The nucleotide sequence of a gene is colinear with the amino acid
... Genetic code is almost universal but not quite ...
... Genetic code is almost universal but not quite ...
Protein synthesis
... PROTEIN SYNTHESIS The carrier molecule is messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) RNA are nucleic acids like DNA but there are some key differences: - There are 3 different forms on RNA – messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). They each have a different function. - RNA is ...
... PROTEIN SYNTHESIS The carrier molecule is messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) RNA are nucleic acids like DNA but there are some key differences: - There are 3 different forms on RNA – messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). They each have a different function. - RNA is ...
Genetics and Protein Synthesis
... next triplet, opening the A site. The new tRNA enters at the A site. When the codon in the A site is a termination codon, a releasing factor binds to the site, stopping translation and releasing the ribosomal complex and mRNA. ...
... next triplet, opening the A site. The new tRNA enters at the A site. When the codon in the A site is a termination codon, a releasing factor binds to the site, stopping translation and releasing the ribosomal complex and mRNA. ...
No Slide Title
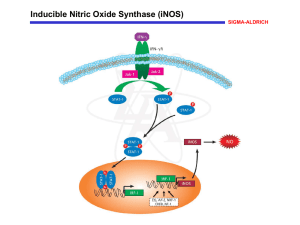
... Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) Macrophages are important for early immune responses to invading microorganisms, and the production of nitric oxide (NO) is central to this function. NO is generated by inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS, macNOS, Type II NOS) following exposure to certain c ...
... Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) Macrophages are important for early immune responses to invading microorganisms, and the production of nitric oxide (NO) is central to this function. NO is generated by inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS, macNOS, Type II NOS) following exposure to certain c ...
AP Biology Study Guide
... o Enzymes involved in DNA Replication: helicase, DNA polymerase (particularly directionality), replication forks, primase, primers, DNA Ligase, telomerase/telomers Protein Synthesis o Transcription - Initiation, Elongations, Termination (differences in Pro and Eukaryotes), codons, RNA modification, ...
... o Enzymes involved in DNA Replication: helicase, DNA polymerase (particularly directionality), replication forks, primase, primers, DNA Ligase, telomerase/telomers Protein Synthesis o Transcription - Initiation, Elongations, Termination (differences in Pro and Eukaryotes), codons, RNA modification, ...
NUCLEIC ACIDS
... I. Protein Synthesis (2 stage processing of information from DNA to proteins) = gene expression A. chromosomes are divided into segments called genes – genes are directions for building all the proteins needed by an organism B. Not all genes are active (expressed) at the same time. 1. Why: Because t ...
... I. Protein Synthesis (2 stage processing of information from DNA to proteins) = gene expression A. chromosomes are divided into segments called genes – genes are directions for building all the proteins needed by an organism B. Not all genes are active (expressed) at the same time. 1. Why: Because t ...
BioIIch17notesRNAfilled.p pt
... -mRNA first synthesized needs to be modified before it can leave the nucleus -RNA splicing -primary RNA transcript is about 8000 nucleotides long -only takes about 1200 nucleotides to code for an average size protein of about 400 amino acids -most genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding ...
... -mRNA first synthesized needs to be modified before it can leave the nucleus -RNA splicing -primary RNA transcript is about 8000 nucleotides long -only takes about 1200 nucleotides to code for an average size protein of about 400 amino acids -most genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding ...
Protein Synthesis
... – Single chain that carries genetic information from DNA in nucleus to the cytosol ...
... – Single chain that carries genetic information from DNA in nucleus to the cytosol ...
Unidirectional tandem gene arrays
... humans, the ubiquitination reaction is catalyzed by >500 E3 ligases, each of which transfers ubiquitin ...
... humans, the ubiquitination reaction is catalyzed by >500 E3 ligases, each of which transfers ubiquitin ...
RNA & Transcription
... 5) RNA IS EDITED: sections removed are called Introns while the parts that stay are called exons. The parts of the primary transcript called introns are cut out. Introns appear to match noncoding regions of DNA. In order for this to happen, “Snurps” (snRNA & Protein complexes) bind to form spliceoso ...
... 5) RNA IS EDITED: sections removed are called Introns while the parts that stay are called exons. The parts of the primary transcript called introns are cut out. Introns appear to match noncoding regions of DNA. In order for this to happen, “Snurps” (snRNA & Protein complexes) bind to form spliceoso ...
From Genes to Proteins
... gene for keratin is transcribed and translated by certain skin cells. The series of letters on the next slide represents the sequence of nucleotides in a portion of an mRNA molecule transcribed from the gene for keratin. This mRNA strand and the genetic code on page 211 can be used to determine some ...
... gene for keratin is transcribed and translated by certain skin cells. The series of letters on the next slide represents the sequence of nucleotides in a portion of an mRNA molecule transcribed from the gene for keratin. This mRNA strand and the genetic code on page 211 can be used to determine some ...
Lectures by Erin Barley Kathleen Fitzpatrick From Gene to Protein
... • Three properties of RNA enable it to function as an enzyme – It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base-pair with itself – Some bases in RNA contain functional groups that may participate in catalysis – RNA may hydrogen-bond with other nucleic acid molecules ...
... • Three properties of RNA enable it to function as an enzyme – It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base-pair with itself – Some bases in RNA contain functional groups that may participate in catalysis – RNA may hydrogen-bond with other nucleic acid molecules ...
1. ELONGATION
... In eukaryotes, the initial product of transcription, the primary RNA transcript, is processed in several ways before its transport to the cytosol. These processing steps are all performed by specific proteins that bind to the RNA. Until it reaches its final, mature form, the primary transcript is so ...
... In eukaryotes, the initial product of transcription, the primary RNA transcript, is processed in several ways before its transport to the cytosol. These processing steps are all performed by specific proteins that bind to the RNA. Until it reaches its final, mature form, the primary transcript is so ...
Molecular genetics of bacteria
... • Many genes in prokaryotes are grouped together in the DNA and are regulated as a unit. Genes are usually for enzymes that function together in the same pathway. • At the upstream end are sections of DNA that do not code, but rather are binding sites for proteins involved in regulation (turning gen ...
... • Many genes in prokaryotes are grouped together in the DNA and are regulated as a unit. Genes are usually for enzymes that function together in the same pathway. • At the upstream end are sections of DNA that do not code, but rather are binding sites for proteins involved in regulation (turning gen ...
No Slide Title
... 1) UBF (upstream binding factor) binds UCE and core element UBF is a transcription factor: DNA-binding proteins which recruit polymerases and tell them where to begin ...
... 1) UBF (upstream binding factor) binds UCE and core element UBF is a transcription factor: DNA-binding proteins which recruit polymerases and tell them where to begin ...
Document
... • CAP helps regulate other operons that encode enzymes used in catabolic pathways • when glucose levels are low and lactose levels are ...
... • CAP helps regulate other operons that encode enzymes used in catabolic pathways • when glucose levels are low and lactose levels are ...
2015 Schmidt W Pulse control and root hair development Nature
... oscillatory expression patterns have also been described for genes that determine the formation of lateral roots5, the number of which increases upon phosphate starvation. Thus it appears that transient gene expression and protein turnover are critical for environmentally mediated tuning of developm ...
... oscillatory expression patterns have also been described for genes that determine the formation of lateral roots5, the number of which increases upon phosphate starvation. Thus it appears that transient gene expression and protein turnover are critical for environmentally mediated tuning of developm ...
Class: AP Bio Unit: Genetics Estimated Date Target Reading
... 11/04/11 Describe how environmental conditions can effect gene expression and how there is a range of gene expression. Differentiate between autosomal inheritance and sexlinked inheritance. ...
... 11/04/11 Describe how environmental conditions can effect gene expression and how there is a range of gene expression. Differentiate between autosomal inheritance and sexlinked inheritance. ...
The genotype is the plan / blueprint for creating an organism
... transcription unit - the part of a gene that gets copied (transcribed) by RNA polymerase coding region – For genes that make (encode) proteins, the coding region is part of the transcription unit. The coding region is the genetic information in the DNA that tells the specific structure (primary ami ...
... transcription unit - the part of a gene that gets copied (transcribed) by RNA polymerase coding region – For genes that make (encode) proteins, the coding region is part of the transcription unit. The coding region is the genetic information in the DNA that tells the specific structure (primary ami ...
DNA Transcription
... – Carry copies of instructions for the assembly of amino acids into proteins – Serve as “messengers” from DNA to the rest of the cell ...
... – Carry copies of instructions for the assembly of amino acids into proteins – Serve as “messengers” from DNA to the rest of the cell ...
The genetic engineers toolkit
... A way of working out the function of a gene by creating a non functioning one in an organism so you can see its effects. Gene knockdown A way of making the mRNA non functional ...
... A way of working out the function of a gene by creating a non functioning one in an organism so you can see its effects. Gene knockdown A way of making the mRNA non functional ...
Poster
... in maintaining the nervous system, which regulates important functions such as breathing, heart rate, thinking, and movement. Mice lacking Cabin1 die early in development, and other Cabin1 malfunctions have been linked to cancer. As the nervous system develops, neurons require guidance to determine ...
... in maintaining the nervous system, which regulates important functions such as breathing, heart rate, thinking, and movement. Mice lacking Cabin1 die early in development, and other Cabin1 malfunctions have been linked to cancer. As the nervous system develops, neurons require guidance to determine ...
slides - ODU Computer Science
... •tRNA bind to specific amino acid (AUG) on mRNA to start •tRNA brings a.a. to ribosome •At least one tRNA exists for each amino acid Example of a tRNA http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/T/Translation.html ...
... •tRNA bind to specific amino acid (AUG) on mRNA to start •tRNA brings a.a. to ribosome •At least one tRNA exists for each amino acid Example of a tRNA http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/T/Translation.html ...
HW Answers pg. 241,2..
... • The modifications that are made to the primary mRNA transcript include capping and tailing and the excision of introns. Capping involves the addition of a 7-methyl guanosine to the 5' end of the primary mRNA transcript. Tailing consists of the addition of 200 to 300 adenine nucleotides to the 3' e ...
... • The modifications that are made to the primary mRNA transcript include capping and tailing and the excision of introns. Capping involves the addition of a 7-methyl guanosine to the 5' end of the primary mRNA transcript. Tailing consists of the addition of 200 to 300 adenine nucleotides to the 3' e ...