• Transcription Transcription • Translation Information flow in
... inhibits prokaryotic peptide chain initiation, also induces mRNA misreading ...
... inhibits prokaryotic peptide chain initiation, also induces mRNA misreading ...
Nuclear functions in space and time: Gene
... types of nuclear bodies, including nucleoli, Cajal bodies, PML bodies, speckles and paraspeckles (Fig. 1; for review, see [18]. These bodies primarily occupy the interchromatin space and in some cases are associated with specific gene loci and/or their RNA products. The nucleolus, for example, assem ...
... types of nuclear bodies, including nucleoli, Cajal bodies, PML bodies, speckles and paraspeckles (Fig. 1; for review, see [18]. These bodies primarily occupy the interchromatin space and in some cases are associated with specific gene loci and/or their RNA products. The nucleolus, for example, assem ...
Lecture 4
... Gene prediction for Pol II transcribed genes. Upstream Enhancer elements. Upstream Promoter elements. GC box (-90nt) (20bp), CAAT box (-75 nt)(22bp) ...
... Gene prediction for Pol II transcribed genes. Upstream Enhancer elements. Upstream Promoter elements. GC box (-90nt) (20bp), CAAT box (-75 nt)(22bp) ...
Translate your creativity
... usage. Linear templates are favored over circular ones. Overnight incubation increases the amount of the produced protein. ...
... usage. Linear templates are favored over circular ones. Overnight incubation increases the amount of the produced protein. ...
Pre – AP Biology
... bacteria. The bacteria will then be able to Transcribe and Translate off of this new inserted DNA and thus make that protein. This has been done for numerous human medicines such as Insulin or Human Growth Hormone. – Eukaryotes DO have introns. This allows them to take out the introns and rearrange ...
... bacteria. The bacteria will then be able to Transcribe and Translate off of this new inserted DNA and thus make that protein. This has been done for numerous human medicines such as Insulin or Human Growth Hormone. – Eukaryotes DO have introns. This allows them to take out the introns and rearrange ...
ap® biology 2009 scoring guidelines - AP Central
... “RNA polymerase is an enzyme that attaches to a DNA sequence and begins transcribing it to mRNA.” “[I]t undergoes RNA splicing by the spliceosomes. These enzymes cut out the intron.” “Ribosomes are where proteins are made.” “When tRNA attaches, it brings with it an amino acid.” The maximum of 4 poin ...
... “RNA polymerase is an enzyme that attaches to a DNA sequence and begins transcribing it to mRNA.” “[I]t undergoes RNA splicing by the spliceosomes. These enzymes cut out the intron.” “Ribosomes are where proteins are made.” “When tRNA attaches, it brings with it an amino acid.” The maximum of 4 poin ...
chromatin fiber
... 5. Heterochromatin is tightlypacked chromatin within the nucleus (more dense), while euchromatin is loosely-packed chromatin within the nucleus (less dense) 6. Heterochromatin is found in areas where there are few to no genes present (specifically the in and around the centromere and the telomeres, ...
... 5. Heterochromatin is tightlypacked chromatin within the nucleus (more dense), while euchromatin is loosely-packed chromatin within the nucleus (less dense) 6. Heterochromatin is found in areas where there are few to no genes present (specifically the in and around the centromere and the telomeres, ...
March10NaturalSelection
... Genetics: A discrete 4 letter alphabet (AGCT), packaged into genes that code for proteins, balled up into chromosomes Variation and Heredity Letters can mutate Chromosomes crossover to create sperm & eggs Sperm and eggs combine to make new offspring Each cell has the same DNA A tremendously complica ...
... Genetics: A discrete 4 letter alphabet (AGCT), packaged into genes that code for proteins, balled up into chromosomes Variation and Heredity Letters can mutate Chromosomes crossover to create sperm & eggs Sperm and eggs combine to make new offspring Each cell has the same DNA A tremendously complica ...
Protein Synthesis
... Process in which a gene is used to build a protein resulting in the presence of a particular phenotype (physical characteristic) Phenotypic variation among organisms is due to genotypic variation (differences in the sequence of their DNA bases) Differences exist between species and within a sp ...
... Process in which a gene is used to build a protein resulting in the presence of a particular phenotype (physical characteristic) Phenotypic variation among organisms is due to genotypic variation (differences in the sequence of their DNA bases) Differences exist between species and within a sp ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide File
... 9. What are the reactants and products of glycolysis? Where does it occur? What happens if there isn’t sufficient oxygen available? ...
... 9. What are the reactants and products of glycolysis? Where does it occur? What happens if there isn’t sufficient oxygen available? ...
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis-New
... How Insulin is Built 4. The mRNA is received by a ribosome in the rough E.R., which starts translating the mRNA codons into amino acids. 5. The protein is built, one amino acid at a time, using ...
... How Insulin is Built 4. The mRNA is received by a ribosome in the rough E.R., which starts translating the mRNA codons into amino acids. 5. The protein is built, one amino acid at a time, using ...
Figure 18.19 Regulation of a metabolic pathway
... genes that act together and code for the enzymes that control a particular metabolic pathway; consists of an operator, promoter, and the genes they control ...
... genes that act together and code for the enzymes that control a particular metabolic pathway; consists of an operator, promoter, and the genes they control ...
Transcription Study Guide
... DNA - the molecule that stores and encodes an organism’s genetic information. DNA is a double helix molecule made up of two twisted strands that are held together by hydrogen bonds between paired nucleotides. The two strands are chemically oriented in opposite directions. DNA polymerase - a molecula ...
... DNA - the molecule that stores and encodes an organism’s genetic information. DNA is a double helix molecule made up of two twisted strands that are held together by hydrogen bonds between paired nucleotides. The two strands are chemically oriented in opposite directions. DNA polymerase - a molecula ...
Genomics and Forensics - MCCC Faculty & Staff Web Pages
... Tandemly repetitive sequences, about 10% of genome Interspersed repetitive DNA, 5-20% of genome, these subdivided as SINES (< 500bp) or LINES (≥ 500bp) ...
... Tandemly repetitive sequences, about 10% of genome Interspersed repetitive DNA, 5-20% of genome, these subdivided as SINES (< 500bp) or LINES (≥ 500bp) ...
DNA
... • DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones forming beads • These beads pack together, forming nucleosomes. • These coil to make chromatin • When the chromatin (stringy DNA) coils it make a chromosome ...
... • DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones forming beads • These beads pack together, forming nucleosomes. • These coil to make chromatin • When the chromatin (stringy DNA) coils it make a chromosome ...
1) Definition of the gene
... in all cells in the body. There are about 2,000 housekeeping genes. Examples: Na/K-ATPase – enzyme that pumps Na out, and K out, to maintain normal ion distribution inside the cell Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH): converts pyruvate to acetyl Co-A, at the entry point to the TCA cycle ...
... in all cells in the body. There are about 2,000 housekeeping genes. Examples: Na/K-ATPase – enzyme that pumps Na out, and K out, to maintain normal ion distribution inside the cell Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH): converts pyruvate to acetyl Co-A, at the entry point to the TCA cycle ...
English Version
... (2) Regulation of gene expression in lysogen and lysis pathway. 4. Translational regulation in prokaryotes. (1) Attenuation. (2) Regulon. (3) Coordinate synthesis of ribosomal proteins and rRNA. ...
... (2) Regulation of gene expression in lysogen and lysis pathway. 4. Translational regulation in prokaryotes. (1) Attenuation. (2) Regulon. (3) Coordinate synthesis of ribosomal proteins and rRNA. ...
AP Protein Sythesis
... suggested that genes coded for enzymes each disease (phenotype) is caused by non-functional gene product ...
... suggested that genes coded for enzymes each disease (phenotype) is caused by non-functional gene product ...
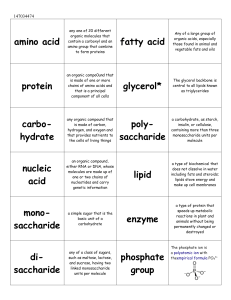
biology name
... 7. What is the name of the sugar in DNA? ________________________________________ 8. What is the name of the sugar in RNA? ________________________________________ 9. What is the site of protein synthesis? ___________________ 10. The ___RNA from the nucleus attaches to the RNA on the ribosome while ...
... 7. What is the name of the sugar in DNA? ________________________________________ 8. What is the name of the sugar in RNA? ________________________________________ 9. What is the site of protein synthesis? ___________________ 10. The ___RNA from the nucleus attaches to the RNA on the ribosome while ...