The 9-Phenyl-9-fluorenyl Group for Nitrogen Protection in
... This is strongly supported by the fact that the proton NMR shows a methyl ester resonance at 2.92 ppm (an unusually upfield chemical shift). So, achieving a stereoelectronically favorable conformation during deprotonation would require the ester group to rotate into the region of space occupied by t ...
... This is strongly supported by the fact that the proton NMR shows a methyl ester resonance at 2.92 ppm (an unusually upfield chemical shift). So, achieving a stereoelectronically favorable conformation during deprotonation would require the ester group to rotate into the region of space occupied by t ...
Dess-Martin Periodinane
... One of the mildest reagents for the selective oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones. High yields can be obtained at ambient temperatures, under neutral conditions, in chloroform, dichloromethane or acetonitrile: J. Org. Chem., 48, 4155 (1983); J. Am. Chem. Soc., 113, 7 ...
... One of the mildest reagents for the selective oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones. High yields can be obtained at ambient temperatures, under neutral conditions, in chloroform, dichloromethane or acetonitrile: J. Org. Chem., 48, 4155 (1983); J. Am. Chem. Soc., 113, 7 ...
Selectivity of sodium borohydride
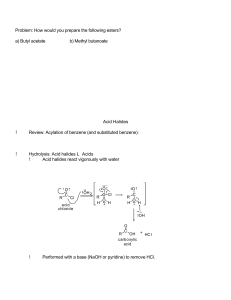
... Lithium aluminum hydride is very reactive and must be used with caution under anhydrous conditions, typically in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran (THF) solvents, and is capable of reducing a wide range of functional groups including aldehydes, ketones, esters, carboxylic acids, amides, nitriles and ...
... Lithium aluminum hydride is very reactive and must be used with caution under anhydrous conditions, typically in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran (THF) solvents, and is capable of reducing a wide range of functional groups including aldehydes, ketones, esters, carboxylic acids, amides, nitriles and ...
CC 2 097-110..7686hdisk chapter .. Page97
... is a preliminary mechanism that requires additional verification, the observations presented clearly point to a new type of redox photochemistry available for suitably designed anthraquinones and possibly other ketones. In summary, we have discovered a new type of photochemistry available for simple ...
... is a preliminary mechanism that requires additional verification, the observations presented clearly point to a new type of redox photochemistry available for suitably designed anthraquinones and possibly other ketones. In summary, we have discovered a new type of photochemistry available for simple ...
Time-of-Flight Neutron Structure of D
... carboxylate O of Asp257, which was found for D2O in the native enzyme structure. The O of the hydroxyl group appears to remain bound to M2 and now lies close to C1 of the bound product xylulose. Lys289 is well-ordered unlike the structure in 4XIS and in the native XI structure, and its Nζ has three ...
... carboxylate O of Asp257, which was found for D2O in the native enzyme structure. The O of the hydroxyl group appears to remain bound to M2 and now lies close to C1 of the bound product xylulose. Lys289 is well-ordered unlike the structure in 4XIS and in the native XI structure, and its Nζ has three ...
The Synthesis of trans-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III
... (Here, Oxygen acts as an Oxidizing Agent and is reduced from O0 to O2-.) However, Co3+ is unstable in an aqueous environment, being readily reduced back to Co2+. To prevent this from happening, the resulting Co3+ can be stabilized by adding an Ethylenediamine ligand. Hence, if the oxidation is carri ...
... (Here, Oxygen acts as an Oxidizing Agent and is reduced from O0 to O2-.) However, Co3+ is unstable in an aqueous environment, being readily reduced back to Co2+. To prevent this from happening, the resulting Co3+ can be stabilized by adding an Ethylenediamine ligand. Hence, if the oxidation is carri ...
Triphase Catalysis. Applications to Organic Synthesis`
... of a variety of reagent^.^^-^^ More recent procedures have relied on the use of sodium thiosulfate2Tand combinations of sodium iodide and sodium thiosulfate.28Dehalogenation of certain uic-dibromides can also be carried out under triphase conditions employing catalytic amounts of sodium iodide, la, ...
... of a variety of reagent^.^^-^^ More recent procedures have relied on the use of sodium thiosulfate2Tand combinations of sodium iodide and sodium thiosulfate.28Dehalogenation of certain uic-dibromides can also be carried out under triphase conditions employing catalytic amounts of sodium iodide, la, ...
1 CHAPTER ONE Palladium in Organic Synthesis 1.1 Background
... However, one of the main complications that has been problematic in the development of Pd(II) methodology is the difficulty of reoxidizing Pd(0) → Pd(II). Completion of the catalytic cycle to regenerate Pd(II) requires the presence of a stoichiometric oxidant, such as CuCl2, Cu(OAc)2, benzoquinone, ...
... However, one of the main complications that has been problematic in the development of Pd(II) methodology is the difficulty of reoxidizing Pd(0) → Pd(II). Completion of the catalytic cycle to regenerate Pd(II) requires the presence of a stoichiometric oxidant, such as CuCl2, Cu(OAc)2, benzoquinone, ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.