaches the end of the gene where it stops. ...
AP-ppt-PCR
... DNA microarray analysis Microscopic DNA attached to solid surface like glass, silicon Allows us to answer questions about gene activity ...
... DNA microarray analysis Microscopic DNA attached to solid surface like glass, silicon Allows us to answer questions about gene activity ...