Bellwork:
... 3. mRNA tells ribosomes what proteins to make 4. mRNA attaches to ribosome and forms a pattern (codon) to make a protein 5. tRNA in cytoplasm comes to ribosome. It “translates” the code (codon=three base pairs) and goes and gets the specific amino acid that matches up with the codon. This is the ant ...
... 3. mRNA tells ribosomes what proteins to make 4. mRNA attaches to ribosome and forms a pattern (codon) to make a protein 5. tRNA in cytoplasm comes to ribosome. It “translates” the code (codon=three base pairs) and goes and gets the specific amino acid that matches up with the codon. This is the ant ...
Study guide for exam 2 Spring 2017
... What are the major phases of the cell cycle? What happens during those stages? Remember the importance of the S-phase. Be familiar with the major stages of mitosis. What occurs during each of these stages? How many daughter cells result from mitosis? Understand the significance of mitosis. How does ...
... What are the major phases of the cell cycle? What happens during those stages? Remember the importance of the S-phase. Be familiar with the major stages of mitosis. What occurs during each of these stages? How many daughter cells result from mitosis? Understand the significance of mitosis. How does ...
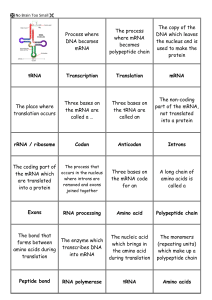
Gene expression flash cards
... The view that nucleic acids / DNA determines protein structure is known as The Central Dogma ...
... The view that nucleic acids / DNA determines protein structure is known as The Central Dogma ...
Nucleic Acids - cpprashanths Chemistry
... • Polymers of nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides joined by condensation reactions • They are held together by covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of another - called phosphodiester bonds ...
... • Polymers of nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides joined by condensation reactions • They are held together by covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of another - called phosphodiester bonds ...
Transcription and Translation
... The instructions for protein structure are carried in the genes, which are sequences of DNA nucleotides. Three nucleotides code for an amino acid, e.g. AAA on the transcribing strand codes for phenylalanine whilst AAT codes for leucine. So, successive triplets of DNA nucleotides determine the sequen ...
... The instructions for protein structure are carried in the genes, which are sequences of DNA nucleotides. Three nucleotides code for an amino acid, e.g. AAA on the transcribing strand codes for phenylalanine whilst AAT codes for leucine. So, successive triplets of DNA nucleotides determine the sequen ...
Protein Synthesis
... • Translation is performed by the ribosome – the protein builder of the cell. • The ribosome consists of two smaller parts – the 60S and the 40S subunits. (The number refers to the size and the S is for the “sedimentation rate” of the molecule when placed in a centrifuge.) • The ribosome recognizes ...
... • Translation is performed by the ribosome – the protein builder of the cell. • The ribosome consists of two smaller parts – the 60S and the 40S subunits. (The number refers to the size and the S is for the “sedimentation rate” of the molecule when placed in a centrifuge.) • The ribosome recognizes ...
Gene - Hal
... and olfactory epithelium. However, the role(s) of Mist1 in these tissues remains to be elucidated. The molecular mechanisms that regulate transcription of the Mist1 gene are unknown. Previous studies of eukaryotic class II promoters have shown that they can be dissected into a basal core promoter (f ...
... and olfactory epithelium. However, the role(s) of Mist1 in these tissues remains to be elucidated. The molecular mechanisms that regulate transcription of the Mist1 gene are unknown. Previous studies of eukaryotic class II promoters have shown that they can be dissected into a basal core promoter (f ...
on February 28, 2008 Downloaded from www.sciencemag.org
... (21), and the human PLZF protein, which is occasionally involved in chromosomal translocations in human promyelocytic leukemia (22). The regions of NH2-terminal homology among ZFPJS, ttk, Br-c, PLZF, and BCL-6 also share homology with viral proteins (for example, VA55R) of the poxvirus family (23) a ...
... (21), and the human PLZF protein, which is occasionally involved in chromosomal translocations in human promyelocytic leukemia (22). The regions of NH2-terminal homology among ZFPJS, ttk, Br-c, PLZF, and BCL-6 also share homology with viral proteins (for example, VA55R) of the poxvirus family (23) a ...
A primer on the structure and function of genes
... Operator: a region of DNA that indicates the starting point for reading the coding sequences of bacterial structure genes and controls the expression of those genes via interaction with a repressor. ...
... Operator: a region of DNA that indicates the starting point for reading the coding sequences of bacterial structure genes and controls the expression of those genes via interaction with a repressor. ...
Biology 1 Notes Chapter 12 - DNA and RNA Prentice Hall pages
... bonds, and then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. ...
... bonds, and then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. ...
E. coli Inducible Expression Vectors E. coli Expression Vectors with
... E. coli Inducible Expression Vectors E. coli expression vectors are available with the following promoters: T5 or T7 (IPTG-inducible), rhaBAD (rhamnose-inducible), ara (arabinose and IPTG-inducible) and phoA (induced by phosphate starvation). These vectors express in any strain of E. coli, except T7 ...
... E. coli Inducible Expression Vectors E. coli expression vectors are available with the following promoters: T5 or T7 (IPTG-inducible), rhaBAD (rhamnose-inducible), ara (arabinose and IPTG-inducible) and phoA (induced by phosphate starvation). These vectors express in any strain of E. coli, except T7 ...
ppt presentation
... The precise role of 25-nt RNA in PTGS remains to be determined. However, because they are long enough to convey sequence specificity yet small enough to move through plasmodesmata, it is possible that they are ...
... The precise role of 25-nt RNA in PTGS remains to be determined. However, because they are long enough to convey sequence specificity yet small enough to move through plasmodesmata, it is possible that they are ...
BIOL 1406 - Ch. 16-18 Review
... A geneticist found that a particular mutation had no effect on the protein made by a gene. This silent mutation probably involved A. deletion of one nucleotide. B. alteration of the start codon. C. insertion of one nucleotide. D. deletion of the entire gene. E. substitution of one nucleotide. ...
... A geneticist found that a particular mutation had no effect on the protein made by a gene. This silent mutation probably involved A. deletion of one nucleotide. B. alteration of the start codon. C. insertion of one nucleotide. D. deletion of the entire gene. E. substitution of one nucleotide. ...
Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes.
... promoter is now unmasked and RNA polymerase can now bind and initiate transcription. However it won’t do this very frequently without the help of the cAMP-CAP bound to the activation site. This protein complex binding puts a 90o kink in the DNA and interacts with the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. ...
... promoter is now unmasked and RNA polymerase can now bind and initiate transcription. However it won’t do this very frequently without the help of the cAMP-CAP bound to the activation site. This protein complex binding puts a 90o kink in the DNA and interacts with the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. ...
Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes.
... promoter is now unmasked and RNA polymerase can now bind and initiate transcription. However it won’t do this very frequently without the help of the cAMP-CAP bound to the activation site. This protein complex binding puts a 90o kink in the DNA and interacts with the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. ...
... promoter is now unmasked and RNA polymerase can now bind and initiate transcription. However it won’t do this very frequently without the help of the cAMP-CAP bound to the activation site. This protein complex binding puts a 90o kink in the DNA and interacts with the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. ...
E. coli Inducible Expression Vectors E. coli Expression Vectors with
... E. coli Inducible Expression Vectors E. coli expression vectors are available with the following promoters: T5 or T7 (IPTG-inducible), rhaBAD (rhamnose-inducible), ara (arabinose and IPTG-inducible) and phoA (induced by phosphate starvation). These vectors express in any strain of E. coli, except T7 ...
... E. coli Inducible Expression Vectors E. coli expression vectors are available with the following promoters: T5 or T7 (IPTG-inducible), rhaBAD (rhamnose-inducible), ara (arabinose and IPTG-inducible) and phoA (induced by phosphate starvation). These vectors express in any strain of E. coli, except T7 ...
English Version
... Purpose and requirements: 1. To know digestion and absorption process of lipids and familiar with the process of fat mobilization and the rate-limiting enzyme. 2. Grasp of β-oxidation of fatty acids and regulate factors. Understand other degradation ways of fatty acids. Grasp of the definitions, the ...
... Purpose and requirements: 1. To know digestion and absorption process of lipids and familiar with the process of fat mobilization and the rate-limiting enzyme. 2. Grasp of β-oxidation of fatty acids and regulate factors. Understand other degradation ways of fatty acids. Grasp of the definitions, the ...
In_Vitro_Translation
... There are two approaches to in vitro protein synthesis based on the starting genetic material: RNA or DNA. Standard translation systems, such as reticulocyte lysates and wheat germ extracts, use RNA as a template; whereas "coupled" and "linked" systems start with DNA templates, which are transcribed ...
... There are two approaches to in vitro protein synthesis based on the starting genetic material: RNA or DNA. Standard translation systems, such as reticulocyte lysates and wheat germ extracts, use RNA as a template; whereas "coupled" and "linked" systems start with DNA templates, which are transcribed ...
Messenger RNA
... construct a house, the DNA "blueprint" tells the cell how to build the organism. Yet, how can a heart be so different from a brain if all the cells contain the same instructions? Although much work remains in genetics, it has become apparent that a cell has the ability to turn off most genes and onl ...
... construct a house, the DNA "blueprint" tells the cell how to build the organism. Yet, how can a heart be so different from a brain if all the cells contain the same instructions? Although much work remains in genetics, it has become apparent that a cell has the ability to turn off most genes and onl ...
Document
... The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to DNA during transcription and separates the DNA strands. It then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which to assemble nucleotides into a complementary strand of RNA. RNA polymerase binds only to promoters, regions of DNA that have specific base sequences. Pro ...
... The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to DNA during transcription and separates the DNA strands. It then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which to assemble nucleotides into a complementary strand of RNA. RNA polymerase binds only to promoters, regions of DNA that have specific base sequences. Pro ...
AP Biology Discussion Notes
... Nirenberg "for their interpretation of the genetic code and its function in protein synthesis". ...
... Nirenberg "for their interpretation of the genetic code and its function in protein synthesis". ...
Reverse Transcriptase PCR
... evolutionary stage of the organism. 3. Aphids and water-fleas as well as some protozoa have the 18S rRNA with mol. wt of 0.9 x 10(6) against an overwhelming pressure of evolution to conserve the rRNA molecule of 0.7 x 10(6) daltons. 4. All the Deuterostomes examined were distinguished from Protostom ...
... evolutionary stage of the organism. 3. Aphids and water-fleas as well as some protozoa have the 18S rRNA with mol. wt of 0.9 x 10(6) against an overwhelming pressure of evolution to conserve the rRNA molecule of 0.7 x 10(6) daltons. 4. All the Deuterostomes examined were distinguished from Protostom ...
ppt 2015 edit
... many copies of an RNA made from one copy of DNA. – Regulation of gene expression can be effected by having specific controls at each element of the pathway between DNA and proteins. – The more elements there are in the pathway, the more opportunities there are to control it in different circumstance ...
... many copies of an RNA made from one copy of DNA. – Regulation of gene expression can be effected by having specific controls at each element of the pathway between DNA and proteins. – The more elements there are in the pathway, the more opportunities there are to control it in different circumstance ...
Chapter 12 DNA and RNA - Northwestern High School
... (mRNA), then DNA returns to normal – RNA Editing (pre-mRNA) • Not all RNA strands are perfect, some have introns and exons. • Introns are useless parts, exons are good parts, introns are removed and exons are pushed together to form one whole sequence, then capped. ...
... (mRNA), then DNA returns to normal – RNA Editing (pre-mRNA) • Not all RNA strands are perfect, some have introns and exons. • Introns are useless parts, exons are good parts, introns are removed and exons are pushed together to form one whole sequence, then capped. ...
Biology - secondary
... • Cellular respiration release more energy per glucose molecule than aerobic cellular respiration 107-110 • Building big muscles is an example of catabolic metabolism 119 • 109-Cellular formation is the breakdown of food without O2 • The RNA molecule that contains the code for a polypeptide chain of ...
... • Cellular respiration release more energy per glucose molecule than aerobic cellular respiration 107-110 • Building big muscles is an example of catabolic metabolism 119 • 109-Cellular formation is the breakdown of food without O2 • The RNA molecule that contains the code for a polypeptide chain of ...