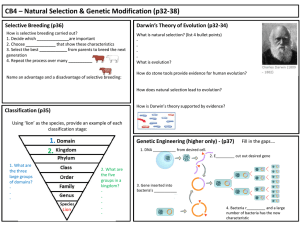
CB4 – Natural Selection and GM
... 2. Choose _____________ that show these characteristics 3. Select the best ____________ from parents to breed the next generation 4. Repeat the process over many ___________ ...
... 2. Choose _____________ that show these characteristics 3. Select the best ____________ from parents to breed the next generation 4. Repeat the process over many ___________ ...
Evolution and Classification Review
... • Darwin’s visit to these islands, the differences in the animals, and his observations that habitat can affect the adaptations of organisms. ...
... • Darwin’s visit to these islands, the differences in the animals, and his observations that habitat can affect the adaptations of organisms. ...
Evolution and Classification Review
... • Darwin’s visit to these islands, the differences in the animals, and his observations that habitat can affect the adaptations of organisms. ...
... • Darwin’s visit to these islands, the differences in the animals, and his observations that habitat can affect the adaptations of organisms. ...
What you need to know for the Packet 11 test:
... Prentice Hall Review Book pages 71-86 (all information) Textbook-You should refer to chapters 15, 16 and 17, however, you are not responsible for all information. You should have a clear understanding of: ...
... Prentice Hall Review Book pages 71-86 (all information) Textbook-You should refer to chapters 15, 16 and 17, however, you are not responsible for all information. You should have a clear understanding of: ...
What do I need to know for the test?
... How is the number of phenotypes related to the number of genes that control the trait? What type of distribution curve can be seen with polygenic inheritance? Tell the 3 ways natural selection can affect the distributions of phenotypes in a bell-shaped curve? Be able to identify examples of each of ...
... How is the number of phenotypes related to the number of genes that control the trait? What type of distribution curve can be seen with polygenic inheritance? Tell the 3 ways natural selection can affect the distributions of phenotypes in a bell-shaped curve? Be able to identify examples of each of ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... On human cooperation III. • These culturally transmitted practices presuppose advanced cognitive and linguistic capacities, possibly accounting for the distinctive forms of altruism found in our species. ...
... On human cooperation III. • These culturally transmitted practices presuppose advanced cognitive and linguistic capacities, possibly accounting for the distinctive forms of altruism found in our species. ...
B1.8_evolution_checklist
... have evolved from life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Outline the process of evolution by natural selection: differences between genes causes variation within a species; some individuals are best suited to survive and reproduce; the genes that enabled these individuals to s ...
... have evolved from life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Outline the process of evolution by natural selection: differences between genes causes variation within a species; some individuals are best suited to survive and reproduce; the genes that enabled these individuals to s ...
Biology Quiz 2 Answers and explanations Note there were two forms
... weeds could become resistant, therefore the product would no longer be effective, and 2) genetic diversity of the weeds could decrease after continued selection. This was an analogous example to bacteria and selection by antibiotics. A third possibility exists (but not an answer on the quiz); no evo ...
... weeds could become resistant, therefore the product would no longer be effective, and 2) genetic diversity of the weeds could decrease after continued selection. This was an analogous example to bacteria and selection by antibiotics. A third possibility exists (but not an answer on the quiz); no evo ...
Chapter 11 - Amazon Web Services
... • Ecological approaches stem from geographical theories relating the region in which a culture is found to its subsistence practices. In American anthropology this eventually became the culture and food area concepts of the early 20th century. © 2014 Mark Moberg ...
... • Ecological approaches stem from geographical theories relating the region in which a culture is found to its subsistence practices. In American anthropology this eventually became the culture and food area concepts of the early 20th century. © 2014 Mark Moberg ...
Natural Selection
... • Homologous features- similar structure in different species • Analogous features - similar function different structure (convergent evolution) • Vestigial organs ...
... • Homologous features- similar structure in different species • Analogous features - similar function different structure (convergent evolution) • Vestigial organs ...
Cultural Anthropology`s big names
... • A 19th century scholar who developed the evolutionary approach • Pioneered the comparative study of culture ...
... • A 19th century scholar who developed the evolutionary approach • Pioneered the comparative study of culture ...
Cultural Evolution models and their tragic flaws
... – Some cultures get labeled as “childlike” and others as “mature” in their thinking – Assumes primitive / developed languages ...
... – Some cultures get labeled as “childlike” and others as “mature” in their thinking – Assumes primitive / developed languages ...
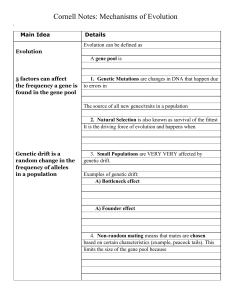
Mechanisms of Evolution Mechanisms of Evolution
... (“fixed”) in a population by chance (esp. in small populations) ...
... (“fixed”) in a population by chance (esp. in small populations) ...
Chapter 4, Studying Culture: Approaches And Methods
... Label theses stages: Savagery, Barbarism, Civilization. Place any new cultures in the classification. Invent an explanation for why the people in one stage developed into the next stage. ...
... Label theses stages: Savagery, Barbarism, Civilization. Place any new cultures in the classification. Invent an explanation for why the people in one stage developed into the next stage. ...
Book Review Evolution in 4 dimensions
... developmental processes that can explain trends in evolutionary change that have thus far been inpenetrable, eg: genetic assimilation. This is the mechanism, recently established, where elements of behavioural sequences, eg: song, or elaborate nest building are built over evolutionary time by some e ...
... developmental processes that can explain trends in evolutionary change that have thus far been inpenetrable, eg: genetic assimilation. This is the mechanism, recently established, where elements of behavioural sequences, eg: song, or elaborate nest building are built over evolutionary time by some e ...
No Slide Title
... Feldman and Cavalli-Sforza (1989) modelled the relationship between the spread of the gene for lactose absorption and the spread of the cultural trait. Their analysis supported the hypothesis that the cultural practise of dairy farming created the selection pressure favouring this gene. ...
... Feldman and Cavalli-Sforza (1989) modelled the relationship between the spread of the gene for lactose absorption and the spread of the cultural trait. Their analysis supported the hypothesis that the cultural practise of dairy farming created the selection pressure favouring this gene. ...