Chapter 21 - HCC Learning Web
... • Using available DNA sequences, geneticists can study genes directly in an approach called reverse genetics • The identification of protein coding genes within DNA sequences in a database is called gene annotation • Gene annotation is largely an automated process • Comparison of sequences of previo ...
... • Using available DNA sequences, geneticists can study genes directly in an approach called reverse genetics • The identification of protein coding genes within DNA sequences in a database is called gene annotation • Gene annotation is largely an automated process • Comparison of sequences of previo ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... Why? DNA has the genetic code for the protein that needs to be made, but proteins are made by the ribosomes—ribosomes are outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. DNA is too large to leave the nucleus (double stranded), but RNA can leave the nucleus (single stranded). ...
... Why? DNA has the genetic code for the protein that needs to be made, but proteins are made by the ribosomes—ribosomes are outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. DNA is too large to leave the nucleus (double stranded), but RNA can leave the nucleus (single stranded). ...
Transcription and Translation Reproduction is one of the basic
... The Human Genome Project has led us to understand that there are a number of recognizable patterns observed in DNA. It has been estimated that there are approximately 25,000 protein-coding genes in the human genome. In addition, some genes are transcribed to produce other forms of RNA other than mRN ...
... The Human Genome Project has led us to understand that there are a number of recognizable patterns observed in DNA. It has been estimated that there are approximately 25,000 protein-coding genes in the human genome. In addition, some genes are transcribed to produce other forms of RNA other than mRN ...
ranjan rajeev
... of a bHLH transcription factor during anther development process in rice. Previously, by using microarray, qRT-PCR and promoter-reporter assay in transgenic system we reported OsbHLH142 as an anther specific gene in rice. Expression analysis of OsbHLH142 transcripts through qPCR and its protein prof ...
... of a bHLH transcription factor during anther development process in rice. Previously, by using microarray, qRT-PCR and promoter-reporter assay in transgenic system we reported OsbHLH142 as an anther specific gene in rice. Expression analysis of OsbHLH142 transcripts through qPCR and its protein prof ...
Structure of Proteins
... able to carry out its function. However, some changes in amino acid may not have any effect. Nonsense – these substitutions change the codon from an amino acid to a stop codon. The shortened protein is generally non-functional or its function is affected. Splice-site – these substitutions affect the ...
... able to carry out its function. However, some changes in amino acid may not have any effect. Nonsense – these substitutions change the codon from an amino acid to a stop codon. The shortened protein is generally non-functional or its function is affected. Splice-site – these substitutions affect the ...
Student book links
... Students can confuse the terms: sense strand; coding strand; and template strand – carefully define these terms and revisit when necessary. Some students find it difficult to distinguish between the terms: locus; gene; and allele. Using different functional and structural models of chromosomes and g ...
... Students can confuse the terms: sense strand; coding strand; and template strand – carefully define these terms and revisit when necessary. Some students find it difficult to distinguish between the terms: locus; gene; and allele. Using different functional and structural models of chromosomes and g ...
Epigenetics - Current Issues in Human Genetics
... Holt. (2007). Epigenetics:Environmental factors can alter the way our genes are expressed, making even identical twins different. PBS. NOVA. Junko, et. al. (2009). Transgenerational Rescue of a Genetic Deficit in LTP and Memory Formation by Juvenile Enrichment. Journal of Neuroscience. 1496-1502. ...
... Holt. (2007). Epigenetics:Environmental factors can alter the way our genes are expressed, making even identical twins different. PBS. NOVA. Junko, et. al. (2009). Transgenerational Rescue of a Genetic Deficit in LTP and Memory Formation by Juvenile Enrichment. Journal of Neuroscience. 1496-1502. ...
Virtual Lac Operon Activity[1].
... Control of transcription is often a complex process. The presence of one molecule may prevent transcription while the presence of a different molecule may stimulate transcription but only if the first molecule is not present. Multiple transcription factors and complex interactions between the factor ...
... Control of transcription is often a complex process. The presence of one molecule may prevent transcription while the presence of a different molecule may stimulate transcription but only if the first molecule is not present. Multiple transcription factors and complex interactions between the factor ...
DNA
... - With the exception of small proteins designed for simple tasks, a vast array of more complex and regulatory proteins are not monolithic but rather modular—ie they can be divided into constituent parts or regions specialized for specific roles - Such specialized parts/regions of modular proteins ar ...
... - With the exception of small proteins designed for simple tasks, a vast array of more complex and regulatory proteins are not monolithic but rather modular—ie they can be divided into constituent parts or regions specialized for specific roles - Such specialized parts/regions of modular proteins ar ...
DNA-RNA-Protein Synthesis
... Decide as a group how to build a model of DNA. The artist should draw it for the group and label each base subunit (nitrogen base) according to the model. The recorder should write down the process (pair, unzip…) what’s on the sides, in the middle, and attaching the two strands. The builder/demolish ...
... Decide as a group how to build a model of DNA. The artist should draw it for the group and label each base subunit (nitrogen base) according to the model. The recorder should write down the process (pair, unzip…) what’s on the sides, in the middle, and attaching the two strands. The builder/demolish ...
HERE
... • Three bases make up the base sequence. • The three bases are called the CODON. • Scientists use tables to determine the correct match of codon to amino acids. • There are 21 amino acids in the body. ...
... • Three bases make up the base sequence. • The three bases are called the CODON. • Scientists use tables to determine the correct match of codon to amino acids. • There are 21 amino acids in the body. ...
Mentor: James A. MacKay Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka
... Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive go ...
... Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive go ...
Exam 4
... B) Prokaryotic mRNA receives a 5’ cap before translation C) In prokaryotes, transcription and translation of an RNA molecule can occur at the same time D) Prokaryotic DNA includes a promoter for each gene E) Prokaryotic ribosomes stop translating at one of three stop codons 35. Which of the followin ...
... B) Prokaryotic mRNA receives a 5’ cap before translation C) In prokaryotes, transcription and translation of an RNA molecule can occur at the same time D) Prokaryotic DNA includes a promoter for each gene E) Prokaryotic ribosomes stop translating at one of three stop codons 35. Which of the followin ...
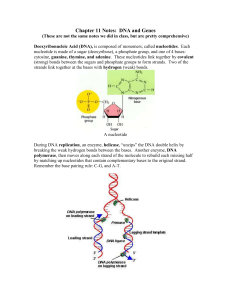
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA is single stranded. ...
... base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA is single stranded. ...
Microbial Genetics
... It is semi-conservative; half from the “parent” half newly synthesized. It’s initiated at a replication fork; DNA must be unwound and unbound into two single strands. ...
... It is semi-conservative; half from the “parent” half newly synthesized. It’s initiated at a replication fork; DNA must be unwound and unbound into two single strands. ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • Two families of 5S rRNA genes studied are oocyte and somatic genes – Oocyte genes are expressed only in oocytes – Somatic genes are expressed both in oocytes and somatic cells – Somatic genes form more stable complexes with transcription factors ...
... • Two families of 5S rRNA genes studied are oocyte and somatic genes – Oocyte genes are expressed only in oocytes – Somatic genes are expressed both in oocytes and somatic cells – Somatic genes form more stable complexes with transcription factors ...
BP 32: Posters - DNA/RNA - DPG
... DNA is carried out by RNA Polymerase II (Pol II) in low DNA density regions. While this organization reflects a need to unfold DNA for Pol II access, the causal origin of this spatial organization remains unclear. Here, we investigate if and how transcribing Pol II organizes DNA. Using zebrafish emb ...
... DNA is carried out by RNA Polymerase II (Pol II) in low DNA density regions. While this organization reflects a need to unfold DNA for Pol II access, the causal origin of this spatial organization remains unclear. Here, we investigate if and how transcribing Pol II organizes DNA. Using zebrafish emb ...
“Adventures in Eukaryotic Gene Expression: Transcription, Splicing, Polyadenylation, and RNAi”
... Anders Virtanen: ...
... Anders Virtanen: ...
DNA vs RNA
... • This is one of the biggest questions in biology, which we all know is the study of life. • So, can some of the monsters we see on Halloween, for example, ghosts, vampires, werewolves, and zombies actually exist? ...
... • This is one of the biggest questions in biology, which we all know is the study of life. • So, can some of the monsters we see on Halloween, for example, ghosts, vampires, werewolves, and zombies actually exist? ...
Transcription, Translation
... 2. tRNA – transports amino acids to the mRNA to make a protein 3. rRNA – make up ribosomes, which make protein. ...
... 2. tRNA – transports amino acids to the mRNA to make a protein 3. rRNA – make up ribosomes, which make protein. ...
Protein Synthesis - Overview
... The mRNA consists of nucleotides that code for a specific amino acid. The code is in triplet called a CODON (3 nucleotides = 1 amino acid). Amino acids are brought into place by a molecule known as transfer RNA (tRNA). This process is known as translation. Peptide bonds occur b/w amino acids. ...
... The mRNA consists of nucleotides that code for a specific amino acid. The code is in triplet called a CODON (3 nucleotides = 1 amino acid). Amino acids are brought into place by a molecule known as transfer RNA (tRNA). This process is known as translation. Peptide bonds occur b/w amino acids. ...
From RNA to protein
... The sequence of a coding (sense, non-template) strand of DNA, read 5’ – 3’, specifies a sequence of amino acids (read Nterminus to C-terminus) via a triplet code. Each triplet is called a codon and 4 bases give 43 possible combinations. Reading the DNA code: There are 64 codons; 61 represent amino a ...
... The sequence of a coding (sense, non-template) strand of DNA, read 5’ – 3’, specifies a sequence of amino acids (read Nterminus to C-terminus) via a triplet code. Each triplet is called a codon and 4 bases give 43 possible combinations. Reading the DNA code: There are 64 codons; 61 represent amino a ...
Document
... DNA carries four nucleotides: A, T, G, and C • Three nucleotide codon in messenger RNA (mRNA) specifies one amino acid ...
... DNA carries four nucleotides: A, T, G, and C • Three nucleotide codon in messenger RNA (mRNA) specifies one amino acid ...
No Slide Title
... passing both strands of double-stranded DNA through a break. * Eukaryotic topoisomerases isolated to date only relax supercoiled DNA, while prokaryotic topoisomerases (gyrases) can, given ATP, add supercoils. * TopoII releases catenated daughter molecules at the end of replication. Inhibitors like e ...
... passing both strands of double-stranded DNA through a break. * Eukaryotic topoisomerases isolated to date only relax supercoiled DNA, while prokaryotic topoisomerases (gyrases) can, given ATP, add supercoils. * TopoII releases catenated daughter molecules at the end of replication. Inhibitors like e ...







![Virtual Lac Operon Activity[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010559846_1-7885f04a16c1dd22b8c6591726a1d937-300x300.png)