CHEM 203 Topics Discussed on Nov. 20 Principle: protonation of
... Principle: protonation of alcohols transforms the OH group into an incipient molecule of H2O, which is the conjugate base of a strong Bronsted acid, H3O+ (pKa ≈ –2). So, H2O can function as a leaving group in SN2/SN1 or E2/E1 reactions (cf. the case of ethers; notes of Nov. 16) Note: the OH group pe ...
... Principle: protonation of alcohols transforms the OH group into an incipient molecule of H2O, which is the conjugate base of a strong Bronsted acid, H3O+ (pKa ≈ –2). So, H2O can function as a leaving group in SN2/SN1 or E2/E1 reactions (cf. the case of ethers; notes of Nov. 16) Note: the OH group pe ...
C7 Revision Powerpoint Part 1
... that can be made by fermentation and there are optimum conditions of pH and temperature. • Ethanol solution can be concentrated by distillation to make products such as whisky and brandy; • Genetically modified E. coli bacteria can be used to convert waste biomass from a range of sources into ethano ...
... that can be made by fermentation and there are optimum conditions of pH and temperature. • Ethanol solution can be concentrated by distillation to make products such as whisky and brandy; • Genetically modified E. coli bacteria can be used to convert waste biomass from a range of sources into ethano ...
Chapter 1 Organoaluminum Reagents for Selective Organic
... Chapter 3. Bulky Aluminum Reagents for Selective Organic Synthesis In chapter 2 we discussed several excellent methods of discriminating various functional groups using bulky aluminum reagents. In this section we focus on the reactions promoted with bulky aluminum reagents which could not be achiev ...
... Chapter 3. Bulky Aluminum Reagents for Selective Organic Synthesis In chapter 2 we discussed several excellent methods of discriminating various functional groups using bulky aluminum reagents. In this section we focus on the reactions promoted with bulky aluminum reagents which could not be achiev ...
Ziegler-Natta Catalysts
... In broad terms, Ziegler-Natta catalysts are defined as combinations of a transition metal compound from Groups 3-12 of the Periodic Table with an organometallic compound from Groups 1,2 or 13. Each component alone is incapable of converting olefins to high polymers. (Interactions between catalyst an ...
... In broad terms, Ziegler-Natta catalysts are defined as combinations of a transition metal compound from Groups 3-12 of the Periodic Table with an organometallic compound from Groups 1,2 or 13. Each component alone is incapable of converting olefins to high polymers. (Interactions between catalyst an ...
Solutions
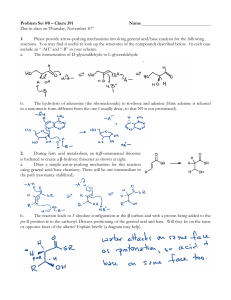
... Please provide arrow-pushing mechanisms involving general acid/base catalysis for the following reactions. You may find it useful to look up the structures of the compounds described below. In each case include an “-AH” and “-B” in your scheme. a. The isomerization of D-glyceraldehyde to L-glycerald ...
... Please provide arrow-pushing mechanisms involving general acid/base catalysis for the following reactions. You may find it useful to look up the structures of the compounds described below. In each case include an “-AH” and “-B” in your scheme. a. The isomerization of D-glyceraldehyde to L-glycerald ...
Lecture 16 Aromatic Diazonium Salts
... Diazonium salt on warming in water gives phenol via SN1 mechanism. The reaction is generally performed in acidic solution to preserve phenol in its unionized form. ...
... Diazonium salt on warming in water gives phenol via SN1 mechanism. The reaction is generally performed in acidic solution to preserve phenol in its unionized form. ...
STRUCTURAL ISOMERISM
... You can also get position isomers on benzene rings. Consider the molecular formula C7H8Cl. There are four different isomers you could make depending on the position of the chlorine atom. In one case it is attached to the side-group carbon atom, and then there are three other possible positions it co ...
... You can also get position isomers on benzene rings. Consider the molecular formula C7H8Cl. There are four different isomers you could make depending on the position of the chlorine atom. In one case it is attached to the side-group carbon atom, and then there are three other possible positions it co ...
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to
... t The cyano group can be hydrolyzed or reduced l Hydrolysis of a cyanohydrin produces an α -hydroxycarboxylic acid l Reduction of a cyanohydrin produces a β -aminoalcohol ...
... t The cyano group can be hydrolyzed or reduced l Hydrolysis of a cyanohydrin produces an α -hydroxycarboxylic acid l Reduction of a cyanohydrin produces a β -aminoalcohol ...
Document
... Syntheses of metal carbonyls Metal carbonyls can be made in a variety of ways. For Ni and Fe, the homoleptic or binary metal carbonyls can be made by the direct interaction with the metal (Equation 1). In other cases, a reduction of a metal precursor in the presence of CO (or using CO as the reduct ...
... Syntheses of metal carbonyls Metal carbonyls can be made in a variety of ways. For Ni and Fe, the homoleptic or binary metal carbonyls can be made by the direct interaction with the metal (Equation 1). In other cases, a reduction of a metal precursor in the presence of CO (or using CO as the reduct ...
-1- GLOSSARY OF CHEM 1110 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TERMS
... thus the reactivity of even complex molecules can be predicted. functional isomers: compounds which have the same molecular formula that possess different functional groups. geometric isomers: stereoisomers which differ in the geometry around either a carbon-carbon double bond or ring. halo group (X ...
... thus the reactivity of even complex molecules can be predicted. functional isomers: compounds which have the same molecular formula that possess different functional groups. geometric isomers: stereoisomers which differ in the geometry around either a carbon-carbon double bond or ring. halo group (X ...
20.4 Acid-Base Properties of Carboxylic Acids
... wish to separate. How might you take advantage of the acidity of one component in the mixture to accomplish the ...
... wish to separate. How might you take advantage of the acidity of one component in the mixture to accomplish the ...
Aldehydes Ketones
... Hemiacetals and Hemiketals are formed by reacting only one equivalent of alcohol with the aldehyde or ketone in the presence of an acid catalyst. Further reaction with a second alcohol forms the acetal or ketal. A diol, with two –OH groups on the same molecule, can be used to form cyclic acetals ...
... Hemiacetals and Hemiketals are formed by reacting only one equivalent of alcohol with the aldehyde or ketone in the presence of an acid catalyst. Further reaction with a second alcohol forms the acetal or ketal. A diol, with two –OH groups on the same molecule, can be used to form cyclic acetals ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.