BIOL212TestTopicsAPR2012
... organisms and the unity and diversity of life Evolution is supported by an overwhelming amount of scientific evidence Genetic variation makes evolution possible The Hardy-Weinberg equation can be used to test whether a population is evolving Natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow can alter ...
... organisms and the unity and diversity of life Evolution is supported by an overwhelming amount of scientific evidence Genetic variation makes evolution possible The Hardy-Weinberg equation can be used to test whether a population is evolving Natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow can alter ...
Learning Targets: Evidence for Evolution Unit 1. I can develop a
... 1. I can develop a discussion/explain Natural Selection using the following terms/phrases: *population *struggle for existence *variation *mutation *mates *competition *resources *environment *phenotypic advantage * offspring * produce more offspring than environment can sustain * favorable phenotyp ...
... 1. I can develop a discussion/explain Natural Selection using the following terms/phrases: *population *struggle for existence *variation *mutation *mates *competition *resources *environment *phenotypic advantage * offspring * produce more offspring than environment can sustain * favorable phenotyp ...
Guided Notes2: Mechanisms of Evolution:
... the name of the book he published in 1859? __________________________________ 2. From Malthus, Darwin understood that not all offspring within a species will ____________________. From Lyell, he knew that the earth is very, very old and that ________________ occurs slowly. 3. _____________________ s ...
... the name of the book he published in 1859? __________________________________ 2. From Malthus, Darwin understood that not all offspring within a species will ____________________. From Lyell, he knew that the earth is very, very old and that ________________ occurs slowly. 3. _____________________ s ...
Changes Over Time - Effingham County Schools
... be less effective, and the frequency of resistant insects in the population ...
... be less effective, and the frequency of resistant insects in the population ...
More Evolution and Hardy Weinberg! KEY
... 1. What are the mechanisms for evolution? Give a brief description of each Genetic drift: change in gene pool in a small population (chance) gene flow: immigration or emigration of genes mutation: random change of the genes natural selection: a random act upon population evolve 2. What is the bottl ...
... 1. What are the mechanisms for evolution? Give a brief description of each Genetic drift: change in gene pool in a small population (chance) gene flow: immigration or emigration of genes mutation: random change of the genes natural selection: a random act upon population evolve 2. What is the bottl ...
Genetic Algorithms
... for purple (B) and white (b) blossoms. At its most fundamental level, inheritance in organisms occurs by passing discrete heritable units, called genes, from parents to progeny.[31] This property was first observed by Gregor Mendel, who studied the segregation of heritable traits in pea plants.[12][ ...
... for purple (B) and white (b) blossoms. At its most fundamental level, inheritance in organisms occurs by passing discrete heritable units, called genes, from parents to progeny.[31] This property was first observed by Gregor Mendel, who studied the segregation of heritable traits in pea plants.[12][ ...
Ch 17 RNO
... Describe, in detail, the three patterns produced by natural selection on polygenic traits. a. Describe directional, stabilizing, and disruptive selection. b. Review and draw graph examples using those on page 489 What is genetic drift? Be detailed in your explanation. Describe the characteristics of ...
... Describe, in detail, the three patterns produced by natural selection on polygenic traits. a. Describe directional, stabilizing, and disruptive selection. b. Review and draw graph examples using those on page 489 What is genetic drift? Be detailed in your explanation. Describe the characteristics of ...
Evolution Choice Board
... describing the theory of natural selection. The letter should be at least one page long. ...
... describing the theory of natural selection. The letter should be at least one page long. ...
Population Genetics and evolution with notes
... Darwin developed his theory of natural selection before knowledge of genetics Populations evolve, not individuals! An organism is born with its phenotype, and it never changes during its lifetime Evolution occurs as a population’s genes and their frequencies change over time Gene Pool: all of th ...
... Darwin developed his theory of natural selection before knowledge of genetics Populations evolve, not individuals! An organism is born with its phenotype, and it never changes during its lifetime Evolution occurs as a population’s genes and their frequencies change over time Gene Pool: all of th ...
Evolution Mini Test Study Guide
... You should be able to do the following: (a) SHORT ESSAY QUESTION: Describe Darwin’s theory of evolution using the following terms: natural selection, evolution, fitness, and adaptation. (b) Describe evidence of evolution such as the fossil record, geographic distribution, anatomical structures, embr ...
... You should be able to do the following: (a) SHORT ESSAY QUESTION: Describe Darwin’s theory of evolution using the following terms: natural selection, evolution, fitness, and adaptation. (b) Describe evidence of evolution such as the fossil record, geographic distribution, anatomical structures, embr ...
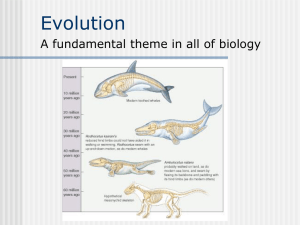
Evolution
... Darwin’s rationale for natural selection: 1) All species produce _______ offspring High reproductive _________ 2) Resources (food, shelter) are ________ Causes a ________ for survival Intraspecific competition 3) Individuals of a population differ somewhat Genetic variation 4) Individuals with “___ ...
... Darwin’s rationale for natural selection: 1) All species produce _______ offspring High reproductive _________ 2) Resources (food, shelter) are ________ Causes a ________ for survival Intraspecific competition 3) Individuals of a population differ somewhat Genetic variation 4) Individuals with “___ ...
lecture26
... 2 frequency of deleterious genes is now high because natural selection has been artificially reduced ...
... 2 frequency of deleterious genes is now high because natural selection has been artificially reduced ...
Extra Credit For Biology 4: _____ Points Evolution
... According to the tree what is the group that is most closely related to dinosaurs and birds? ...
... According to the tree what is the group that is most closely related to dinosaurs and birds? ...
Worksheet Chapter 5.1
... . Biological evolution that happens by chance is called . Natural selection is the process by which traits that improve an organism’s chances for survival and are passed on more frequently to a future than those that do not. Natural selection follows three conditions: organisms produce more than can ...
... . Biological evolution that happens by chance is called . Natural selection is the process by which traits that improve an organism’s chances for survival and are passed on more frequently to a future than those that do not. Natural selection follows three conditions: organisms produce more than can ...
Genetic Evolution vs. Cultural Evolution
... • The rates at which results can be observed are drastically different, yet the concept of information exchange is exactly the same • We will now further investigate the ways in which these two factors have evolved or changed over time… ...
... • The rates at which results can be observed are drastically different, yet the concept of information exchange is exactly the same • We will now further investigate the ways in which these two factors have evolved or changed over time… ...
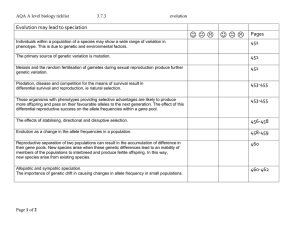
doc 3.7.3 evolution checklist
... Reproductive separation of two populations can result in the accumulation of difference in their gene pools. New species arise when these genetic differences lead to an inability of members of the populations to interbreed and produce fertile offspring. In this way, new species arise from existing s ...
... Reproductive separation of two populations can result in the accumulation of difference in their gene pools. New species arise when these genetic differences lead to an inability of members of the populations to interbreed and produce fertile offspring. In this way, new species arise from existing s ...
Chapter 4 Heredity and Evolution
... Members of each gene pair separate so each gamete contains one member of a pair. fertilization Full number of chromosomes is restored and members of gene pairs are reunited. ...
... Members of each gene pair separate so each gamete contains one member of a pair. fertilization Full number of chromosomes is restored and members of gene pairs are reunited. ...
WLHS / Biology / Monson Name Date Per READING GUIDE: 17.1
... 7) PREDICT: Suppose a dominant allele causes a plant disease that usually kills the plant before it can reproduce. Over time, what would probably happen to the frequency of that dominant allele in the population? ...
... 7) PREDICT: Suppose a dominant allele causes a plant disease that usually kills the plant before it can reproduce. Over time, what would probably happen to the frequency of that dominant allele in the population? ...
READING GUIDE: 17.1 – Genes and Variation (p. 482
... 7) PREDICT: Suppose a dominant allele causes a plant disease that usually kills the plant before it can reproduce. Over time, what would probably happen to the frequency of that dominant allele in the population? ...
... 7) PREDICT: Suppose a dominant allele causes a plant disease that usually kills the plant before it can reproduce. Over time, what would probably happen to the frequency of that dominant allele in the population? ...